Position in CSS
 Madhavan vv
Madhavan vv
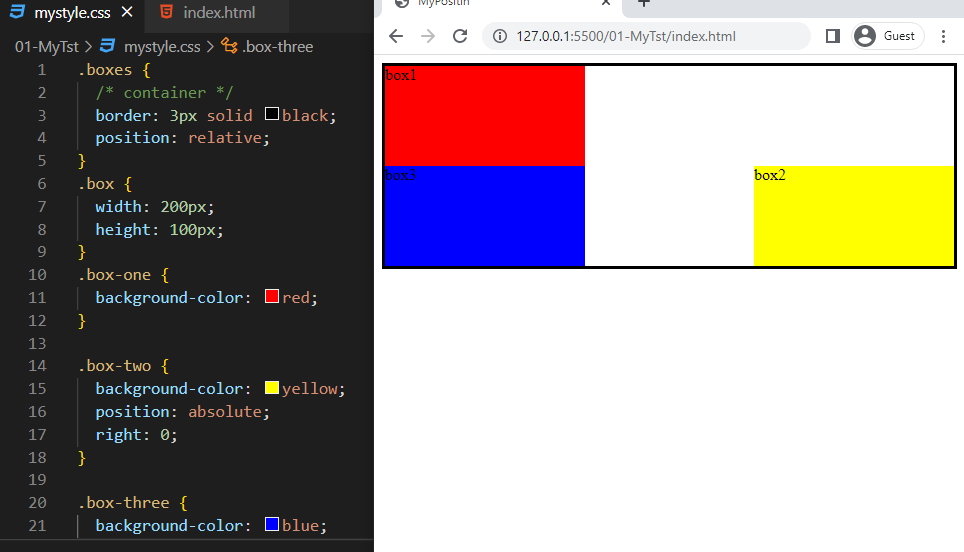
The position CSS property sets how an element is positioned in a document.
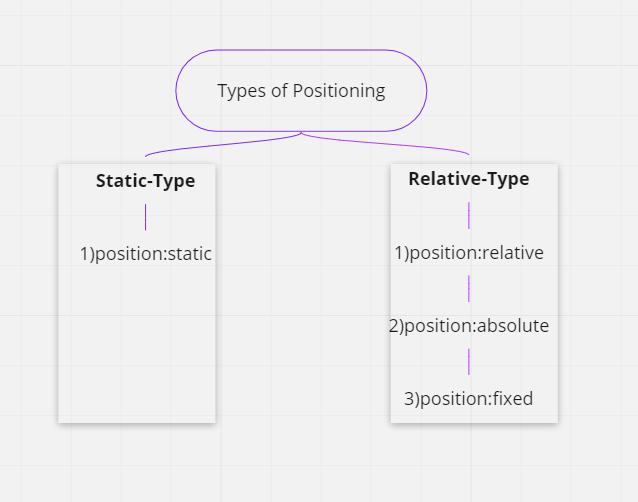
position: static;
The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document.
The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have no effect.
This is the default value.
