Java 8 Stream API Interview Questions and Answers
 Anusha SP
Anusha SP
Hey Reader,
If you are preparing for a Java interview, then this article would be most useful. Since, after the continuous upgradation of Java versions, the interview questions also increased. Here, I have listed the most commonly asked Java 8 Stream API interview questions and answers.
The contents of the article include Interview questions on the following topics with examples:
Stream API Interview questions and answers
Stream API
Stream API is one of the hot topics to be chosen by the interviewer in interviews. Let us read and know the most used concepts of stream API questions. Let us see some of the questions and answers to Stream API of Java 8.
What is stream API?
Java 8 provides a new additional package called java.util.stream This package consists of classes, interfaces and enums to allow functional-style operations on the elements.
We can use stream API using the java.util.stream package.
We can use a stream to filter, collect, print and convert from one data structure to another.
Stream APIs do not store elements. It is functional. Operations performed using stream do not modify its source.
What is the difference between Collection and Stream?
The main difference between a Collection and Stream is that Collection contains its elements but Stream doesn’t.
The stream works on a view where elements are stored by collection or array, but unlike other views, any change made on the stream does not reflect the original collection.
What is an Intermediate operation in Stream API?
Intermediate operations of stream API process the current data and then return the new stream.
When an intermediate operation is executed, it only creates a new stream.
Example: map(), limit(), filter(), skip(), flatMap(), sorted(), distinct(), peek()
What is a Terminal operation in Stream API?
As the name suggests terminal means the last operation in the Stream pipeline. Terminal operation traverses the stream and produces a result or a collection but not a new stream.
A stream pipeline consists of a source ( Collection, array, function or I/O channel) it will invoke an intermediate operation in the pipeline lastly the terminal operation is performed which makes the stream pipeline consumed and marked closed.
We can have only one terminal operation at the end of the pipeline. If any operation is performed on a closed stream, it will result in java.lang.IllegalStateException; stream has already been operated upon or closed.
Example:
collect()
forEach()
forEachOrdered()
findAny()
findFirst()
toArray()
reduce()
count()
min()
max()
anyMatch()
allMatch()
noneMatch()
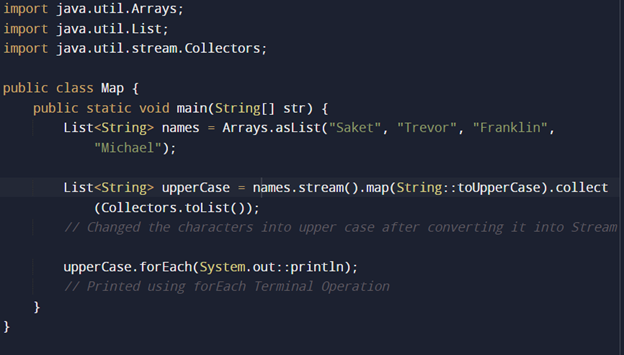
What does the map() function do? Why do you use it?
The map() function performs map functional operation in java. This means it can transform one type of object into others.
Example: consider we have a list of Strings and want to convert a List of Integer, we can use map() by applying a function to convert String to integer eg: parseInt() to map() and it will apply that to all elements of the list and give a list of Integer.
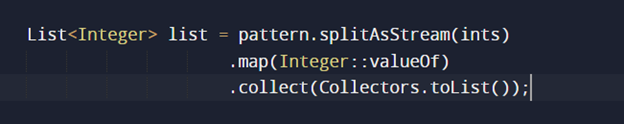
What does the filter() method do? When do you use it?
The filter method is used to filter elements that satisfy a certain condition that is specified using a Predicate function.
A predicate function is nothing but a function that takes an Object and returns a boolean.
For example, if you have a List of Integer and you want a list of even integers
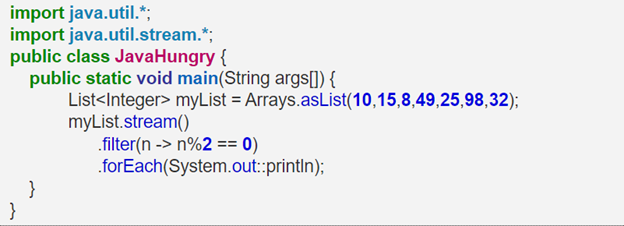
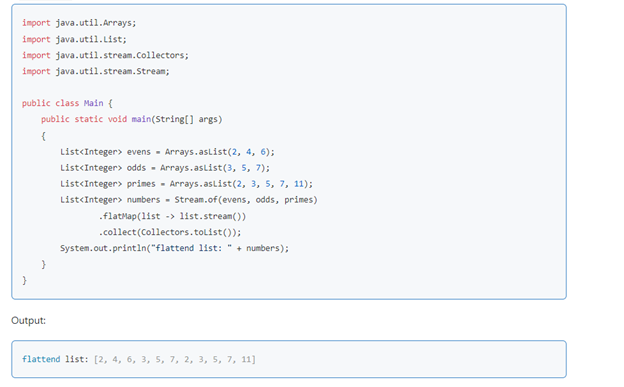
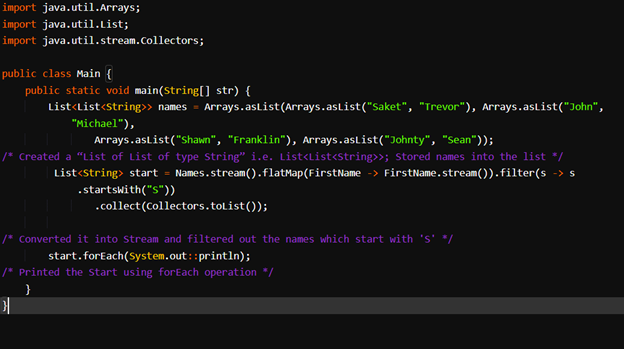
What does the flatMap() method do?
