How to make a Jest Test for Error Boundaries
 Diego Ballesteros (Relatable Code)
Diego Ballesteros (Relatable Code)

Own your error
Error boundaries are a nifty part of the React API to handle errors. Basically, an error that occurs within the error boundary propagates to said error boundary to control it.
With this functionality, you can choose what to do with the error as well as provide a fallback component to display to the user.
Breaking it down
The error boundary is one of a handful of cases where you are required to use a class component.
At first glance, the error itself is provided by a callback within the lifecycle of React. componentDidCatch is what will receive the error and allow us to access the message and contents of said error.
The most basic functionality of this could be to simply console.error the message for debugging. However, more advanced use cases may include sending the error to a third-party service or displaying some kind of personalized message to the user.
The return of the component is what the sure will see instead of what was originally inside the error boundary. Example below:
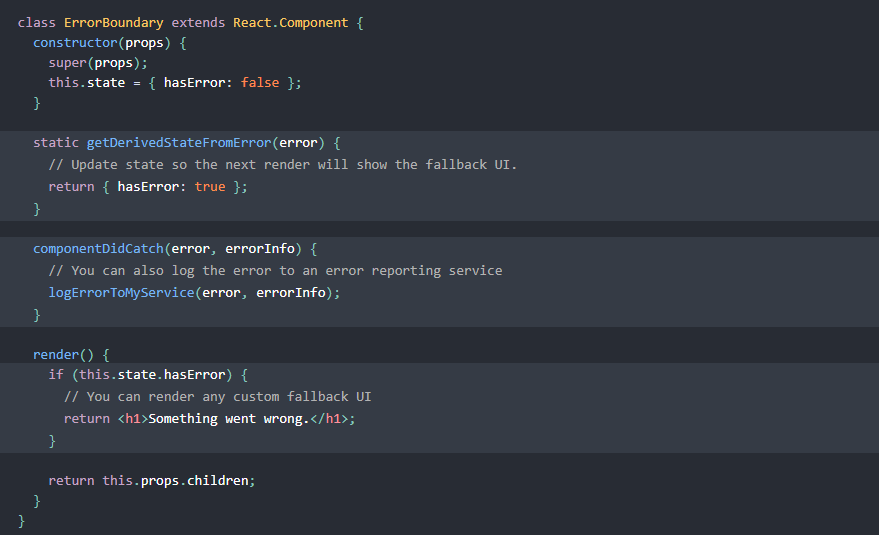
React Docs Error Boundary example
This example is straight from the React docs and provides a simple text follow-up, in a lot of cases this specific portion of the app may become unusable due to said error so you can possibly indicate to the user to reset or retry.
The best way to think of this is a gigantic try catch for your components to handle any unexpected errors.
The Test
I made a slight modification to the component that is returned by the Error Boundary:
Something went wrong.
The following is an example of how to create the test:
import { render, screen } from '@testing-library/react';
import ErrorBoundary from './ErrorBoundary';
import '@testing-library/jest-dom';
describe('Error Boundary', () => {
test('Error Boundary', () => {
const ThrowError = () => {
throw new Error('Test');
};
render(
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<ErrorBoundary />}>
<ThrowError />
</ErrorBoundary>
);
expect(screen.getByTestId('errorboundary')).toBeVisible();
});
});
Essentially what we do is create a component whose sole purpose is to throw an error and make sure that it is correctly displayed. This is quite the basic test but the idea is that now you can expand upon it and test for anything else the error boundary may do!
Find more content at Relatable Code
Originally published at https://relatablecode.com on November 2, 2021.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Diego Ballesteros (Relatable Code) directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Diego Ballesteros (Relatable Code)
Diego Ballesteros (Relatable Code)
🚀 JS/React/Typescript Developer 🛠️ Self-taught developer Check me out on Twitter: https://twitter.com/relatablecoder Or on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/relatablecode/