Getting Started with Python
 Ayush Chandrakar
Ayush ChandrakarTable of contents

What is a programing language?
An ordered set of instructions to be executed by a computer to carry out a specific task is a program. Computers understand the language of 0s and 1s (machine language), but it is difficult for humans to write instructions in 0s and 1s. So we use high programming languages like 𝐏𝐲𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐧.
Features of python
Open-source language.
Easy to understand ( clearly defined syntax)
Case sensitive.
Working with python
we need a python interpreter (online or installed in the system).
- online:-

Or we can use:-python(3.11.1), visual studio codes, Jupiter notebook etc
Using an online compiler
(A)Interactive mode
We simply type a Python statement.
We press enter, the interpreter executes the statement.

(B) script mode
In script mode we write a python program in a file, save it and then execute it .
(the saving part may differ in the different interpreters)
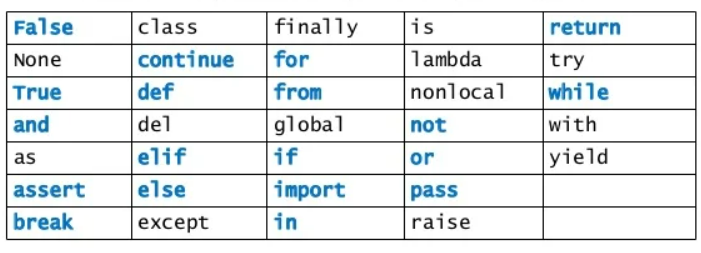
Python Keywords
Reserved words.
Used only for the purpose for which it has been defined.
As python is case-sensitive keywords must be written exactly as given below
Identifiers
Used to identify a variable
Rules
The name begins with ( A-Z, a-z, _ ) only.
It may contain (A-Z, a-z, _ , 0-9) of any length.
(space, special characters, keywords) are invalid
Variables
A variable in a program is uniquely identified by a name (identifier)
Variable in Python refers to an object(value)

output
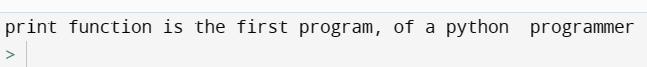
Comments
Not a part of the program.
Used for easy understanding.
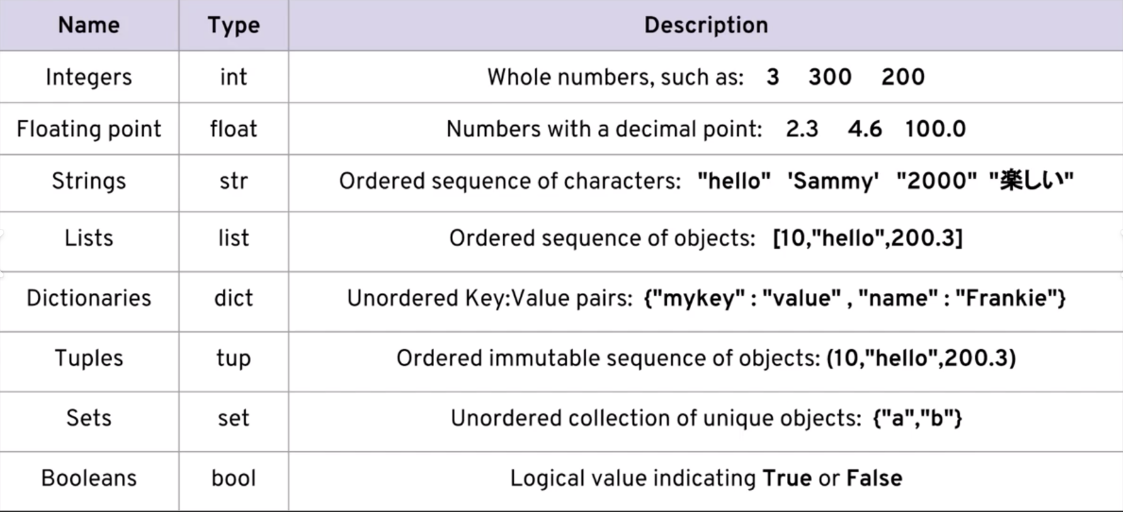
Data types
Every value belongs to a specific data type in python.
Identifies the type of value a variable can hold.
**note:-**only list and string are mutable datatype rest are immutable.
Functions
A named group of instructions that can accomplish a specific task.
can be pre-defined (in the python in the interpreter) OR can be user-defined.
can be called any number of times.

output

Basic functions we need to know
int() [for integers]
float() [for floating point numbers]
<variable> =[ ] [to create a list]
<variable> ='' '' [to create a string]
<variable> =() [to create a tupule]
<variable>={ '' '' : '' " or any number , " " : " " -||- .....} [to create a dictionary]
type() [Function]
If we want to know the type (datatype) of value given to a variable or any other condition we use the type() function.

output

Operators
Used to perform a logical operation on values
the values on which operators work on are called operands
There are many types of operators
Arithmetic operators (+,-,*,/,//,**)
Assignment operators (=,+=,-=,*=,/=,%=,//=,**=)
Logical operators (and,or,not)
Identity operators (is,is not)
Membership operators (in , in not)
## Precedence of operators

input() [Function]
The function prompts the user to enter data.
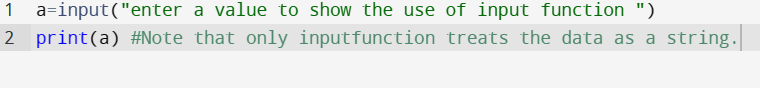
output
A Basic python program

output

Comment for doubt's 🤖
...........🥸............
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ayush Chandrakar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ayush Chandrakar
Ayush Chandrakar
Python 🐍