Flexbox
 Moreshwar Pidadi
Moreshwar Pidadi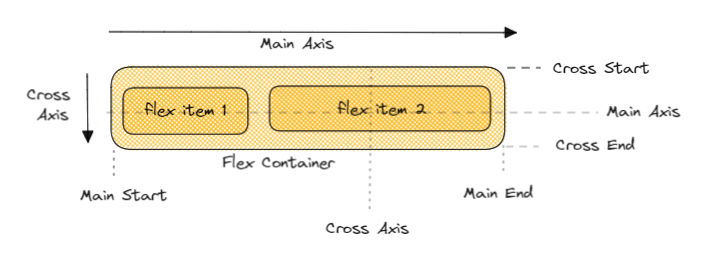
Background
The Flexbox provide the efficient way to lay out and distribute space among items in a container, even when their size is unknown or dynamic hence the word flex came into picture.
It gives a container an ability to alter its items i.e. its width, height and order to the best fill available space.
The flex container expands items to fill available free space or shrink them to prevent overflow.
Flexbox is appropriate to the component of an application, and small scale layouts.
Flexbox Specifications
Since flexbox is a whole module and not a single property, it involves a lot of things including its whole set of properties.
And some of these properties are to set for container and some of these are to be set for flex children i.e. flex items.
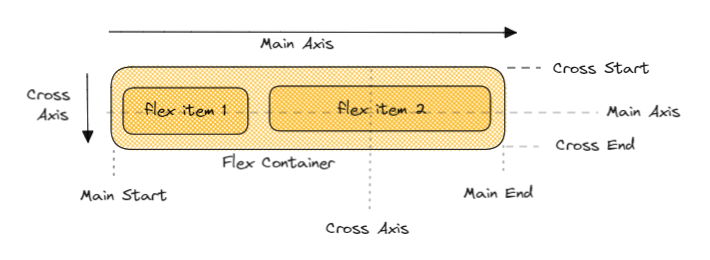
Points to be noted.
The item in the container will be laid out in across main axis or cross axis.
Main axis may not always be horizontal.
Items are placed in between main start and main end.
cross axis is always perpendicular to the main axis.
Properties of Flexbox
In an example below we have all the properties of flex-box i.e. Container (Parent) and Children (Flex Items).
diplay: flex
Syntax: display: flex
This is being applied to the parent container, and it will arrange all the elements in row, which are present in the container.
flex-direction
Syntax: flex-direction: row (default)| column | row-reverse | column-reverse
This will define the direction of the flex i.e. it would define the main axis and cross axis of the flexbox container.
Here, these properties would work in these format.
row: would be its default property and would arrange the elements in left to right.
row-reverse: would arrange the items in right to left, and left to right in rtl.
column: would arrange items in same row but top to bottom.
column-reverse: would arrange item in single column, but in a reverse direction.
flex-wrap
Syntax: flex-wrap: no-wrap| wrap | wrap-reverse
By default the flex items will all try to fit in one line. You can change and allow the items to wrap as needed using this property.
nowrap : It would be the default property,
wrap : All the flex items will wrap into multiple lines from top to bottom.
wrap-reverse : All the flex items will wrap into multiple lines from bottom to top.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Flex</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./flex.css" />
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.pos {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: 700;
padding: 10px;
}
.container {
display: flex;
/* flex-direction: row; default value */
/* flex-direction: column; */
flex-direction: row-reverse;
/* flex-direction: column-reverse; */
width: 300px;
border: 1px dotted #9c1717;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<section class="container">
<div class="pos" id="first">1</div>
<div class="pos" id="second">2</div>
<div class="pos" id="third">3</div>
<div class="pos" id="fourth">4</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>
flex-flow
Syntax: flex-flow: flex-direction flex-wrap
This is an shorthand property for flex direction and flex wrap, and its default values are row and wrap.
##justify-content
Syntax:
justify-content: flex-start | center | flex-end | space-evenly | space-around| space-between | left | right | safe | unsafe
Consider you are making the changes on x-axis of coordinate systems
flex-start: is the default value items are placed from start of the container.flex-end: Items are placed towards the end of container.center: Items are place at the center of the container.space-around: Items are placed evenly and will occupy whole space of the container.space-between: Item are placed in such a way that they are evenly distributed within the container.space-evenly: Items are place in such a way that the spacing between the two items are equal.
align-items
Syntax: align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | stretch (default)| baseline
stretch: Will fill the container with max-width.flex-start: Items are placed at the start (+ve) across y axis here we can say cross axis.flex-end: Items are placed and the bottom of y axis i.e. cross axis.center: Items are at the centered in the cross axis.baseline: items are aligned such as their baselines align
align-content
Syntax: align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | stretch (default)| space-around | space- evenly
This aligns the individual items based on the cross-axis i.e. vertically depending on the flex-direction.
gap property in flexbox
gap, row-gap, column-gap
Gap also know as gutters and tracks, it controls the space in-between the items.
Flex items or Children of the containers
order: They control the order in which the items appears in the flex-container.
flex-grow : Provide the ability if an flex-items needs to grow and its default value is 1,
flex-grow: 1 the respect child will take place the space as per the value provided and
rest space will be distributed equally.
flex-shrink : It defines the ability to shrink the respective flex-item if required here, negative number is invalid. Default value is 0.
flex-basis : It define the space of the item before the remaining space is distributed for other elements. default value is auto.
flex
Syntax:
flex: flex-grow | flex-shrink | flex-basis
flex: This is short hand property, grow, shrink and basis.
Syntax:flex: none | [ <'flex-grow'> <'flex-shrink'>? || <'flex-basis'> ]
align-self
Syntax:
align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
This allows to override the align-items for an individual elements,
Note: The float, vertical-align, have no effect on flex items.
Below are references for flexbox for implementation
##Code
HTML Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Flex</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./flex.css" />
</head>
<body>
<section class="container">
<div class="pos" id="first">1</div>
<div class="pos" id="second">2</div>
<div class="pos" id="third">3</div>
<div class="pos" id="fourth">4</div>
<div class="pos" id="fifth">5</div>
<div class="pos" id="sixth">6</div>
<div class="pos" id="seventh">7</div>
<div class="pos" id="eight">8</div>
<div class="pos" id="nine">9</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>
CSS Code
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.pos {
display: inline-block;
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: 700;
padding: 4px;
margin: 4px;
height: 70px;
border: 2px dotted #565656;
}
.container {
display: flex;
/* flex-direction: row; defalut value */
/* flex-direction: column; */
/* flex-direction: row-reverse; */
flex-wrap: wrap;
/* flex-wrap: nowrap; */
/* flex-direction: column-reverse; */
/* flex-wrap: wrap-reverse; */
justify-content: center;
/* justify-content: flex-start; default */
/* justify-content: flex-end; */
/* justify-content: space-around; */
/* justify-content: space-between; */
/* justify-content: space-evenly; */
/* justify-content: safe; */
/* justify-content: unsafe; */
/* flex-flow: column-reverse wrap; */
/* flex-flow: column-reverse wrap-reverse; */
align-items: flex-start;
/* align-items: flex-end; */
/* align-items: center; */
/* align-items: stretch; */
/* align-items: baseline; */
/* align-content: flex-end; */
/* align-content: flex-start; */
align-content: space-around;
width: 700px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px dotted #9c1717;
}
#first {
order: 4;
}
#eight {
order: -5;
}
#sixth {
order: -1;
align-self: stretch;
background-color: #565656;
/* flex-grow: 2;
flex-basis: 150px;
flex-shrink: 1; */
/* flex: 1 20%; */
/* display: flex;
justify-content: center;
background-color: #7264; */
}
#second {
order: -5;
}
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Moreshwar Pidadi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
Moreshwar Pidadi
Moreshwar Pidadi
#Netflix