Middle of the Linked List
 Navnath Jadhav
Navnath Jadhav2 min read
Table of contents
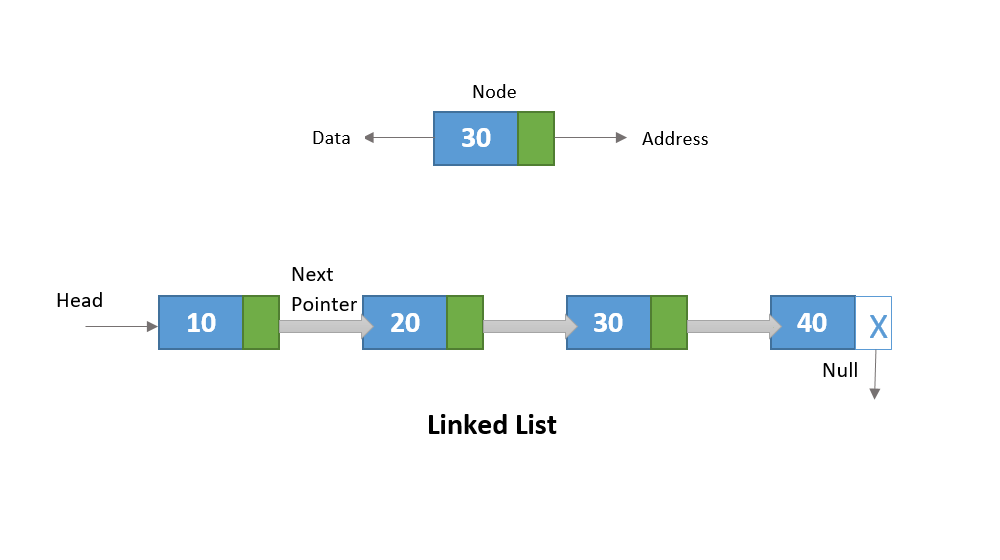
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
Example 1:

Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [3,4,5]
Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3.
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: [4,5,6]
Explanation: Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 100].1 <= Node.val <= 100
Solutions:
Language: Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution
{
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head)
{
int len=0 ;
ListNode temp = head ;
// calculate the length of the linked list
while(temp!=null)
{
temp = temp.next ;
len++ ;
}
// finding middle of linked list
len = len / 2 ;
ListNode currentNode = head ;
// iterate till length of linked list becomes 0
while(len>0)
{
currentNode = currentNode.next; //shifting head forward
len--; //reducing length
}
return currentNode ; //node at which length becomes 0, is middle node
}
}
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Navnath Jadhav directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Navnath Jadhav
Navnath Jadhav
I am a Software Developer