Example:
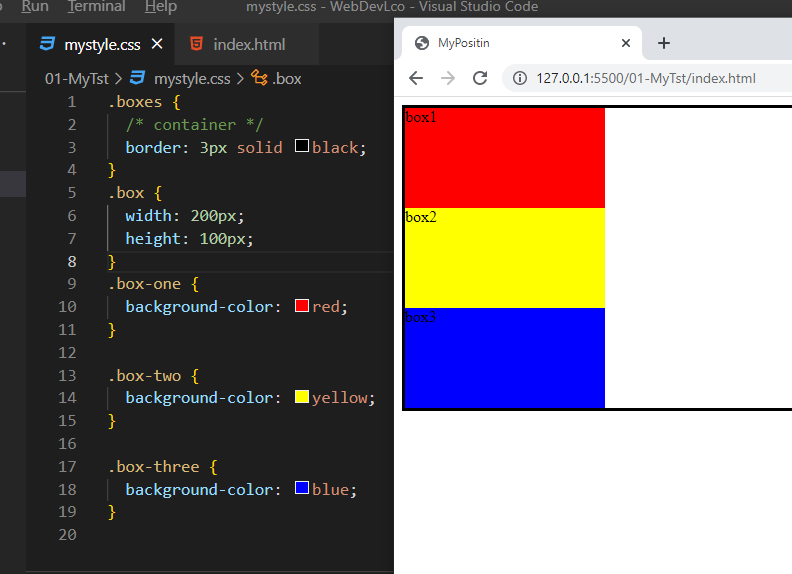
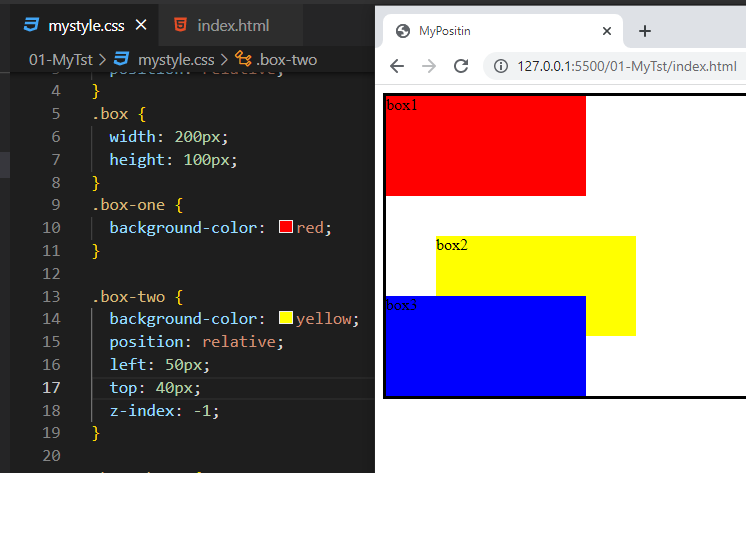
position: relative;
- The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document.
- The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have effect.
- position: relative; does not affect the position of any other elements.
- the space given for the element in the page layout is the same as if position were static.
Example:
position: absolute;
- The element is removed from the normal document flow.
- The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have effect.
position: absolute; affect's the position of other elements (if any).
if the container position set to relative It is positioned relative to its container.if not,It is positioned relative to its closest positioned ancestor, if any; otherwise, it is placed relative to the initial containing block.
Example:
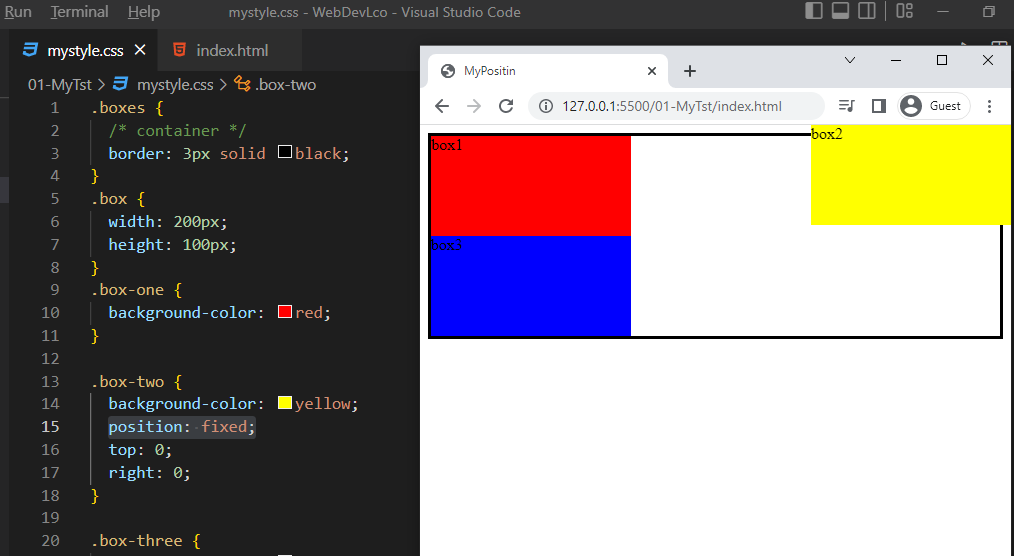
position: fixed;
- The element is removed from the normal document flow.
- The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have effect.
position: fixed; affect's the position of other elements (if any).
It is positioned relative to the initial containing block established by the viewport, Example:
Further reading:MDN Web Docs: CSS Position
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Madhavan vv directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by