Working With Pandas DataFrame On COLAB
 Mohamad Mahmood
Mohamad Mahmood1 min read

Pandas DataFrame is a two-dimensional, size-mutable, tabular data which may contain labeled rows and columns. DataFrame is useful for tabular data manipulation. The class syntax includes four parameters that are the data, index, columns, data type and copy options.
DataFrame(data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None, copy=False)
DataFrame Object Declaration
An example of a DataFrame declaration:
import pandas as pd
# prepare df parameters
data = [['A1', 'B1', 'C1'],
['A2', 'B2', 'C2'],
['A3', 'B3', 'C3']]
columns = ['A', 'B', 'C']
index = [1, 2, 3]
# declare df
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index, columns)
The outcome of the DataFrame declaration above is as follows:
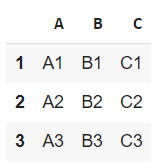
DataFrame object loads data from CSV file
# load the remote data into a Pandas DataFrame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.org/download/crowdflower/text_emotion.csv', on_bad_lines='skip', encoding='latin-1')
DataFrame object saves data as a CSV file
df.to_csv('text_emotion.csv', index = False)
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mohamad Mahmood directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mohamad Mahmood
Mohamad Mahmood
Mohamad's interest is in Programming (Mobile, Web, Database and Machine Learning). He studies at the Center For Artificial Intelligence Technology (CAIT), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM).