一次 MySql 分页查询优化原理分析
 Edward Chu
Edward Chu场景: 有一张财务流水表,未分库分表,目前的数据量为955万+,分页查询使用到了limit,优化之前的查询耗时 16 s 912 ms (execution: 16 s 805 ms, fetching: 107 ms),按照下文的方式调整SQL后,耗时 332 ms (execution: 158 ms, fetching: 174 ms);
操作: 查询条件放到子查询中,子查询只查主键ID,然后使用子查询中确定的主键关联查询其他的属性字段;
原理: 减少回表操作,利用延迟关联或者子查询优化超多分页场景。
-- 优化前 SQL
SELECT 各种字段
FROM `table_name`
WHERE 各种条件
LIMIT 0,10;
-- 优化后SQL
SELECT 各种字段
FROM `table_name` main_tale
RIGHT JOIN
(
SELECT 子查询只查主键
FROM `table_name`
WHERE 各种条件
LIMIT 0,10;
) temp_table ON temp_table.主键 = main_table.主键
MySQL 用 limit 为什么会影响性能?
前言
说明一下MySQL的版本:
mysql> select version();
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 5.7.17 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
表结构:
mysql> desc test;
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | bigint(20) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| val | int(10) unsigned | NO | MUL | 0 | |
| source | int(10) unsigned | NO | | 0 | |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
id为自增主键,val为非唯一索引。 向表中添加 500 万条数据:
mysql> select count(*) from test;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5242882 |
+----------+
1 row in set (4.25 sec)
我们知道,当limit offset rows中的offset很大时,会出现效率问题:
mysql> select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5;
+---------+-----+--------+
| id | val | source |
+---------+-----+--------+
| 3327622 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327632 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327642 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327652 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327662 | 4 | 4 |
+---------+-----+--------+
5 rows in set (15.98 sec)
为了达到相同的目的,我们一般会改写成如下语句:
mysql> select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) b on a.id=b.id;
+---------+-----+--------+---------+
| id | val | source | id |
+---------+-----+--------+---------+
| 3327622 | 4 | 4 | 3327622 |
| 3327632 | 4 | 4 | 3327632 |
| 3327642 | 4 | 4 | 3327642 |
| 3327652 | 4 | 4 | 3327652 |
| 3327662 | 4 | 4 | 3327662 |
+---------+-----+--------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.38 sec)
时间相差很明显。
为什么会出现上面的结果?我们看一下 select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5; 的查询过程:
查询到索引叶子节点数据。根据叶子节点上的主键值去聚簇索引上查询需要的全部字段值。
类似于下面这张图:
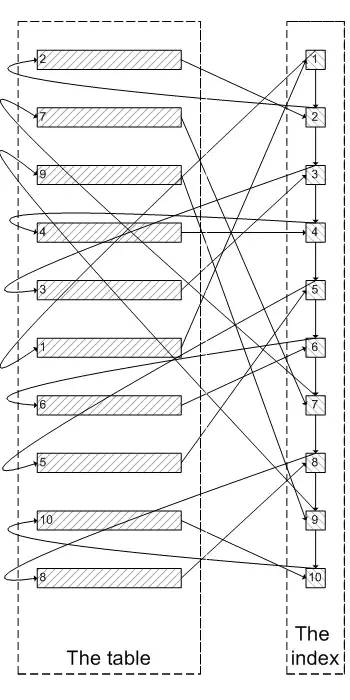 像上面这样,需要查询 300005 次索引节点,查询 300005 次聚簇索引的数据,最后再将结果过滤掉前 300000 条,取出最后 5 条。MySQL 耗费了大量随机 I/O 在查询聚簇索引的数据上,而有 300000 次随机 I/O 查询到的数据是不会出现在结果集当中的。
像上面这样,需要查询 300005 次索引节点,查询 300005 次聚簇索引的数据,最后再将结果过滤掉前 300000 条,取出最后 5 条。MySQL 耗费了大量随机 I/O 在查询聚簇索引的数据上,而有 300000 次随机 I/O 查询到的数据是不会出现在结果集当中的。
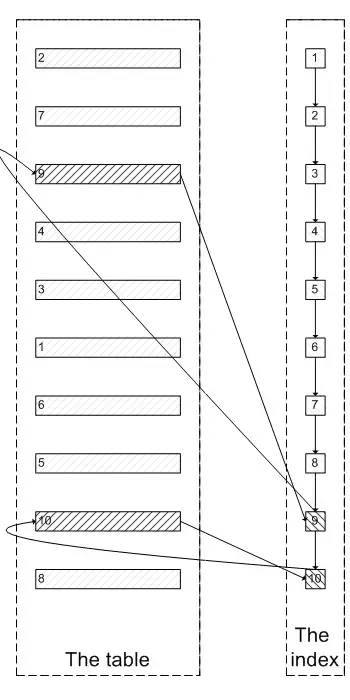
肯定会有人问:既然一开始是利用索引的,为什么不先沿着索引叶子节点查询到最后需要的5个节点,然后再去聚簇索引中查询实际数据。这样只需要 5 次随机 I/O,类似于下面图片的过程:
证实
下面我们实际操作一下来证实上述的推论:
为了证实 select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5 是扫描 300005 个索引节点和 300005 个聚簇索引上的数据节点,我们需要知道 MySQL 有没有办法统计在一个 sql 中通过索引节点查询数据节点的次数。