The flatMap() function is an extension of the map function. Apart from transferring one object into another, it also flattens it.
Example: Consider you have a list of list data and you want to combine all elements of lists into just one list. In this case, we can use flatMap()
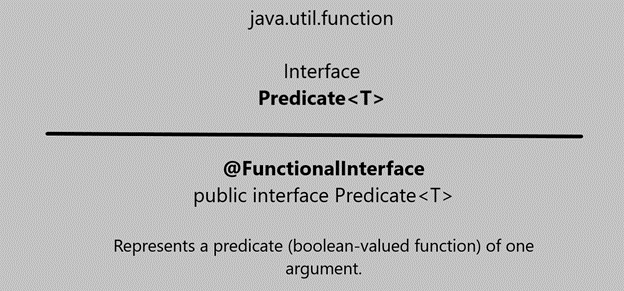
What is predicate Interface in Java stream?
A Predicate is a functional interface that represents a function, which takes an Object and returns a boolean.
It is used in several Stream methods like filter(), which uses Predicate to filter unwanted elements.
What does the peek() method do in Stream API?
The peek() method of the Stream class allows us to see through a Stream pipeline.
We can peek through each step and print meaningful messages on the console. It is generally used for debugging issues related to lambda expression and Stream processing.
What is the difference between map() and flatMap() of Stream API?
The key difference between map() vs flatMap() in Java 8:
The function you pass to the map() operation returns a single value.
The function you pass to the flatMap() operation returns a Stream of value.
The flatMap() is a combination of map and flat operation.
The map() is used for transformation only, but flatMap() is used for both transformation and flattening.
Example for map():
Example for flatMap():
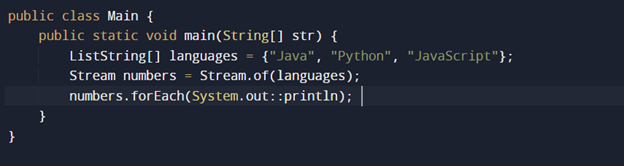
Can we convert an Array into a Stream?
Yes, you can use Java to transform an array into a stream.
The Stream class provides a factory method to make a Stream from an array, such as Stream.of(T…), which accepts a variable parameter, also we can supply an array to it.
What is the difference between Stream API and Collection API?
Stream API
Collection API
It was introduced in Java 8 Standard Edition version.
It was introduced in Java version 1.2
There is no use of the Iterator and Spliterators.
With the help of forEach, we can use the Iterator and Spliterators to iterate the elements and perform an action on each item or element.
An infinite number of features can be stored.
A countable number of elements can be stored.
Consumption and Iteration of elements from the Stream object can be done only once.
Consumption and Iteration of elements from the Collection object can be done multiple times.
It is used to compute data.
It is used to store data.
What are the Stateful and stateless intermediate operations of Stream API?
Stateful operations are skip(), distinct(),limit() and sorted(). Rest all other stream operations are stateless.
When an operation requires retaining the information of the elements it has processed so far to process the current element then it is a stateful operation.
Example: Distinct operation requires keeping track of all the values it has processed so far, based on this information only it can decide whether the current value is unique or it has been processed before and accordingly either will add the current value to the new stream(which is the output of the distinct operation) or neglect the value and not add it to the new stream.
What is the difference between Stream’s findFirst() and findAny()?
As the name suggests, the findFirst() method is used to find the first element from the stream whereas the findAny() method is used to find any element from the stream.
The findFirst() is pre-deterministic whereas the findAny() is non-deterministic. In programming, Deterministic means the output is based on the input or initial state of the system.
What is a parallel stream? How to convert the list into a parallel stream?
One of the prominent features of Java 8 is Java Parallel Stream. It is meant for utilizing the various cores of the processor.
All the Java code will usually have only one processing stream, where it is sequentially executed. But by using parallel streams, one can separate the Java code into more than one stream, which is executed in parallel on their separate cores, and the result is the combination of the individual results.
The order in which they are executed is not in our control. Hence, it is suggested to use a parallel stream when the order of execution of individual items does not affect the final result.
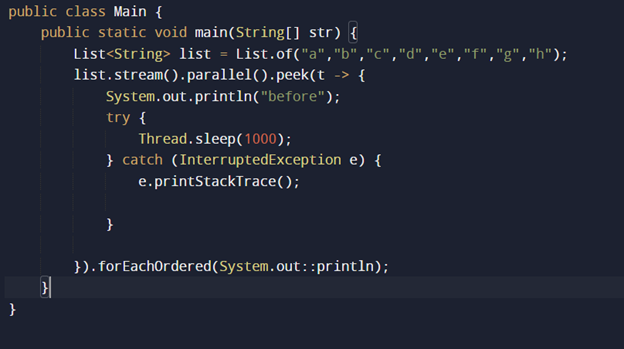
Thank you for reading the article. Please like, share and comment. it will encourage me to write more such articles. Do share your valuable suggestions, I appreciate your honest feedback!!!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Anusha SP directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Anusha SP
Anusha SP
SDE | Developer | Enthusiastic learner | Content Writer