Your Ultimate Regular Expression (Regex) Cheat Sheet 👑😎
 Devang Tomar
Devang Tomar
A regular expression (regex) is a pattern in input text that the regex engine attempts to match. A pattern is made up of one or more character literals, operators, or structures. It excels in searching for and manipulating text strings, as well as text file processing. Hundreds of lines of programming code can be readily replaced by a single regex line. This blog will introduce you to basic to sophisticated regex ideas that will aid you in your development work.

Why Regex? 🙋🏻♀️
Regular expressions simplify searching and replacing processes. A frequent use case is finding a substring that matches a pattern and replacing it with something else. One of the most intriguing features is that, once you’ve mastered the syntax, you can use this tool in (almost) any programming language with only minor differences in the support of the most advanced features and syntax versions supported by the engines.

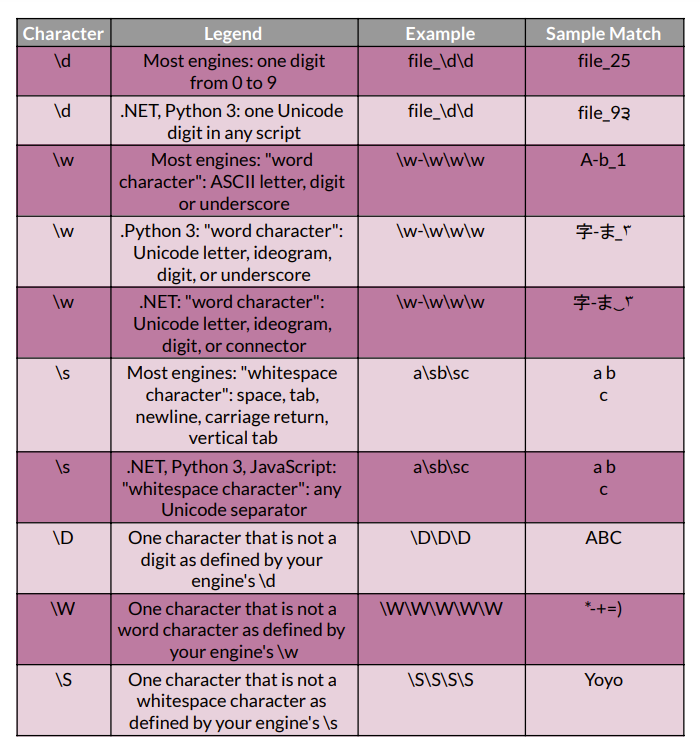
Characters 🔣
The most fundamental regex idea is the character class. It translates a small set of characters into a wider set of characters.
Groups 🫂
A group expression is used to perform operations on all objects in a group. A group expression can be used to apply an operator to a group or to find a specific text before or after each member of the group. The parentheses are the grouping operator, and the “|” is used to divide the items.