我只能通过间接的方式来证实:
InnoDB 中有 buffer pool。里面存有最近访问过的数据页,包括数据页和索引页。所以我们需要运行两个 sql,来比较 buffer pool 中的数据页的数量。
预测结果是运行 select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5); 之后,buffer pool 中的数据页的数量远远少于 select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5; 对应的数量,因为前一个 sql 只访问 5 次数据页,而后一个 sql 访问 300005 次数据页。
select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5
mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name;
Empty set (0.04 sec)
可以看出,目前 buffer pool 中没有关于 test 表的数据页。
mysql> select * from test where val=4 limit 300000,5;
+---------+-----+--------+
| id | val | source |
+---------+-----+--------+|
3327622 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327632 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327642 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327652 | 4 | 4 |
| 3327662 | 4 | 4 |
+---------+-----+--------+
5 rows in set (26.19 sec)
mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name;
+------------+----------+
| index_name | count(*) |
+------------+----------+
| PRIMARY | 4098 |
| val | 208 |
+------------+----------+2 rows in set (0.04 sec)
可以看出,此时 buffer pool 中关于 test 表有 4098 个数据页,208 个索引页。
select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) ; 为了防止上次试验的影响,我们需要清空 buffer pool,重启 mysql。
mysqladmin shutdown
/usr/local/bin/mysqld_safe &
mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name;
Empty set (0.03 sec)
运行sql:
mysql> select * from test a inner join (select id from test where val=4 limit 300000,5) b on a.id=b.id;
+---------+-----+--------+---------+
| id | val | source | id |
+---------+-----+--------+---------+
| 3327622 | 4 | 4 | 3327622 |
| 3327632 | 4 | 4 | 3327632 |
| 3327642 | 4 | 4 | 3327642 |
| 3327652 | 4 | 4 | 3327652 |
| 3327662 | 4 | 4 | 3327662 |
+---------+-----+--------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.09 sec)
mysql> select index_name,count(*) from information_schema.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE where INDEX_NAME in('val','primary') and TABLE_NAME like '%test%' group by index_name;
+------------+----------+
| index_name | count(*) |
+------------+----------+
| PRIMARY | 5 |
| val | 390 |
+------------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.03 sec)
可以看明显的看出两者的差别:第一个 sql 加载了 4098 个数据页到 buffer pool,而第二个 sql 只加载了 5 个数据页到 buffer pool。符合我们的预测。 也证实了为什么第一个 sql 会慢:读取大量的无用数据行(300000),最后却抛弃掉。而且这会造成一个问题:加载了很多热点不是很高的数据页到 buffer pool,会造成 buffer pool 的污染,占用 buffer pool 的空间。
为了在每次重启时确保清空 buffer pool,我们需要关闭innodb_buffer_pool_dump_at_shutdown 和innodb_buffer_pool_load_at_startup,这两个选项能够控制数据库关闭时 dump 出 buffer pool 中的数据和在数据库开启时载入在磁盘上备份 buffer pool 的数据。
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Edward Chu directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Edward Chu
Edward Chu
Science is gold.