Key RAN Procedures
 Shankar
ShankarTable of contents

When our device UE turn on or a sim is inserted into it, it tries to connect to a network i.e enodeb/gnodeb for synchronization and data transmission from UE to gnode b and vice versa. So when you device try to synchronize for the first time with gnode it go through some different initial procedures which are discussed below.
Initial Access:
When device turns on it and tries to connect to the gnodeb then it searches for the physical cell id provided by gnodeb to connect to synchronize data. Thuis process of searching for cell id and synchronizing data with gnodeb is called as cell search.
Cell Search :
procedure by which a UE acquires time and frequency synchronization with a cell and detects the Cell ID of that cell.
Cell ID:
It is a unique id provided by each gnodeb for making a fair connectioon with UE. Cell ID majorly have two subparts:
- PSS: It stands for Primary Synchronization Signal. As the name suggests, it is the primary signal that a UE searches for initially connecting to gnodeb.
- SSS: Secondary Synchronization Signal
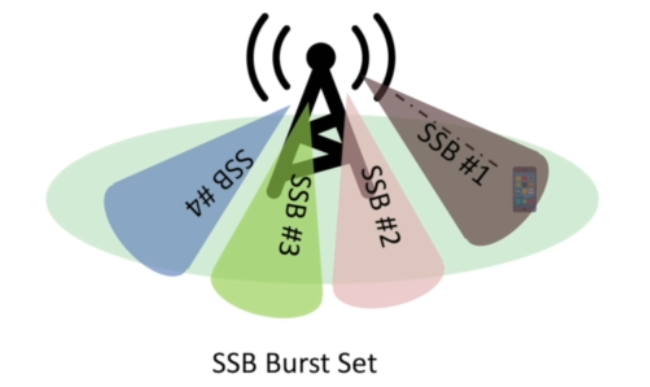
These two together form the cell ID. Other than Cell ID, UE needs one more component for achieving basic info about the cells. So that task is done by PBCH. These two i.e cell id(PSS+SSS) and PBCH forms the SSB(Sync Signal Block).
A gnode contains of several SSBs and SSB with some other SSBs form a SSB Srust Set.
Now lets move onto the procedures that a NR and UR goes through for synchronizing data and establishing a relation.
Procedures:
Scan for PSS:
- The primary role of UE is to scan for PSS.
A gnode contains a bulk of frequency bands. So UE has to decide which one he has to search for and this type is information(search this or this frequency band) is present in SIM card of UE. So UE searches for non-frequency bands and then searches for synchronization signlas. The UE start scanning some preferred frequency bands(as instructed by SIM card). But the that one specific band also contains a lot of bands in it. So searching for a specific band is a bit time consuming and complicated. Then the actual band will be consisting of a resolution of 100kHz. That one specific band is callled as
carrier raster. The carrier raster band is used by UE to detect PSS.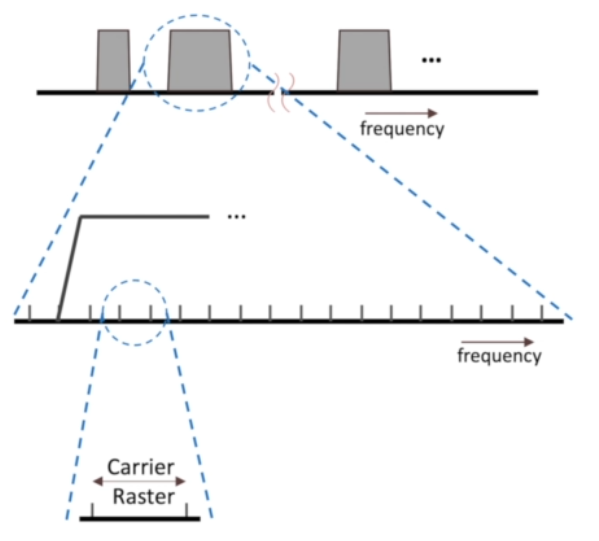
A PSS can take mox of three cell IDs and select on from them.
Represented as: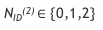
Note: In 4G-LTE, Synchronization Signal transfer is conducted into each 5 milli seconds. Whereas in 5G-NR. scanning for PSS is conducted into every 20 milli seconds. So, 5G-NR is more efficient and conumes low power as compared to LTE.
Scan for SSS:
- After getting PSS, device is aware about transmission timing of SSS.
It can take up to 356 max values.
It contains mac 1008 different physical cell IDs.
Represented as :
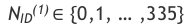
To find cell id use:
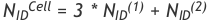
Decode PBCH: It provides the minimum system information.
MIB(Master Information Block):
- System Bandwidth
- System Frame Number(SFI)
- Cell Barred
- SCS(Sub Carrier Spacing)
- Parameter for SBI 1 acquisition
SIB 1(System Information Block 1):
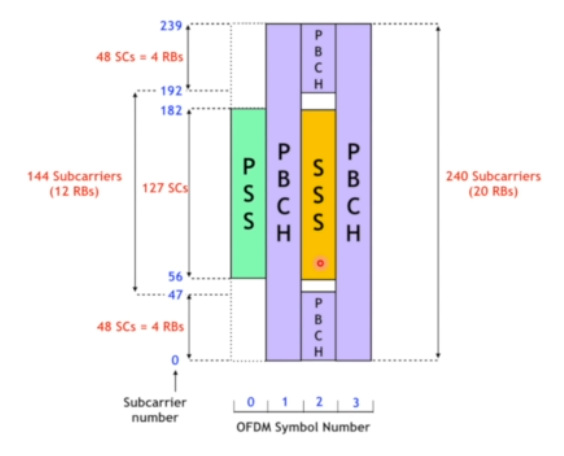
Decode SIB 1: It provides Remaining Minimum System Information(Information Other than MIB)
- Cell Selection Information
- Cell Access information
- Information about other SIBs
Other SIBs: These are those which not necessarily need to know
- Periodic Transmission
- On-demand

Summary
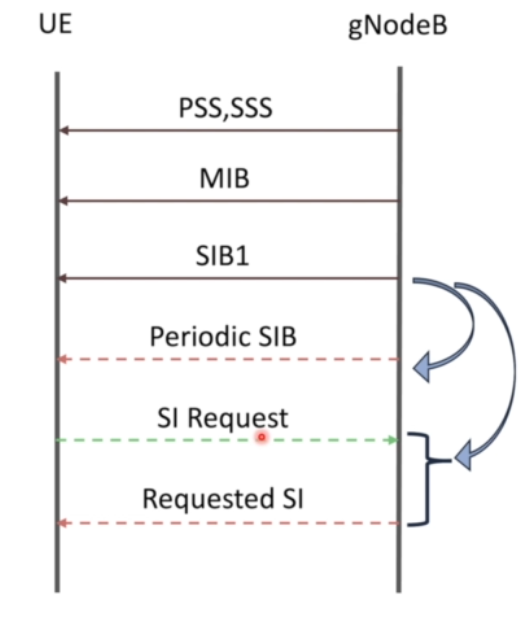
After reading whatever is relevant, then UE decides whether the current is suitable for camping or not. If everything is successful without any errors then UE decides to camp.
In LTE:
In 5G-NR:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shankar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Shankar
Shankar
5G & Cloud