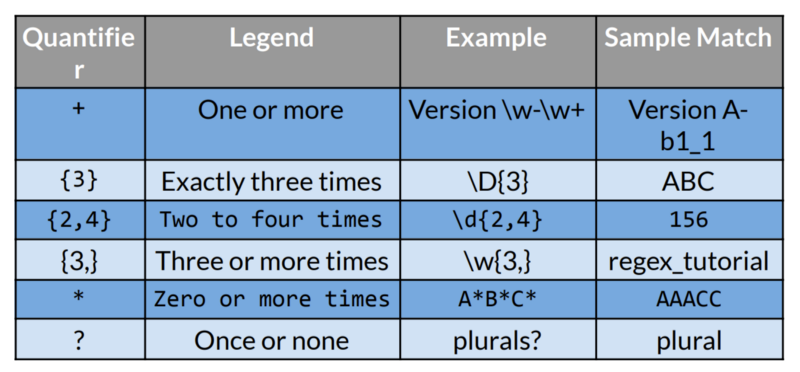
Quantifiers ⚖️
Quantifiers determine the number of characters or expressions to match. Quantifiers describe the number of instances of a character, group, or character class that must exist in the input for a match to be found.
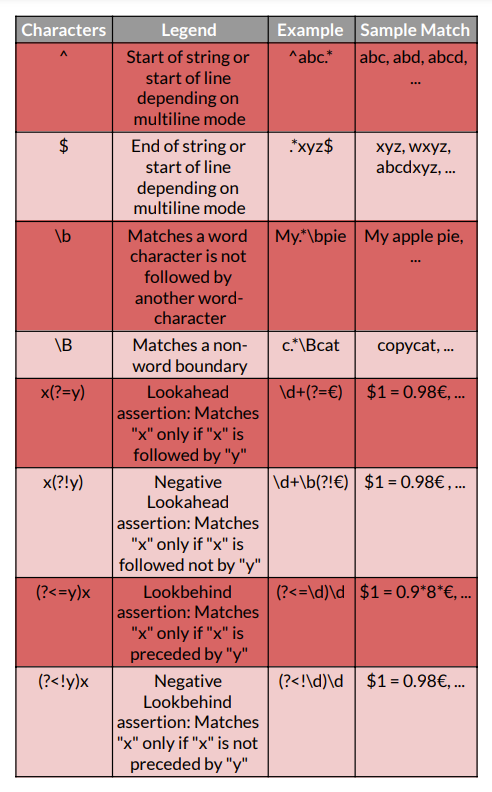
Assertions 🧑🏻🏭
Boundaries, which denote the beginnings and endings of lines and words, and other patterns indicating that a match is conceivable are examples of assertions (including look-ahead, look-behind, and conditional expressions).
Flags 🚩
Flags are appended to the end of a regular expression. They are used to alter the behaviour of the regular expression.

Some useful resources 🪴
Tips to increase the performance 💡
When you require parentheses but not capture, use non-capturing groups.
Do a quick check before attempting a match, if the regex is very complex.
Ex : Does an email address contain ‘@’?Present the most likely option(s) first.
Ex : light green|dark green|brown|yellow|green|pink leafMinimize the amount of looping.
Ex : aaaaaa+ is faster than a{6,}Avoid obvious backtracking
Ex : Mr|Ms|Mrs should be M(?:rs?|s)
Regex sites I use :
Conclusion 💭
To summarise, regex can be used to match strings of data and can be utilised in a variety of ways. Python has a regex library called re that allows you to do this. If you’re on a Unix machine, you can utilise regular expressions in conjunction with grep, awk, or sed. If you wish to access all of these commands on Windows, you can utilise tools like Cygwin.

Connect with Me on Social Media
🐦 Follow me on Twitter: devangtomar7
🔗 Connect with me on LinkedIn: devangtomar
📷 Check out my Instagram: be_ayushmann
Ⓜ️ Checkout my blogs on Medium: Devang Tomar
#️⃣ Checkout my blogs on Hashnode: devangtomar
🧑💻 Checkout my blogs on Dev.to: devangtomar
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Devang Tomar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Devang Tomar
Devang Tomar
👨💻 Creative Software Engineer with 5 years of experience in domains including CI/CD, Networking, Cloud computing, Development, Virtualization, and Linux administration. Passionate about developing forward-thinking solutions to tomorrow's productivity problems. Resourceful and adaptable approach to challenges. 🤹♀️ Skill stack: • Cloud ☁️ : Azure, GCP • Databases 🗃️ : MySQL, PostgreSQL, Elasticsearch • Language 🐍 : Python, JavaScript • Configuration management, deployment & IaC 🛡️ : Ansible, Terraform • Container and orchestration 🐳 : Docker, Kubernetes • Version Control 🗂️ : Git, GitHub • CI/CD 🔄 : Jenkins, GitHub actions, ArgoCD • Continuous Monitoring 📊 : Grafana, ELK, Prometheus 📚 Currently learning: Web development, MLOPS