A guide to Etherscan | Part 1: The Homepage
 Mocha
Mocha
Using Etherscan is much easier than it looks
Etherscan is a block explorer, a powerful tool that allows us to see detailed information about activity happening on the Ethereum blockchain including NFT sales, token transfers, Ethereum name service (ENS) registrations and more!
Learning how to use Etherscan can enable you to check token balances, check the status of your transactions, and even look up source code for your favorite projects. Etherscan is completely free to use and provides an infinite source of value.
Any type of activity that you can see via a block explorer is typically referred to as “on-chain” activity.
What is meant by “on-chain”? ⛓️
“On-chain” refers to transactions or activity that has been validated by the blockchain and are reflected in blockchain explorers.
Depending on the blockchain, this process of validation can be costly and take time to process as it has to be validated according to the consensus rules of the network.
Since the merge, Ethereum has moved from a proof of work (PoW) consensus algorithm to a proof of stake (PoS) consensus algorithm which has resulted in lower transaction fees, greater security, and reduced energy usage.
The consensus algorithm determines which blocks are added to the blockchain and which ones are rejected by the Ethereum blockchain validators.
To get started, let’s head to the Etherscan Homepage (https://etherscan.io/) and figure out what is on the homepage.
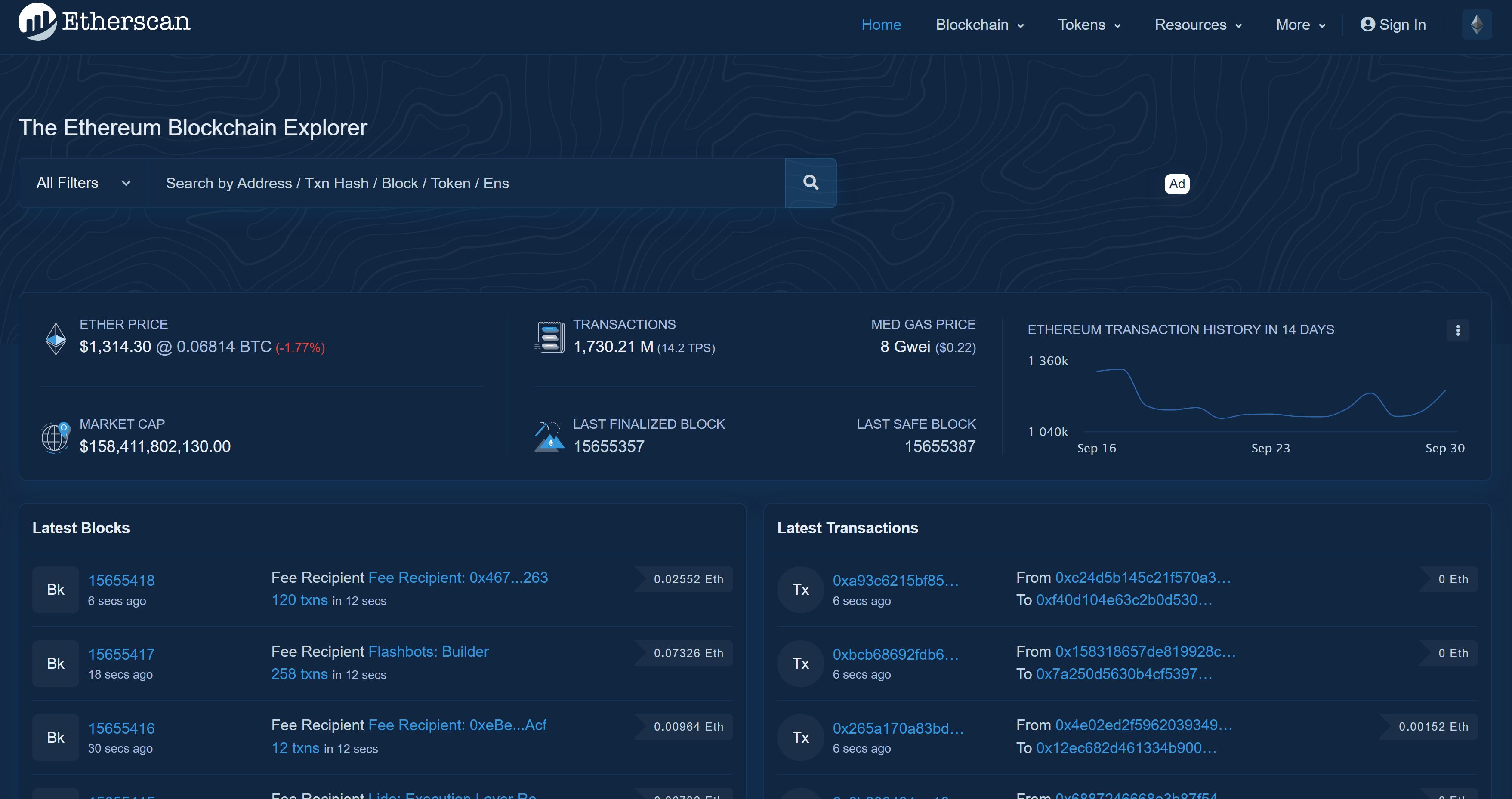
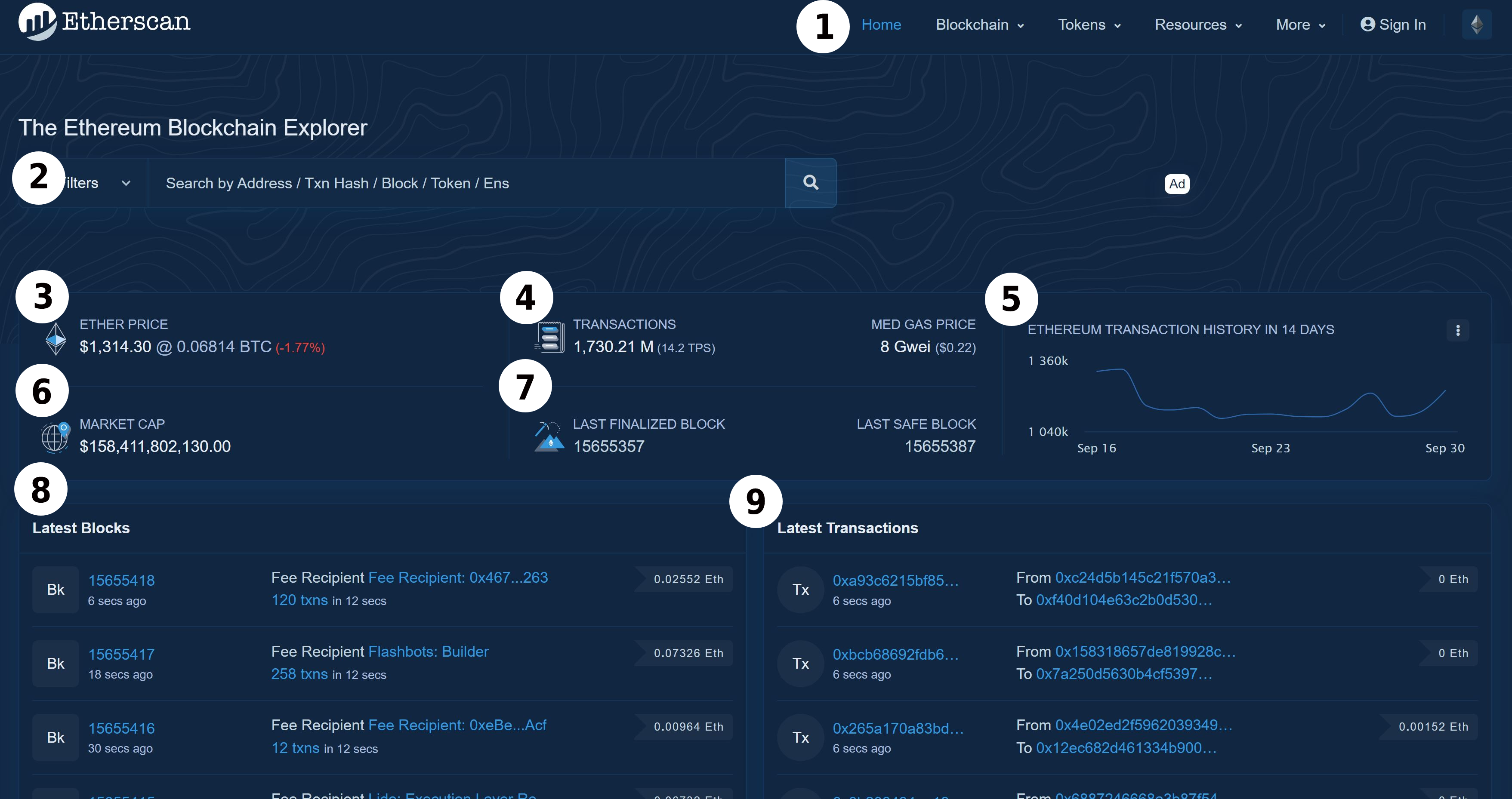
On this page, we can see a few different things.
