Strict Equality & Loose Equality
 Krunal Mandlekar
Krunal Mandlekar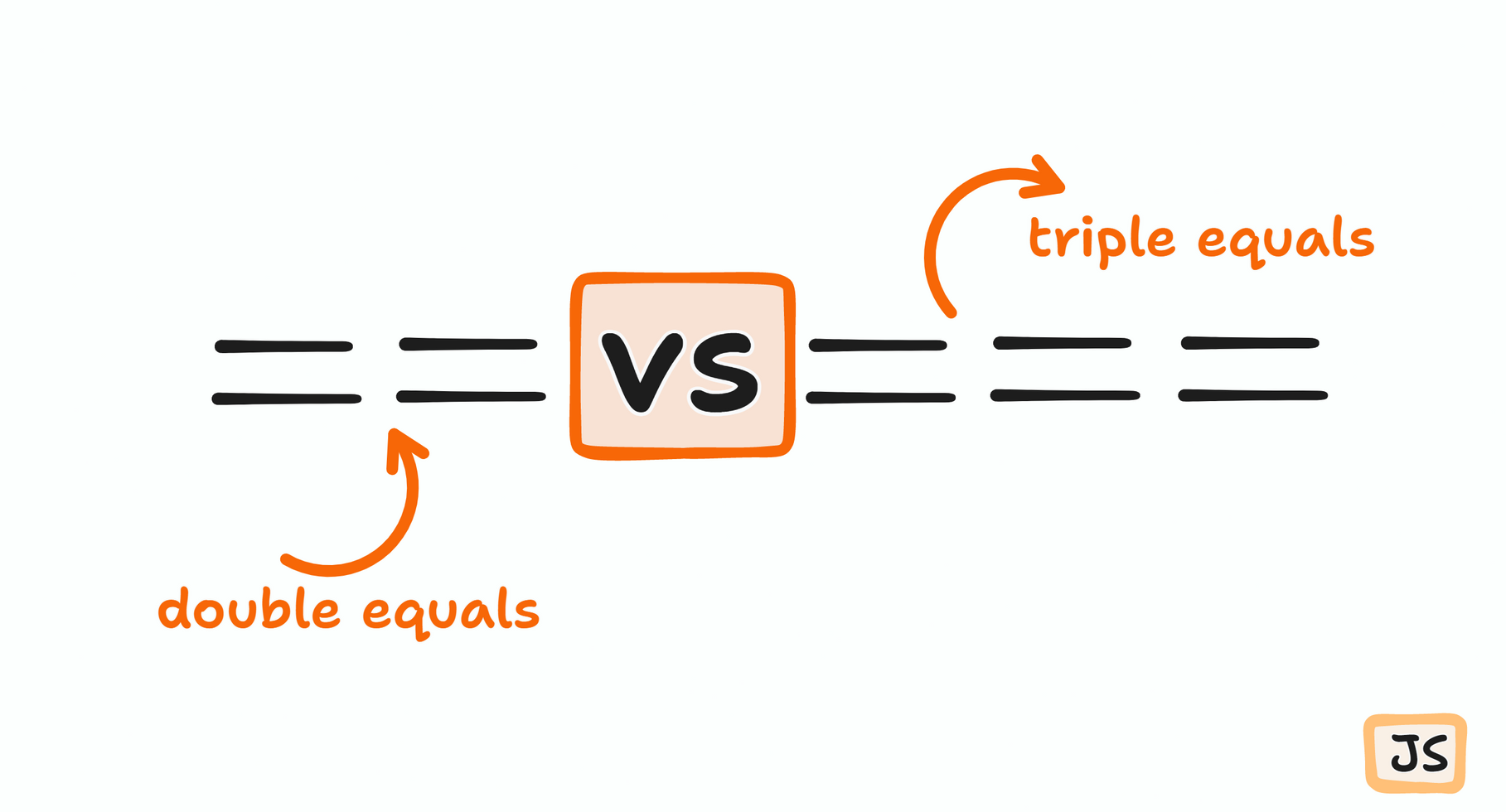
Equality comparison in JavaScript is done by using -
Triple equals
Double equals
Let's get the idea of each operation in brief.
1. Strict Equality (Triple equals)
Triple equals do the comparison without type conversion i.e. While comparing the variables, if the types of varibles are different then it returns false else it returns true
Get the line with an example -
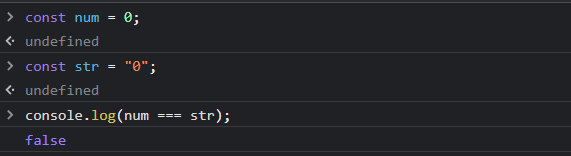
In above example, num is compared with str which are of different type, we use triple equals for the operation and triple equals compare without type comparison as a result it returns false
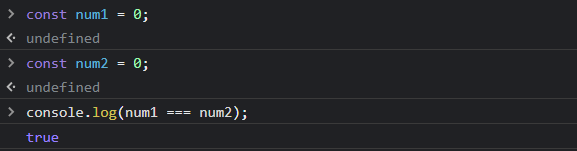
while above example returns true as variables are number and have the same value.
In strict equality operation the value is only equals to itself but there is always an exception and here NaN (Not a Number). NaN returns false with itself too, as strict equality treats NaN unequal to every other value.
2. Loose Equality
Double equals is known as the Loose Equality operator as it checks abstract equality i.e. it convert the data type of variables for comparison when both the variables are not of the same data type.
Get this with the help of example -
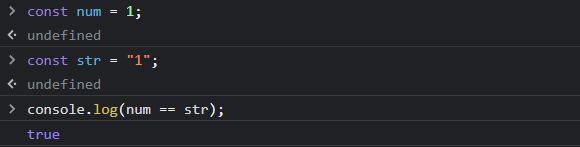
In the above example, str is converted to number type by the operator, and then it is compared to num. After conversion the numeric value of both num and str is equal and hence it returns true as output.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Krunal Mandlekar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
