AND problems
 Hyunwoo Choi
Hyunwoo Choi- AND
Some bit manipulation problems require to use AND in code. In this article, I will introduce couple AND problems and solution. AND is represented by & in C language. AND truth table is shown below.
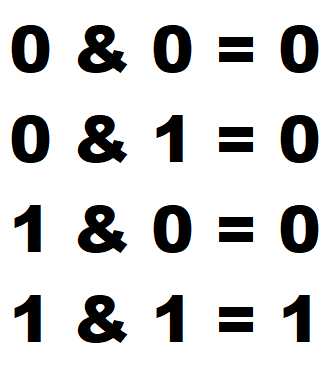
When two bits are 1, result is 1. Rests are 0.
- Problem1: Return number of 1s when given unsigned integer number is represented as binary. Reference:https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/solution/

uint32_t problem1(uint32_t input)
{
uint32_t output = 0;
//Implement logic
return output;
}
Brute force approach would be looping through all bit and increase count if value is 1. Another approach would be repeat input = input & (input - 1) until input = 0.
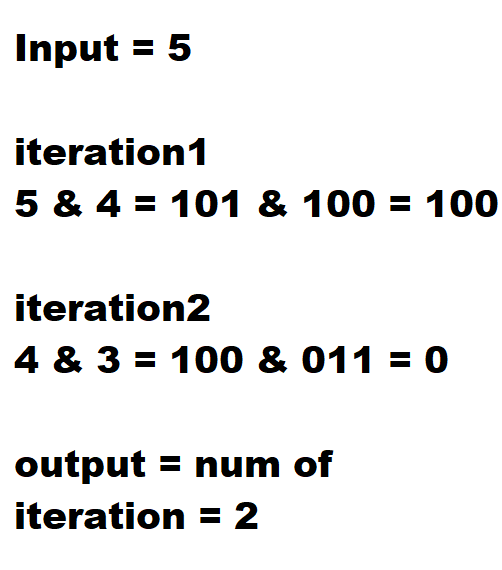 input & (input - 1) always flips the least significant 1-bit in input to 0. So, each iteration will find out 1 in current input.
input & (input - 1) always flips the least significant 1-bit in input to 0. So, each iteration will find out 1 in current input.
- Implementation and test
Create and_problems ceedling project
ceedling module:create[and_problems]and_problems.h
#ifndef AND_PROBLEMS_H #define AND_PROBLEMS_H #include <stdint.h> uint32_t problem1_1(uint32_t input); uint32_t problem1_2(uint32_t input); #endif // AND_PROBLEMS_Hand_problems.c
#include "and_problems.h" uint32_t problem1_1(uint32_t input) { uint32_t output = 0; while(input != 0) { if(input % 2 == 1) { output++; } input /= 2; } return output; } uint32_t problem1_2(uint32_t input) { uint32_t output = 0; while(input != 0) { input = input & (input - 1); output++; } return output; }test_and_problems.c
#include "unity.h" #include "and_problems.h" void setUp(void) { } void tearDown(void) { } void test_and_problem1_example1(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(2, problem1_1(5)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(2, problem1_2(5)); } void test_and_problem1_example2(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem1_1(0)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem1_2(0)); } void test_and_problem1_example3(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(32, problem1_1(0xFFFFFFFF)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(32, problem1_2(0xFFFFFFFF)); }Run test and result
ceedling test:and_problems
Problem2: Given an integer n, return 1 if it is a power of two. Otherwise, return 0. Reference: https://leetcode.com/problems/power-of-two/
uint8_t problem2(uint32_t n) { uint8_t result = 0; //Implement the logic return result; }Implementation and test
Brute force approach would be iterate until n becomes 0 and each time checking if n modulo 2 is not 1 then divide up by 2 and continue. Another approach would be checking if n is equal to n & (-n) assuming n is not 0.
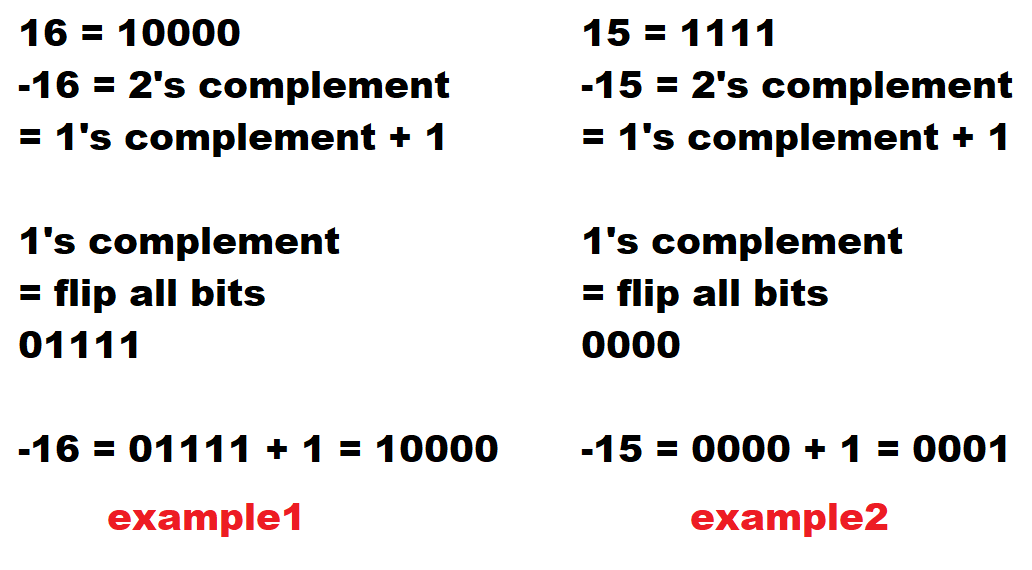
Add function prototype in and_problems.h
uint8_t problem2_1(uint32_t n); uint8_t problem2_2(uint32_t n);Add function in and_problems.c
uint8_t problem2_1(uint32_t n) { uint8_t output = 1; if(n == 0) { output = 0; } else { while(n != 0) { if((n % 2 == 1) && (n != 1)) { output = 0; break; } n /= 2; } } return output; } uint8_t problem2_2(uint32_t n) { uint8_t output = 1; if(n == 0) { output = 0; } else { output = ((n & -n) == n) ? 1 : 0; } return output; }Add test cases in test_and_problems.c
void test_and_problem2_example1(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(1, problem2_1(16)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(1, problem2_2(16)); } void test_and_problem2_example2(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem2_1(15)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem2_2(15)); } void test_and_problem2_example3(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem2_1(0)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(0, problem2_2(0)); } void test_and_problem2_example4(void) { TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(1, problem2_1(1)); TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(1, problem2_2(1)); }Run test and result
ceedling test:and_problems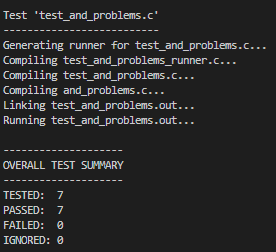
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Hyunwoo Choi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