Navigation Bar
- This includes a link back to the homepage and shortcuts to view different types of blocks, transactions, tokens, statistics, developer tooling, and links to Ethereum testnet block explorers.
Search Bar
- This search bar allows us to search by address, transaction hash, block, token, and ENS. By clicking on "All Filters" before searching, it is also possible to filter the seach based on the chosen parameters.
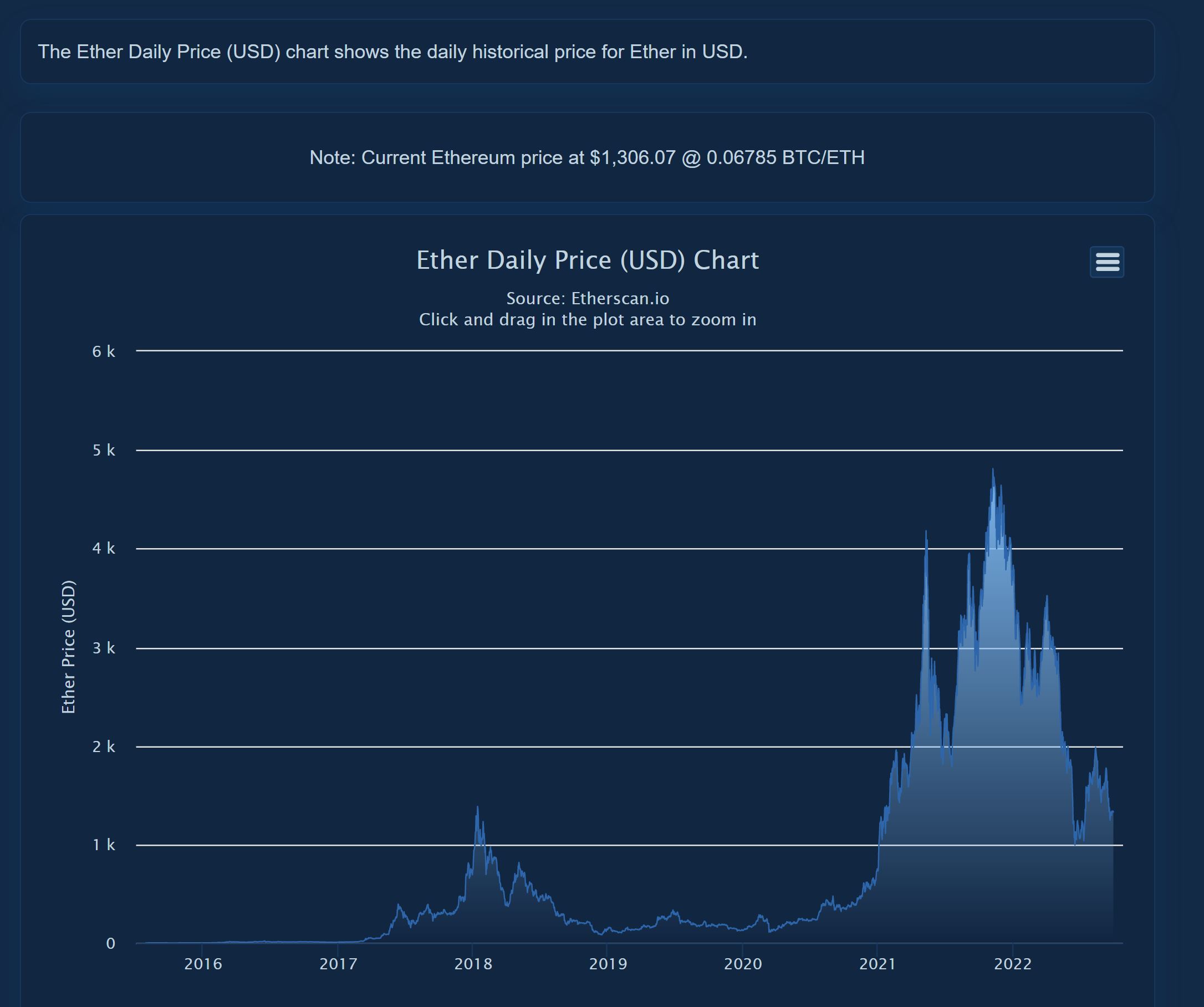
Ether Price
- This shows the current price of Ether (ETH, the native token of the Ethereum blockchain), the current price of Ether in Bitcoin, and the 24 hour price change as a percentage.
- Clicking on this number will show the Ether daily price chart in USD.
Total Transactions, Transactions per Second, Median (Average) Gas Price in Gwei
- This is the total amount of transactions that have been processed by the Ethereum blockchain, updated every 5 minutes. (At the time of writing, this is over 1,730 million!)
The total transactions per second is displayed next to this number in parenthesis (TPS). The average gas price is displayed in Gwei (1 Gwei = 1 billionth of 1 ETH) with a conversion to USD.
- This is the total amount of transactions that have been processed by the Ethereum blockchain, updated every 5 minutes. (At the time of writing, this is over 1,730 million!)
Transaction History for Past 14 Days
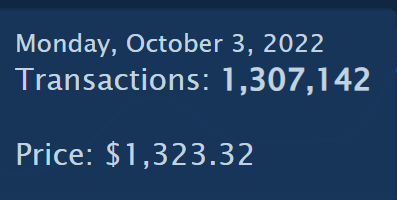
- This chart breaks down the transactions by day for the past 14 days. By hovering over this chart, we can see specific dates, the number of transactions on that day, and the price of ETH on that day.
- By clicking on the three dots in the corner of this chart, we can see a detailed version of this chart.
This chart shows the difficulty for mining ETH (how difficult it is to earn ETH by verifying transactions for the blockchain) , hash rate (the computing power necessary to process transactions in a blockchain), and more. - Since the merge, the difficulty and hash rate are both at 0. See if you can find when the merge happened on the chart!
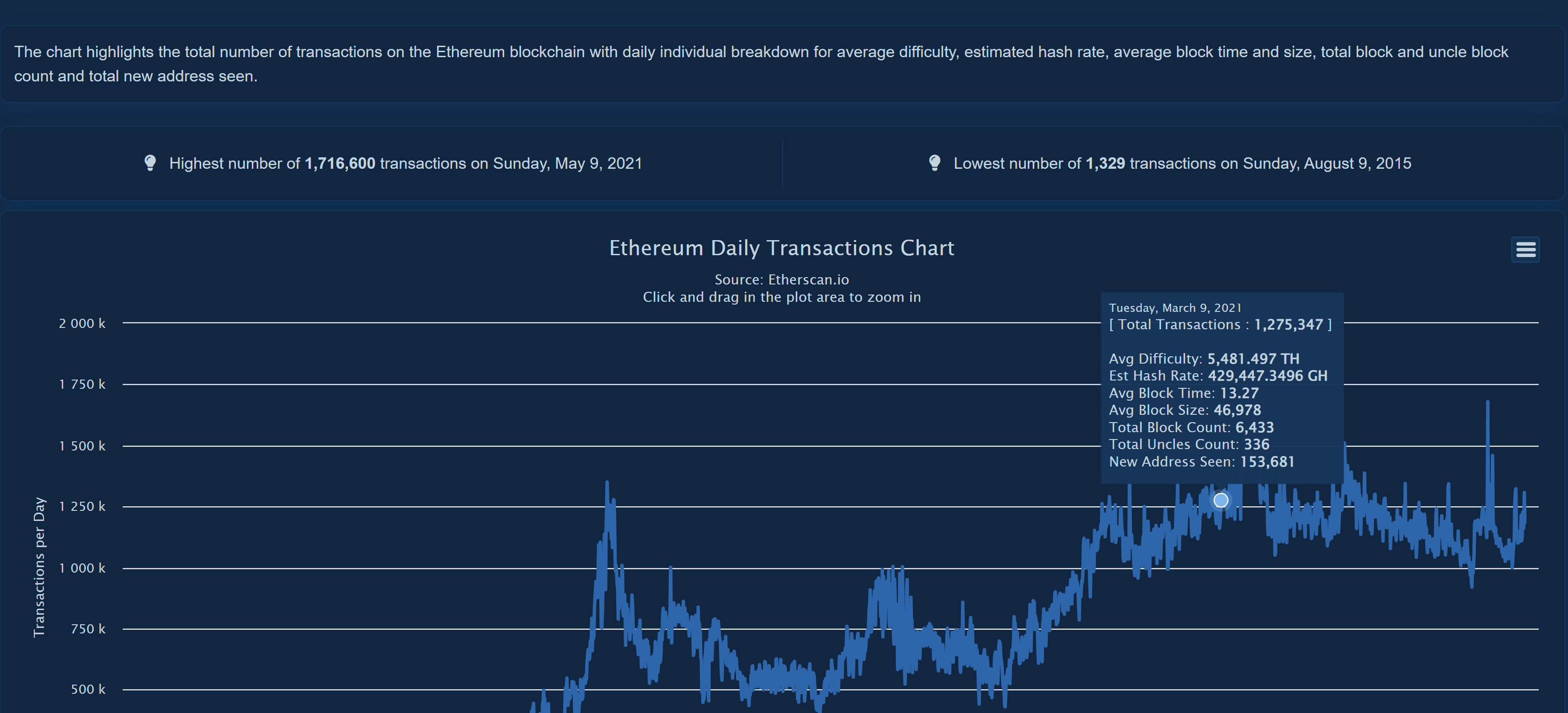
- This chart breaks down the transactions by day for the past 14 days. By hovering over this chart, we can see specific dates, the number of transactions on that day, and the price of ETH on that day.
Market Cap
- Market cap is a measurement of the total value of a cryptocurreny. It’s found by multiplying the total amount of coins by the price of a single coin.
By clicking on the number in this box, we can see a detailed view which shows the distribution of ETH, price per ETH, and more.
- Market cap is a measurement of the total value of a cryptocurreny. It’s found by multiplying the total amount of coins by the price of a single coin.
Last Finalized Block, Last Safe Block
- The last finalized block is the most recent block that has been validated by validators for the Ethereum blockchain. These validators check that the blocks being added to the blockchain are not adding fraudulent information to the blockchain.
The last finalized block cannot be reverted without slashing 1/3 of all Ethereum validators. When slashing occurs, an Ethereum validator loses some or all of their staked ETH as a penalty for not correctly validating blocks to be added to the Ethereum blockchain. - The last safe block is the most recent block added to the blockchain that is unlikely to be reverted. 2/3 of all Ethereum validators have confirmed that this block is safe to add to the blockchain.
- The last finalized block is the most recent block that has been validated by validators for the Ethereum blockchain. These validators check that the blocks being added to the blockchain are not adding fraudulent information to the blockchain.
