How to deploy a high-availability web application us AWS CloudFormation
 Oluwatobi Solomon
Oluwatobi Solomon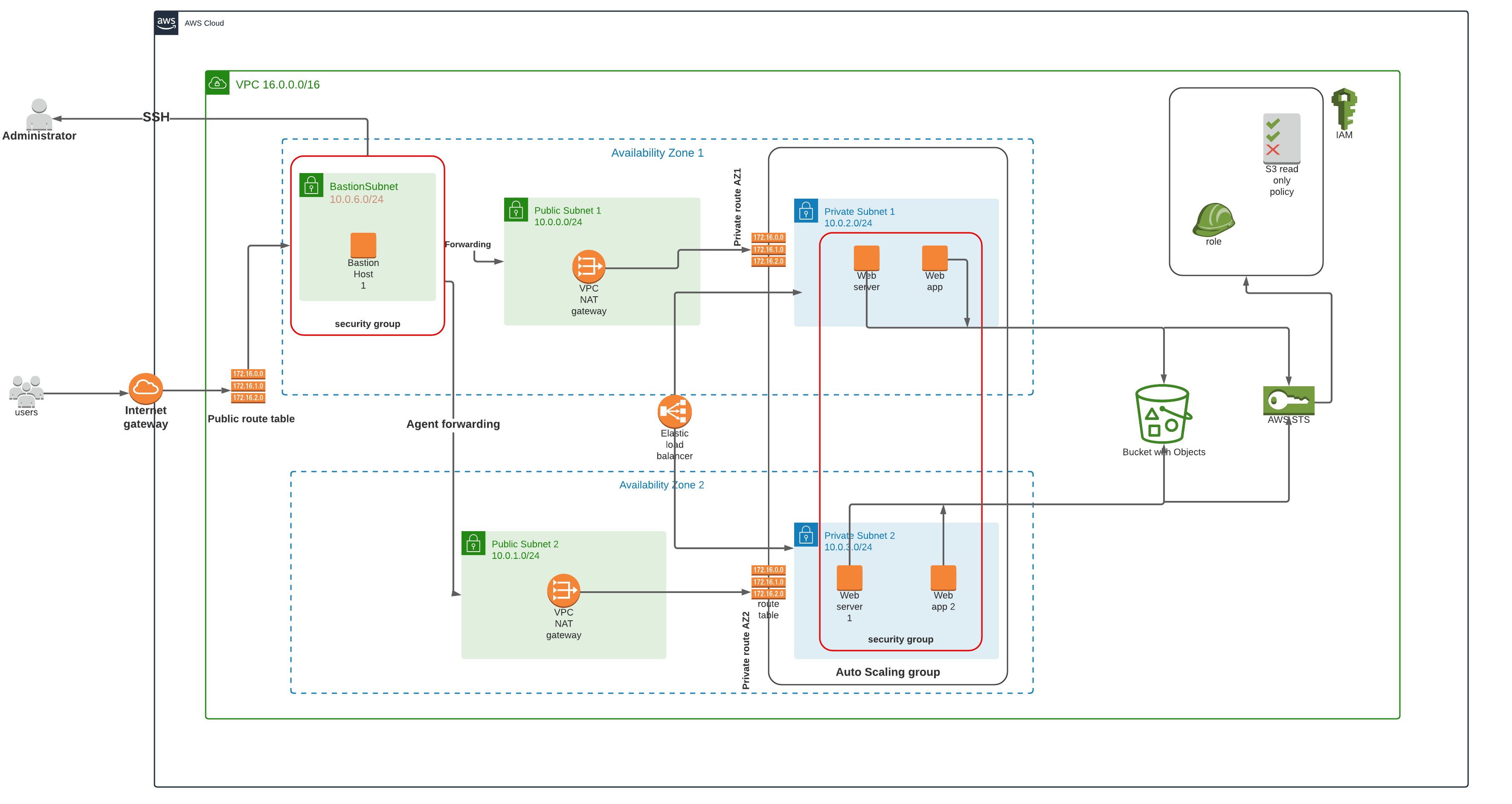
So before we start, you may be asking what is cloudformation, why cloudformation, and what are other tools similar to cloudformation. Don't stress it as all will be covered in this article.
What is CloudFormation
- AWS CloudFormation is a service that helps you model and set up your AWS resources so that you can spend less time managing those resources and more time focusing on your applications that run in AWS. So why cloudormation? AWS CloudFormation can quickly validate values for AWS-specific parameter types before creating your stack. Also, if you use the CloudFormation console, CloudFormation shows a drop-down list of valid values, so you don't have to look up or memorize the correct VPC IDs or key pair names. Alternative to cloudformation includes Ansible, chef, terraform, and any other infrastructure as code tools.
Requirement for High-Availability deployment
- AWS console account
- AWS CLI
- Text Editor e.g. Vscode.
Step 1:
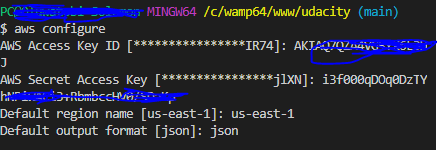
- Configure AWS on your text editor (Vscode) with the secret and access created under the IAM user section. enter the command AWS configure and supply the keys, region, and, file-type as shown below.
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [****************IR74]: Enter you access key
AWS Secret Access Key [****************jlXN]: Enter your secret key
Default region name [us-east-1]: Enter you region
Default output format [json]: json
Step 2
- Identify your network resources (VPC, internet gateway, elastic IP, route table, public and private subnet, nat gateway and others)
- declare the parameters in a newnet.json file as shown below
- declare your resources in a newnet1.yml file as shown below
[ { "ParameterKey": "EnvironmentName", "ParameterValue": "UdagramProjects" }, { "ParameterKey": "VpcCIDR", "ParameterValue": "10.0.0.0/16" }, { "ParameterKey": "PublicSubnet1CIDR", "ParameterValue": "10.0.0.0/24" }, { "ParameterKey": "PublicSubnet2CIDR", "ParameterValue": "10.0.1.0/24" }, { "ParameterKey": "PrivateSubnet1CIDR", "ParameterValue": "10.0.2.0/24" }, { "ParameterKey": "PrivateSubnet2CIDR", "ParameterValue": "10.0.3.0/24" } ]
Description: |
Udacity Project 2 - Network stack
Parameters:
EnvironmentName:
Description: An environment name that will be prefixed to resource names
Type: String
Default: xxx
VpcCIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP Range (CIDR notation) for this VPC
Type: String
Default: 10.0.0.0/16
PublicSubnet1CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet in AZ1
Type: String
Default: 10.0.0.0/24
PublicSubnet2CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet in AZ1
Type: String
Default: 10.0.1.0/24
PrivateSubnet1CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet in AZ1
Type: String
Default: 10.0.2.0/24
PrivateSubnet2CIDR:
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet in AZ1
Type: String
Default: 10.0.3.0/24
Resources:
# NETWORK RESOURCES
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCIDR
EnableDnsHostnames: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Ref EnvironmentName
InternetGateway:
Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Ref EnvironmentName
InternetGatewayAttachment:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment
Properties:
InternetGatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway
VpcId: !Ref VPC
PrivateSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [0, !GetAZs '']
CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Private Subnet (AZ1)
PrivateSubnet2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [1, !GetAZs '']
CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet2CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Private Subnet (AZ2)
PublicSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [0, !GetAZs '']
CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Public Subnet (AZ1)
PublicSubnet2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
AvailabilityZone: !Select [1, !GetAZs '']
CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet2CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Public Subnet (AZ2)
NatGateway1EIP:
Type: AWS::EC2::EIP
DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment
Properties:
Domain: vpc
NatGateway2EIP:
Type: AWS::EC2::EIP
DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment
Properties:
Domain: vpc
NatGateway1:
Type: AWS::EC2::NatGateway
Properties:
AllocationId: !GetAtt NatGateway1EIP.AllocationId
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet1
NatGateway2:
Type: AWS::EC2::NatGateway
Properties:
AllocationId: !GetAtt NatGateway2EIP.AllocationId
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet2
PublicRouteTable:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Public Routes
PrivateRouteTable1:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Public Route (AZ1)
PrivateRouteTable2:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref VPC
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub ${EnvironmentName} Private Route (AZ2)
DefaultPublicRoute:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
GatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway
DefaultPrivateRoute1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable1
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
NatGatewayId: !Ref NatGateway1
DefaultPrivateRoute2:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable2
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
NatGatewayId: !Ref NatGateway2
PublicSubnet1RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet1
PublicSubnet2RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet2
PrivateSubnet1RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable1
SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnet1
PrivateSubnet2RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable2
SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnet2
Outputs:
VPC:
Description: A reference to the created VPC
Value: !Ref VPC
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-VPCID
PublicSubnets:
Description: A list of all public subnets
Value: !Join [',', [!Ref PublicSubnet1, !Ref PublicSubnet2]]
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PUB-NETS
PrivateSubnets:
Description: A list of all public subnets
Value: !Join [',', [!Ref PrivateSubnet1, !Ref PrivateSubnet2]]
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PRIV-NETS
VPCPublicRouteTable:
Description: Public Routing
Value: !Ref PublicRouteTable
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PUB-RT
VPCPrivateRouteTable1:
Description: Private Routing AZ1
Value: !Ref PrivateRouteTable1
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PRI1-RT
VPCPrivateRouteTable2:
Description: Private Routing AZ2
Value: !Ref PrivateRouteTable2
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PRI2-RT
PublicSubnet1:
Description: A ref to the public subnet in AZ1
Value: !Ref PublicSubnet1
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PUB1-SN
BastionSubnet:
Description: A ref to the bastion subnet in AZ1
Value: !Ref PublicSubnet1
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-BAST-SN
PublicSubnet2:
Description: A ref to the public subnet in AZ2
Value: !Ref PublicSubnet2
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PUB2-SN
PrivateSubnet1:
Description: A ref to the private subnet in AZ1
Value: !Ref PrivateSubnet1
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PRI1-SN
PrivateSubnet2:
Description: A ref to the private subnet in AZ2
Value: !Ref PrivateSubnet2
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-PRI2-SN
Copy the above resources code into the newnet1.yml file and save.
Step 3:
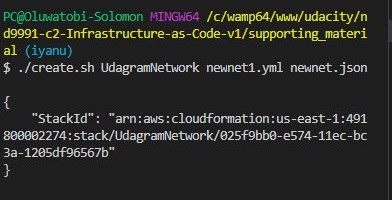
- create two shell files, create.sh, and update.sh respectively. The is to further automate the running of our cloudformation scripts by just calling the shell document to run the task
- Copy the code below in create.sh file and save.
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name $1 --template-body file://$2 --parameters file://$3 --capabilities "CAPABILITY_IAM" "CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM" --region=us-east-1 - Copy the code below in update.sh file and save.
aws cloudformation update-stack --stack-name $1 --template-body file://$2 --parameters file://$3 --capabilities "CAPABILITY_IAM" "CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM" --region=us-east-1 - Open your terminal and change the directory (cd) to your scripts directory before running the code below to avoid a not found error.
if it executes correctly it displays the stack ID and auto-create on the cloudfromation GUI and simultaneously creates all the network resources declared in the newnet1.yml file./create.sh UdagramNetwork newnet1.yml newnet.json
Once this is successful, your network resources as shown below should now be available on your AWS portal
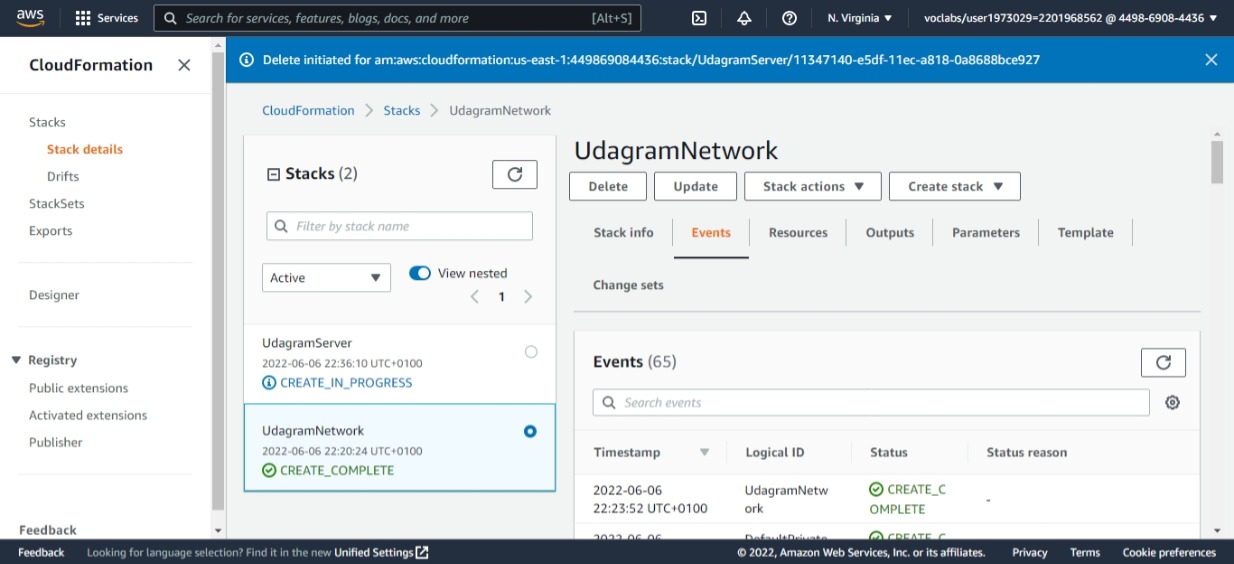 This shows an overview of the network infrastructure
This shows an overview of the network infrastructure
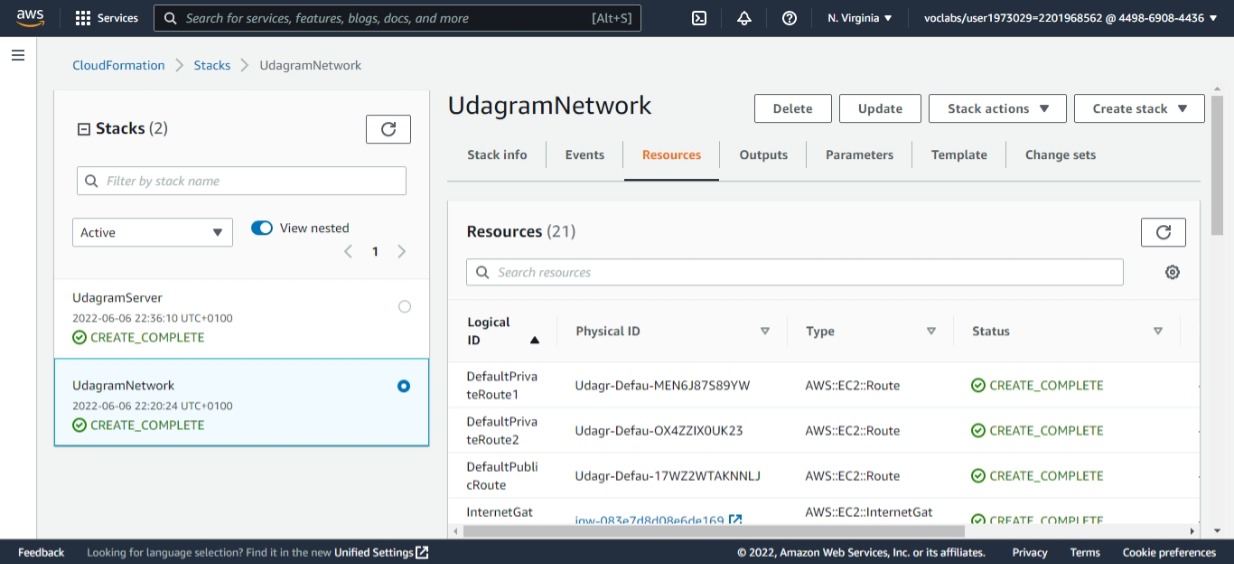 This shows the network resources provisioned (21 Resources)
This shows the network resources provisioned (21 Resources)
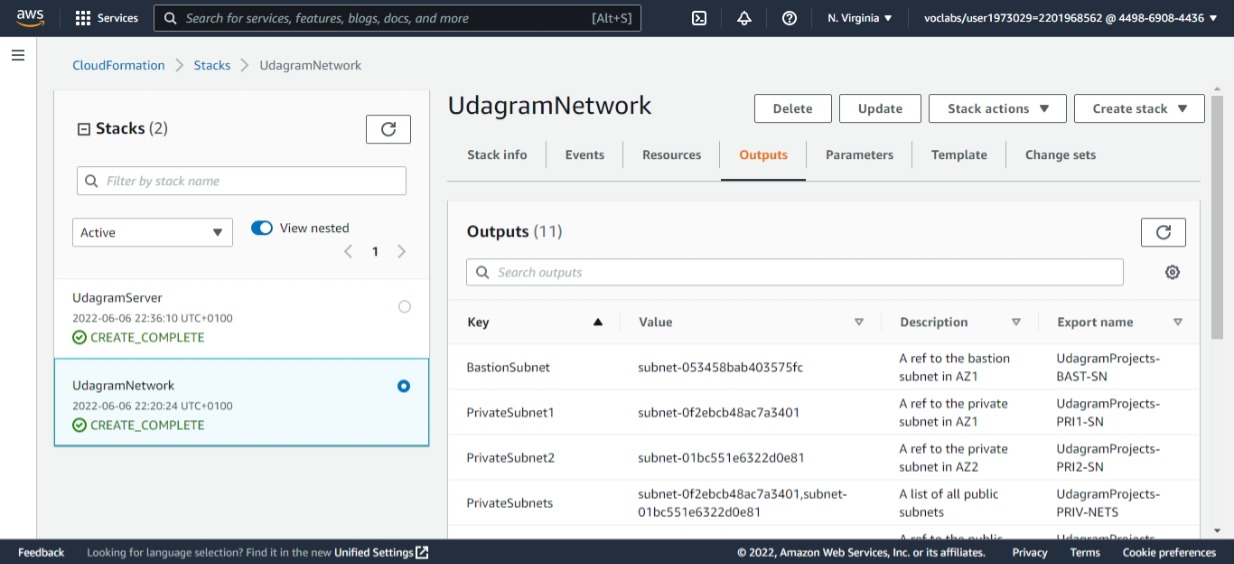 This shows the output of the network resources provisioned
This shows the output of the network resources provisioned
Step 5 Now let us created a bucket for our website and upload the zip file of our high-end app (udagram) to our bucket
- firstly, let's create a bucket with the name
aws s3 mb s3://udagram-0676982224131 --region "us-east-1"- aws – Command to invoke AWS Client
- S3 – Denotes the service where the operation to be performed
- mb – Make bucket command to denote the make bucket operation
- S3://udagram-0676982224131– S3 URI, desired bucket name to be created
- region – keyword to specify on which region the bucket needs to be created us-east-1 – the region name
-Now that our udagram-0676982224131 bucket has been created, let us upload the zip file of our web app to our bucket
aws s3 cp --recursive c:/wamp64/udacity/src.zip s3://udagram-0676982224131/ --region "us-east-1"
Recursive means it will copy the contents of the directories and if the source directory has the subdirectories, then it will be copied too.
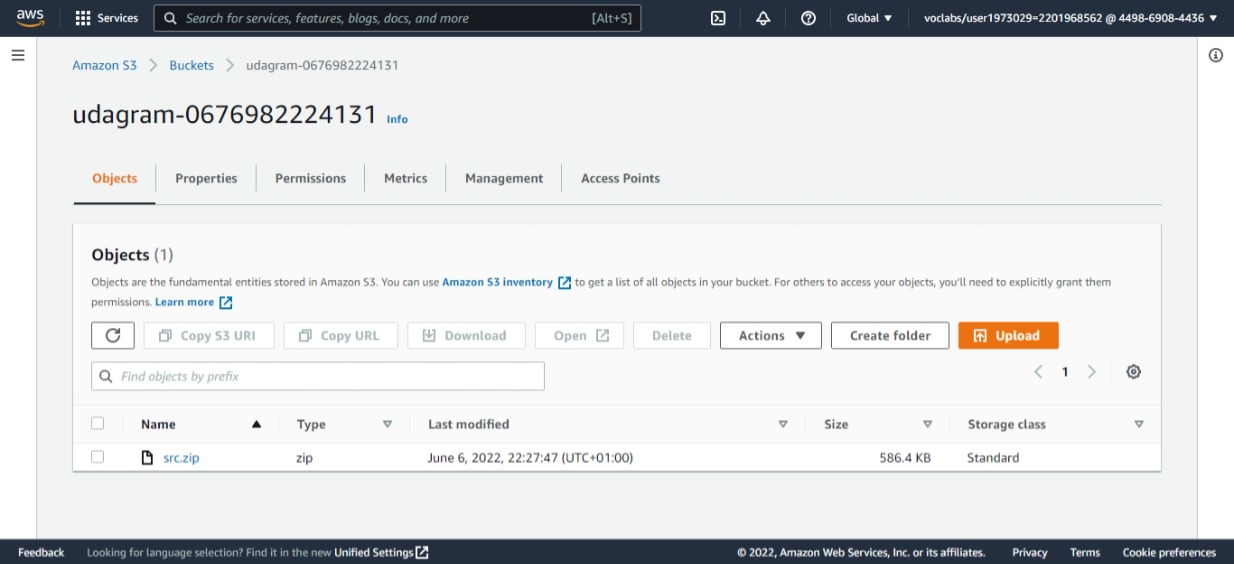 Web file copied successfully
Web file copied successfully
Step 6
- Identify your server resources (load-balancer, target groups, bastion server, EC2 instances, s3 bucket, load-balancer listener, and others)
- declare the parameters in a newser.json file as shown below
declare your resources in a newser1.yml file as shown below
[ { "ParameterKey": "EnvironmentName", "ParameterValue": "UdagramProjects" }, { "ParameterKey": "AMIToUse", "ParameterValue": "ami-005de95e8ff495156" } ]Copy the above parameters into the newser.json file and save.
Description: |
Oluwatobi Solomon Udacity Project 2 | 2022
Parameters:
#Parameters needed for Udagram project
EnvironmentName:
Description: An environment name that will be prefixed to resource names
Type: String
Default: xxx
# S3BucketName:
# Description: >
# A globally unique S3 bucket name.
# Please upload the src.zip to the bucket after creating this stack.
# Type: String
# Default: udagram-0676982224131
# KeyPair:
# Description: The keypair to use for your instances
# Type: String
# Default: keypair
AMIToUse:
Description: The AMI to use for your instances (I am working in us-west-2)
Type: String
Default: ami-005de95e8ff495156
Resources:
# SERVER RESOURCES
LoadBalancerSecGroups:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Allow http traffic to and from load balancer
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-VPCID'
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
SecurityGroupEgress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
WebServerSecGroups:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Allow http and ssh to our load balancer
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-VPCID'
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 22
ToPort: 22
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0 # change to your IP later
SecurityGroupEgress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 0
ToPort: 65535
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
# S3Buckets:
# Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
# Properties:
# AccessControl: PublicRead
# BucketName: !Ref S3BucketName
# MetricsConfigurations:
# - Id: EntireBucket
# WebsiteConfiguration:
# IndexDocument: index.html
# ErrorDocument: error.html
WebAppLaunchConfigs:
Type: AWS::AutoScaling::LaunchConfiguration
Properties:
UserData:
Fn::Base64: !Sub |
#!/bin/bash
apt-get update -y
apt-get install unzip awscli -y
apt-get install apache2 -y
systemctl start apache2.service
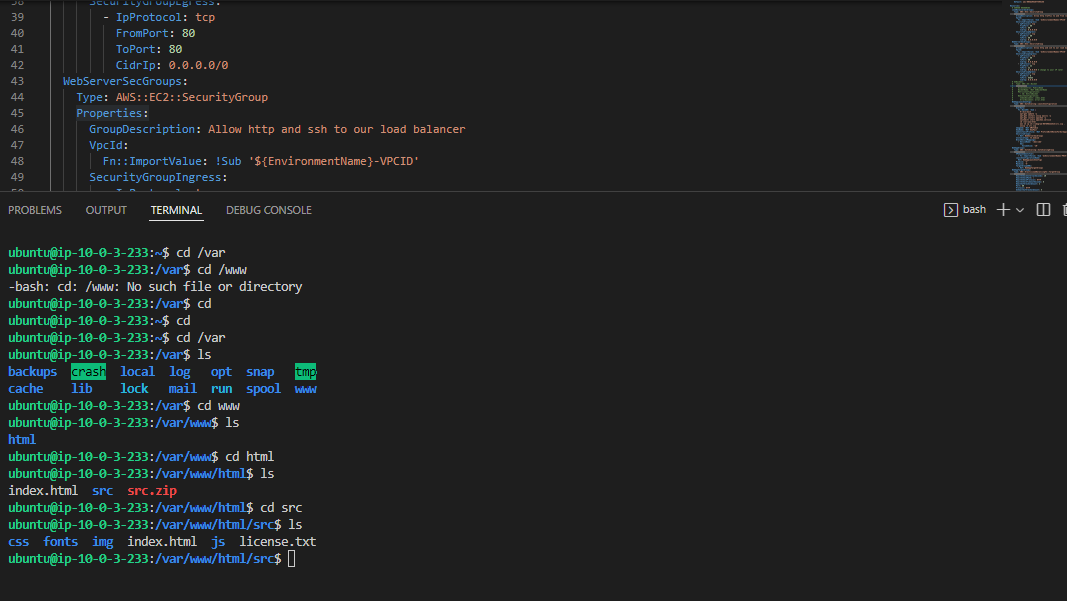
cd /var/www/html
aws s3 cp s3://udagram-0676982224131/src.zip .
