Integrating Django with GraphQL
 Emmanuel Nwaegunwa
Emmanuel NwaegunwaTable of contents
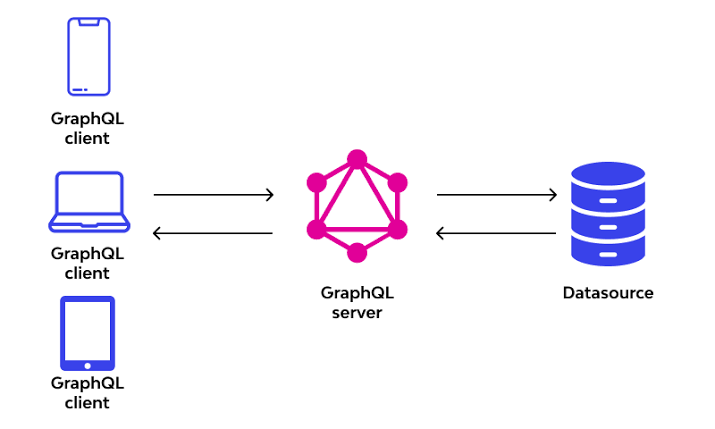
Django is a popular web framework for building robust and scalable web applications. It provides a wide range of features for building web applications, including an ORM, templating engine, and routing system. However, with the rise of GraphQL, many developers are looking for ways to integrate Django with GraphQL to build modern APIs that are flexible and easy to use.
In this article, we'll explore how to use Django with a GraphQL server to build powerful and flexible APIs. We'll cover the basics of GraphQL, including how to define a schema, write queries and mutations, and work with the Django ORM. We'll also look at some best practices for integrating Django with GraphQL and how to troubleshoot common issues.
So, let's get started!
Setting Up a GraphQL Server with Django
The first step in integrating Django with GraphQL is to set up a GraphQL server. There are a few different ways to do this, but the most common method is to use the graphene-django library. This library provides a set of Django-specific tools for building GraphQL APIs, including a Django ORM integration and a set of decorators for defining GraphQL types and fields.
To set up a GraphQL server with Django and graphene-django, you'll need to follow these steps:
Install the
graphene-djangolibrary usingpip install graphene-django.Add
graphene_djangoto yourINSTALLED_APPSlist in your Django settings file.Define a Django app for your GraphQL server. You can do this by running
pythonmanage.pystartapp graphql_app.Add the
graphql_appto yourINSTALLED_APPSlist in your Django settings file.Define a GraphQL schema for your API. You can do this by creating a
schema.pyfile in yourgraphql_appand defining your GraphQL types and fields using thegraphenelibrary. Here's an example of a simple GraphQL schema for aBookmodel:
import graphene
from graphene_django import DjangoObjectType
from .models import Book
class BookType(DjangoObjectType):
class Meta:
model = Book
class Query(graphene.ObjectType):
books = graphene.List(BookType)
def resolve_books(self, info):
return Book.objects.all()
- Create a GraphQL view and URL pattern for your API. You can do this by creating a
views.pyfile in yourgraphql_appand defining a view that uses theGraphQLViewfromgraphene_django. Then, add a URL pattern for your view in your Djangourls.pyfile. Here's an example of a GraphQL view and URL pattern for theBookmodel:
from django.conf.urls import url
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^graphql', views.GraphQLView.as_view(graphiql=True)),
]
- Run your Django server and visit the GraphQL endpoint in your browser. You should see the GraphiQL interface, which is a tool for testing and exploring your GraphQL API.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Emmanuel Nwaegunwa directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Emmanuel Nwaegunwa
Emmanuel Nwaegunwa
Am a software developer with lots of experience in designing and building high-quality, scalable web applications, I am confident in my ability to contribute to a team and deliver projects on time and on budget. My skills in problem-solving and my passion for writing clean, efficient code have allowed me to thrive in fast-paced environments. I am currently seeking employment opportunities and am open to discussing potential roles.