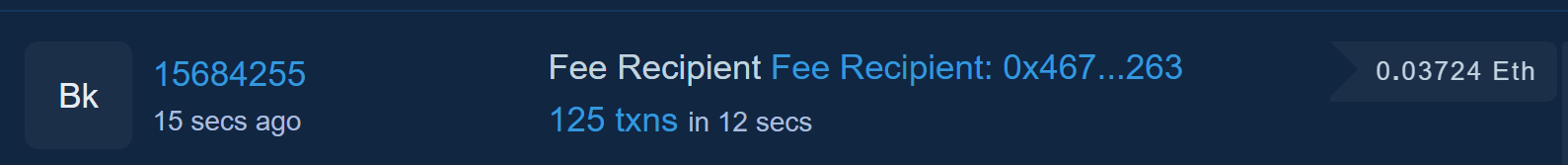
Latest Block
- This panel shows a list of the most recent blocks that are proposed to be added to the blockchain.
- The “Bk” indicates that it is a block.
- The number seen beside “Bk” is the block number with the time the block was proposed to be added to the blockchain under it.
In this screenshot, the block number is 15684255. Clicking this number allows us to see more detailed information about this block. - The fee recipient is who will receive ETH for successfully validating the proposed block.
This can be shown as an address (0x…) or a name tag (ex. Flashbots: Builder). In this screenshot, this is “Fee Recipient: 0x467…263” - The number of transactions within the block and how long it took for the transactions to take place can be found under the fee recipient.
“125 txns in 12 secs” means that 125 transactions took place within 12 seconds. - The final number at the far right is the block reward. This is the amount of ETH the fee recipient will receive for successfully validating the block.
This validator will receive 0.03724 ETH for helping with this block!
- This panel shows a list of the most recent blocks that are proposed to be added to the blockchain.
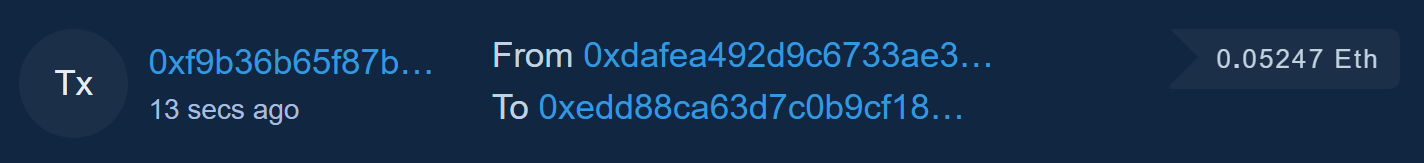
Latest Transaction
- This panel shows the most recent transactions that have been happened on the blockchain.
- The “TK” indicates that it is a transaction.
- The number beside the “TK” is the transaction hash with how long ago the transaction took place.
This is the unique identifier for the transaction. It is similar to a receipt that shows the transaction took place.
Clicking on this number will show us more detailed information about the transaction. In this screenshot, the transaction hash is “0xf9b….” These numbers are typically long with a mix of numbers and letters. - The from and to section shows who the transaction was sent by and who is on the receiving end of the transaction. This can be shown as a wallet address (0x…) or a name tag (somebody.eth).
- The final number on the far right is the value of the transaction. This is the amount sent from the From address and the to the To address. In this example transaction, the value was 0.05247 ETH.
- This panel shows the most recent transactions that have been happened on the blockchain.
At the bottom of the home page, we can see links to company information, resources, and products and services. Here, we can find information about the team working on Etherscan and developer tools such as APIs.
Below this, we can find links to Etherscan’s social media pages as well as a wallet address to make a donation to if we click on the word “Donate” beside the heart.
Hopefully, this helps you with reading information on the home page of Etherscan! It is a lot of information but it gives us a great quick glance of how active the Ethereum community is and current market conditions for the Ethereum ecosystem.
Next time, we’ll learn more about how to read Etherscan’s Transaction Details and Wallet pages so that we can learn how to keep track of our wallets and all the transactions we make!
In the meantime, learn more about Etherscan by following their socials here:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/etherscan
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/etherscan/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/etherscan/
Medium: https://medium.com/etherscan-blog
If you have any questions or just want to say hi, feel free to reach out to me on Twitter! ☕
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mocha directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by