unzip -o src.zip
ImageId: !Ref AMIToUse
# KeyName: !Ref KeyPair
IamInstanceProfile: !Ref ProfileWithRolesForOurApps
SecurityGroups:
- Ref: WebServerSecGroups
InstanceType: t3.medium
BlockDeviceMappings:
- DeviceName: '/dev/sdk'
Ebs:
VolumeSize: '10'
WebAppGroups:
Type: AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup
Properties:
VPCZoneIdentifier:
- Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-PRIV-NETS'
LaunchConfigurationName:
Ref: WebAppLaunchConfigs
MinSize: '4'
MaxSize: '5'
TargetGroupARNs:
- Ref: WebAppTargetGroups
WebAppTargetGroups:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
HealthCheckIntervalSeconds: 10
HealthCheckPath: /
HealthCheckProtocol: HTTP
HealthCheckTimeoutSeconds: 8
HealthyThresholdCount: 2
Port: 80
Protocol: HTTP
UnhealthyThresholdCount: 5
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-VPCID'
WebAppLBs:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer
Properties:
SecurityGroups:
- Ref: LoadBalancerSecGroups
Subnets:
- Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-PUB1-SN'
- Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-PUB2-SN'
Listeners:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
DefaultActions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn:
Ref: WebAppTargetGroups
LoadBalancerArn:
Ref: WebAppLBs
Port: 80
Protocol: HTTP
ALBListenerRules:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::ListenerRule
Properties:
Actions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref 'WebAppTargetGroups'
Conditions:
- Field: path-pattern
Values: [/]
ListenerArn: !Ref 'Listeners'
Priority: 1
BastionServers:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
ImageId: !Ref AMIToUse
# KeyName: !Ref KeyPair
InstanceType: t3.medium
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Bastion Server
NetworkInterfaces:
- AssociatePublicIpAddress: true
DeviceIndex: 0
GroupSet:
- Ref: WebServerSecGroups
SubnetId:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: '${EnvironmentName}-BAST-SN'
UserData:
Fn::Base64: |
#!/bin/bash
apt-get update -y
apt-get install unzip awscli -y
apt-get install apache2 -y
systemctl start apache2.service
S3ReadOnlyEC2s:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-Role
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- ec2.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: '/'
RolePolicy:
Type: AWS::IAM::Policy
Properties:
PolicyName: AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- s3:Put*
- s3:Get*
- s3:List*
Resource:
- arn:aws:s3:::udagram-0676982224131/
- arn:aws:s3:::udagram-0676982224131/*
Roles:
- Ref: S3ReadOnlyEC2s
ProfileWithRolesForOurApps:
Type: AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile
Properties:
Path: '/'
Roles:
- Ref: S3ReadOnlyEC2s
Outputs:
WebAppLoadBalancerDNSNames:
Description: DNS name or Public URL of the Load Balancer
Value: !Join ['', ['http://', !GetAtt WebAppLBs.DNSName]]
Export:
Name: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-LB-DNSName
Copy the above resources into the newnet1.yml file and save.
Step 7 Now is the time to set up our Server infrastructure using cloudformation.
- Open your terminal and change the directory (cd) to your scripts directory before running the code below to avoid a not found error.
if it executes correctly it displays the stack ID and auto-create on the cloudfromation GUI and simultaneously creates all the server resources declared in the newser1.yml file./create.sh UdagramServer newser1.yml newser.json
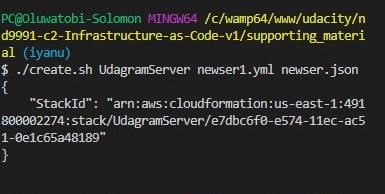
Once this is successful, your server resources as shown below should now be available on your AWS portal
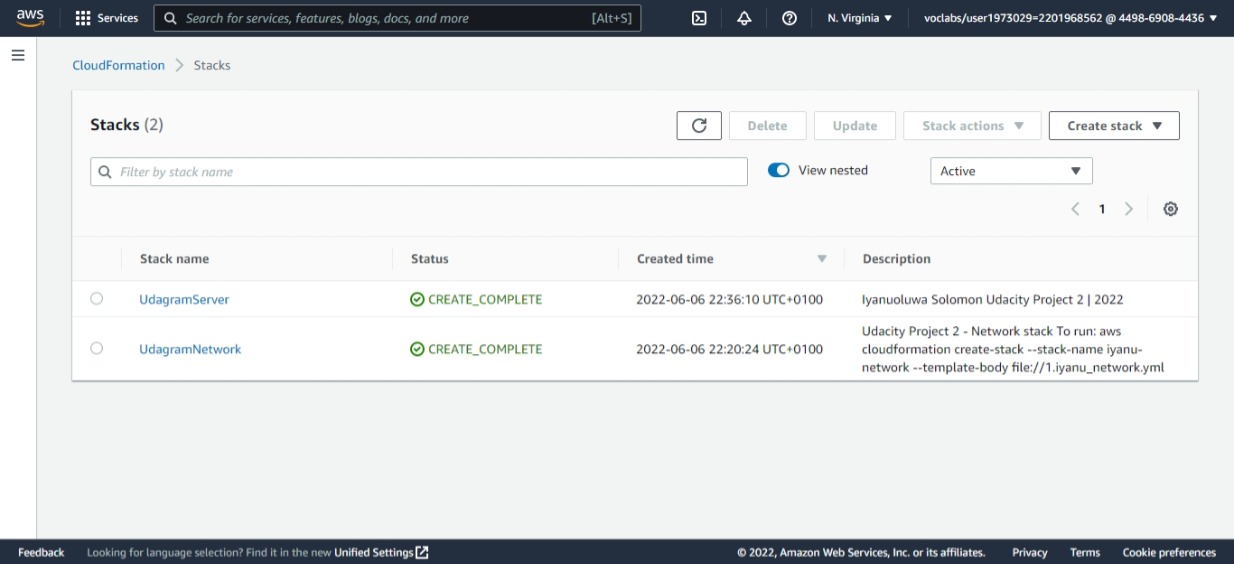 This shows the successful states of the stack created i.e. UdagramNetwork and UdagramServer
This shows the successful states of the stack created i.e. UdagramNetwork and UdagramServer
Below are server resources created upon the successful execution of the UdagramServer
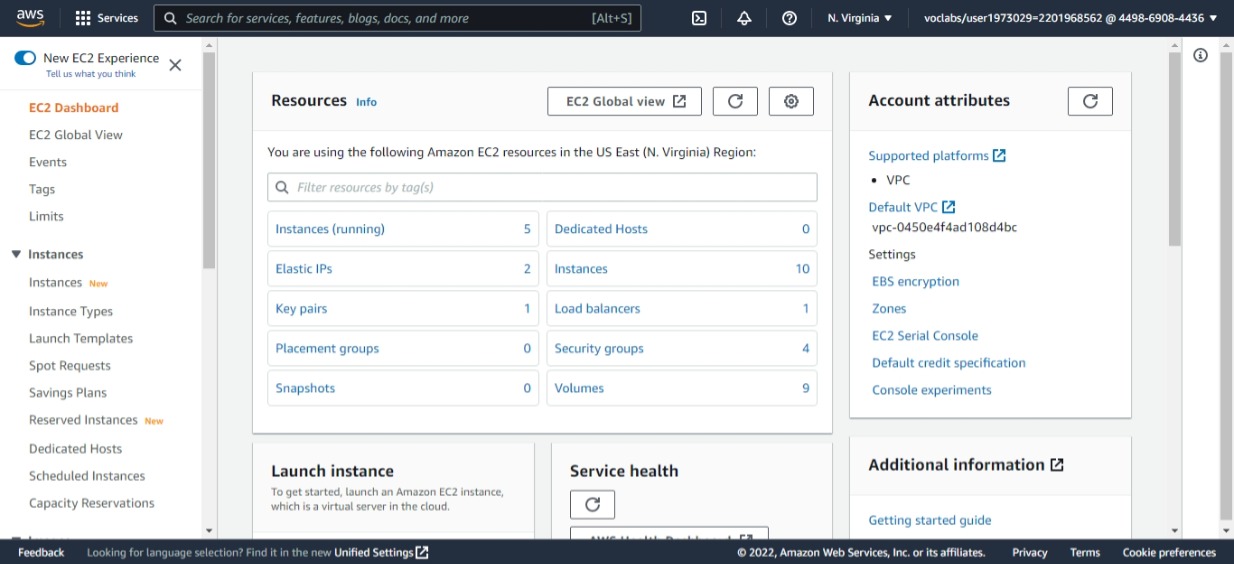 This shows the EC2 resources created
This shows the EC2 resources created
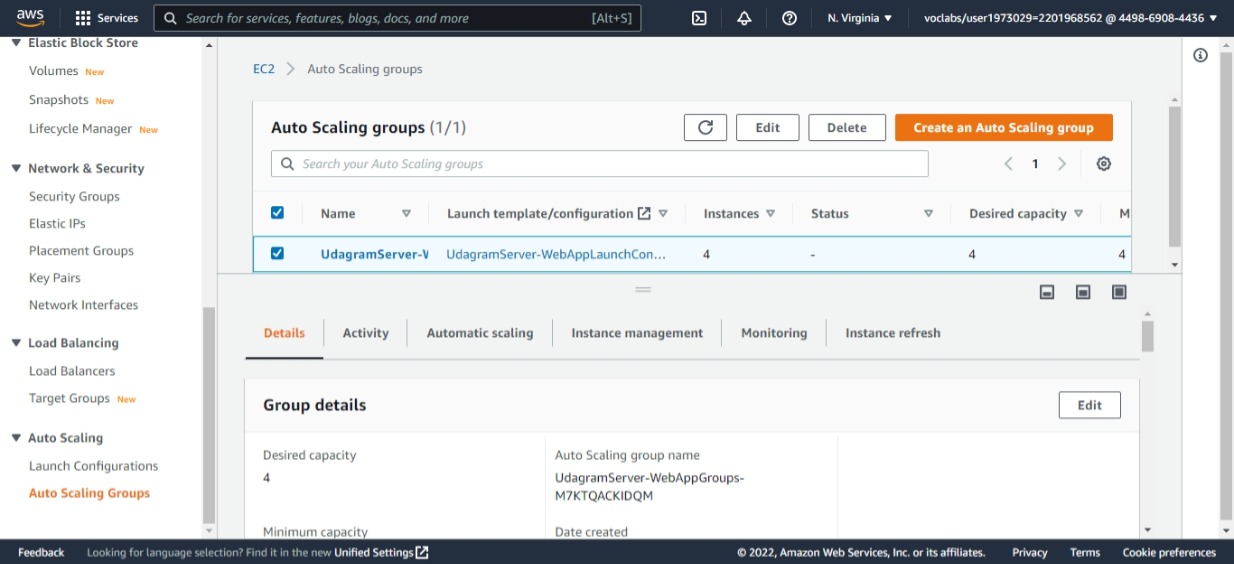 Udagram auto-scaling group created
Udagram auto-scaling group created
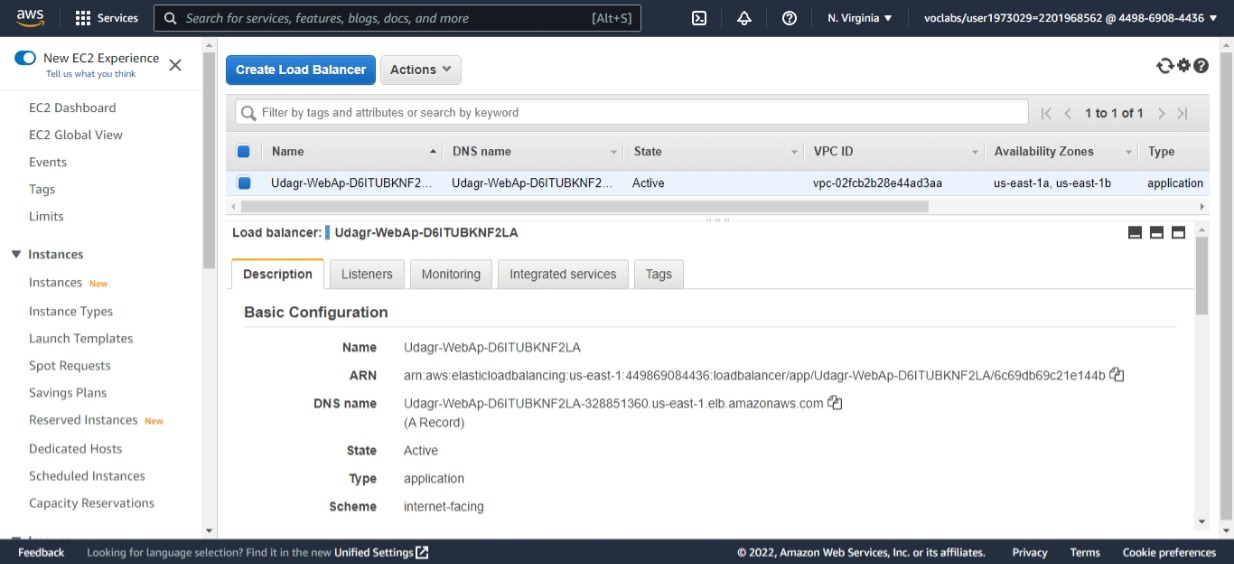 Udagram Load-balancer created
Udagram Load-balancer created
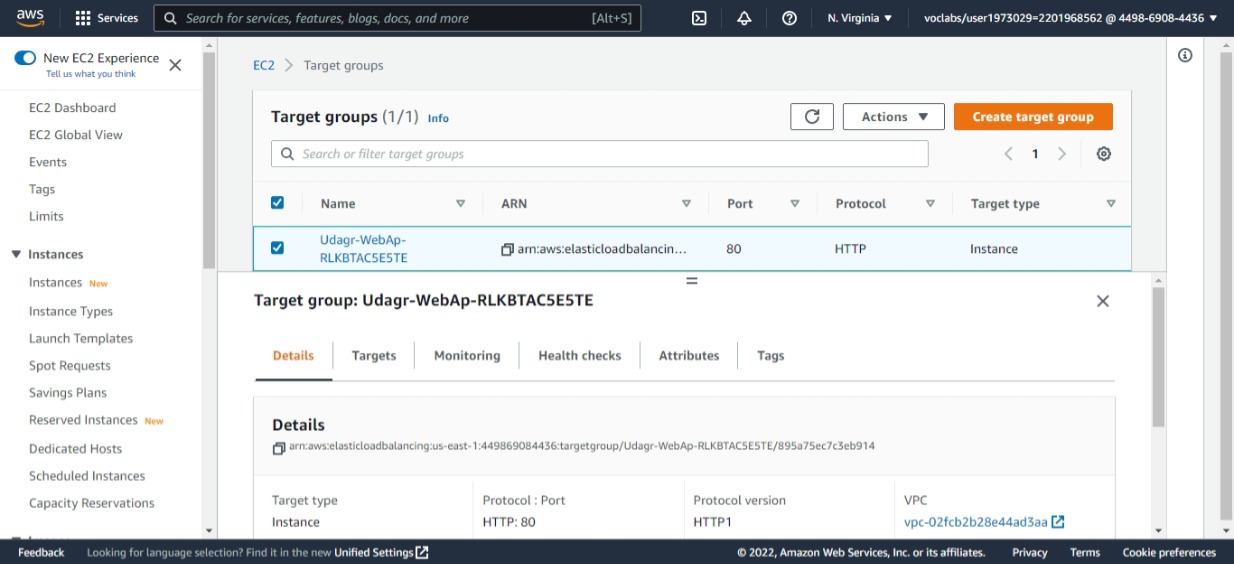 Udagram Target Group created
Udagram Target Group created
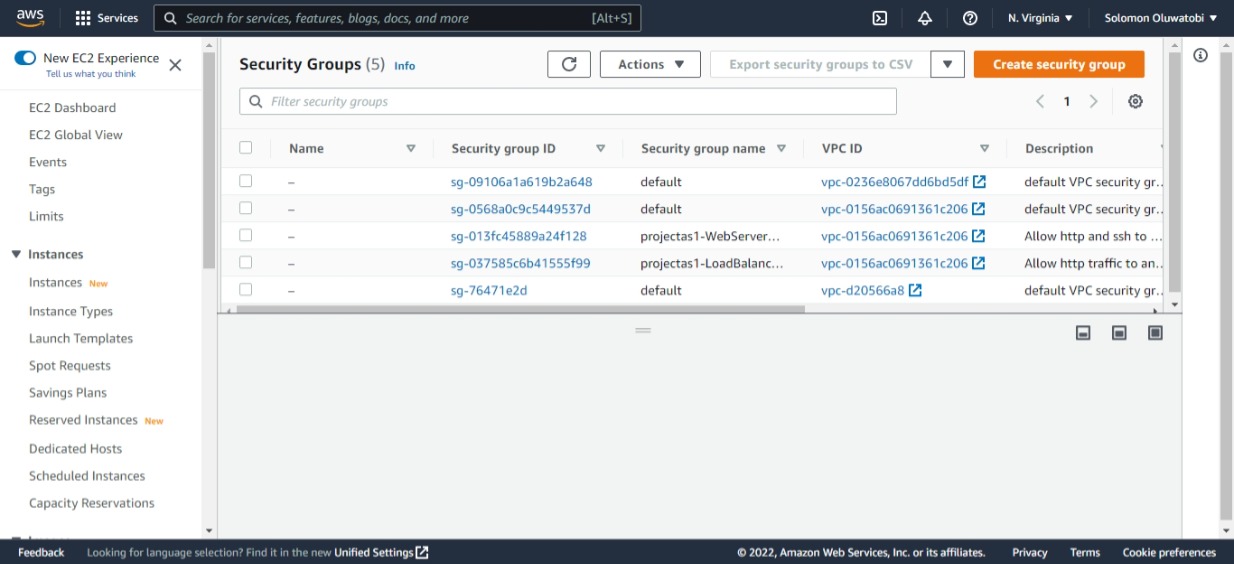 Udagram security group created
Udagram security group created
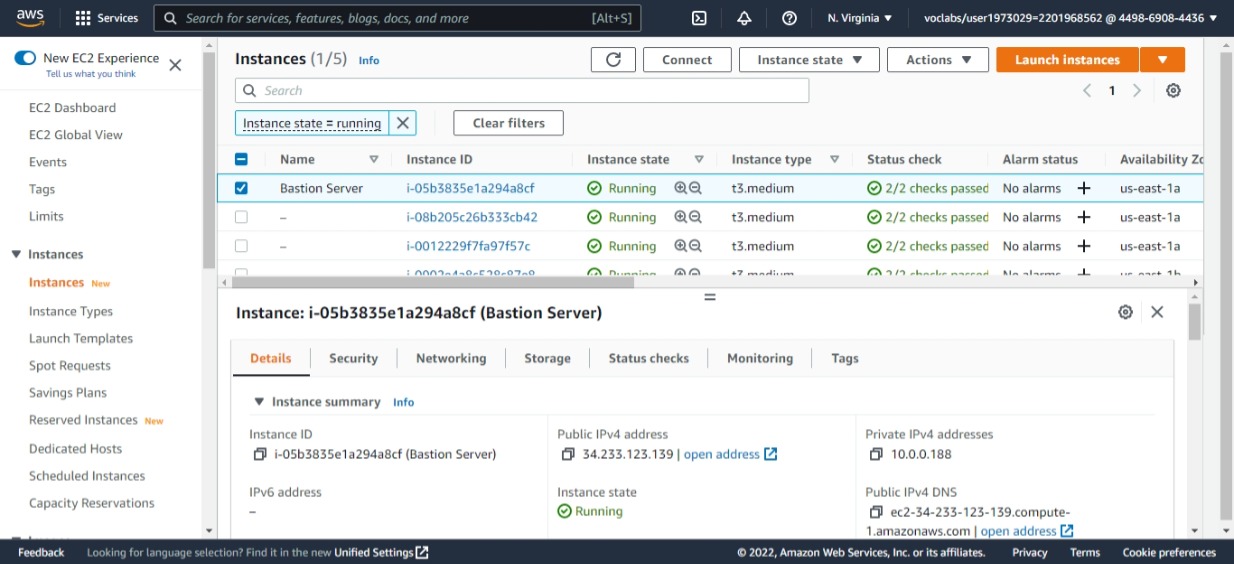 Udagram instances created including the bastion server
Udagram instances created including the bastion server
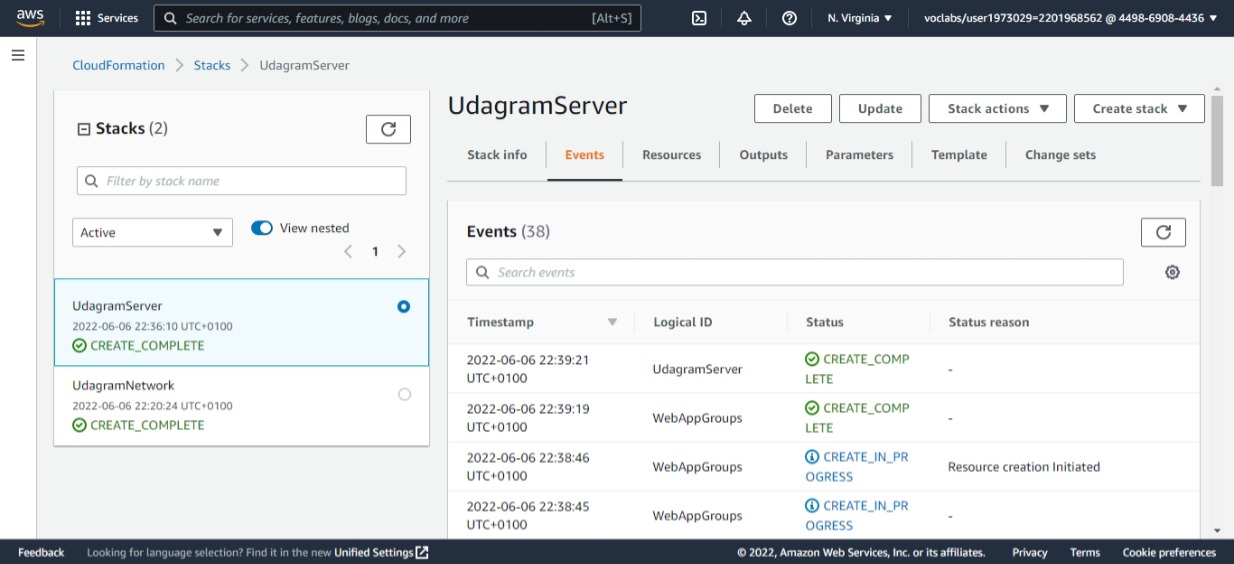 Udagram server events created
Udagram server events created
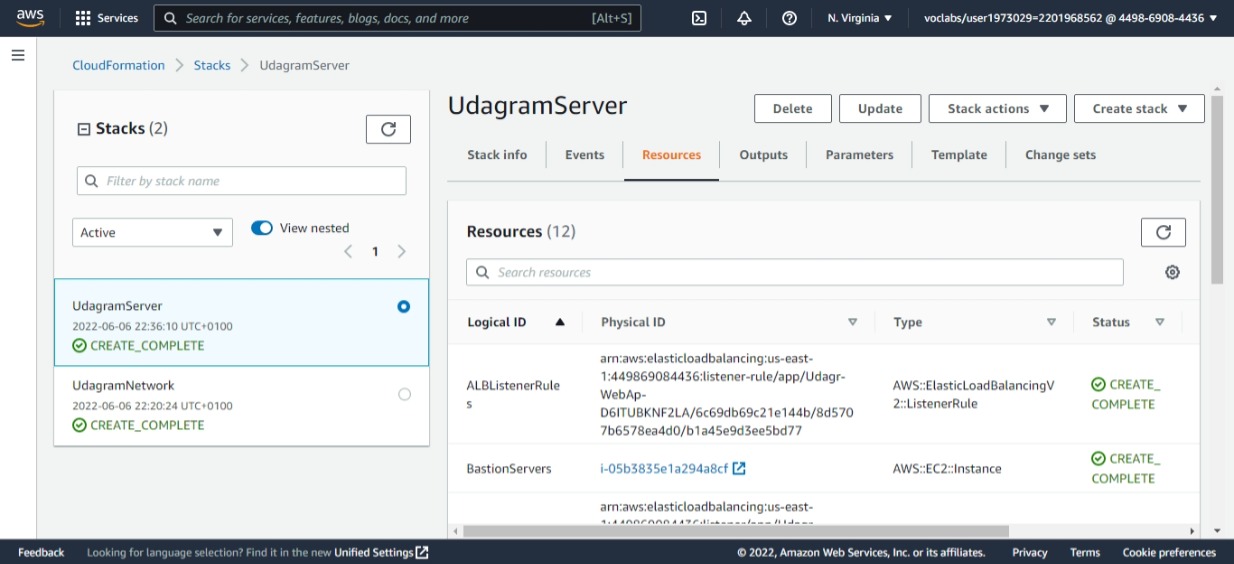 Udagram server resources created (12 Resources)
Udagram server resources created (12 Resources)
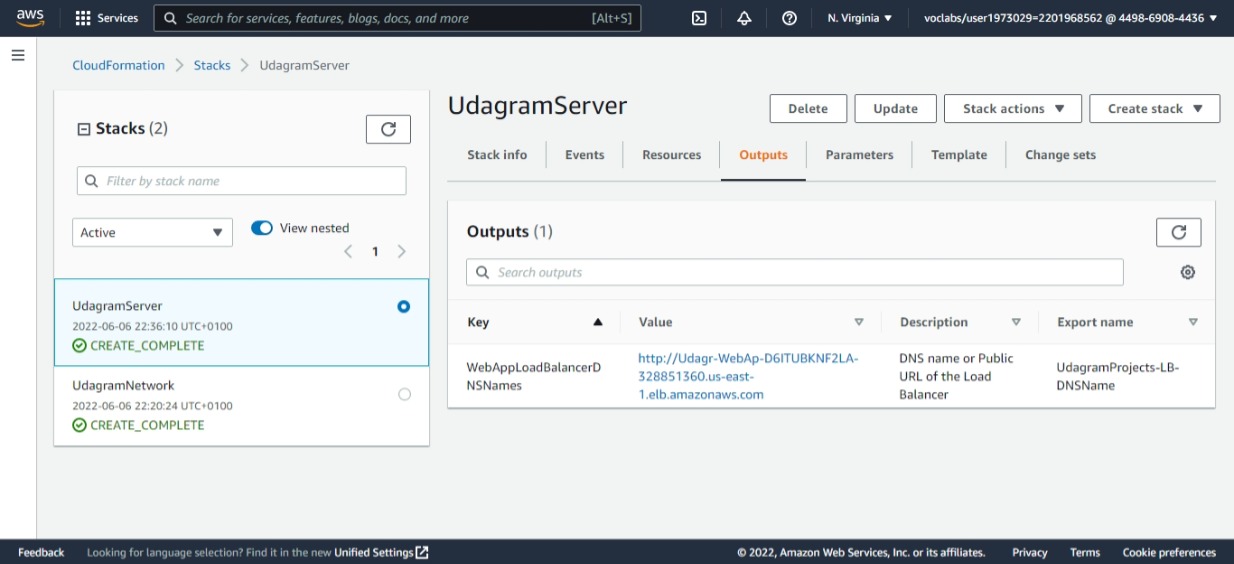 Udagram server output created
Udagram server output created
If all the above is what you see, then you have successfully deployed your high-availability web application through cloudformation.
 HURRAY! OUR APPLICATION IS LIVE
HURRAY! OUR APPLICATION IS LIVE
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Oluwatobi Solomon directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
