Case study: How blue-green deployment helped Mochi
 Quang Le
Quang Le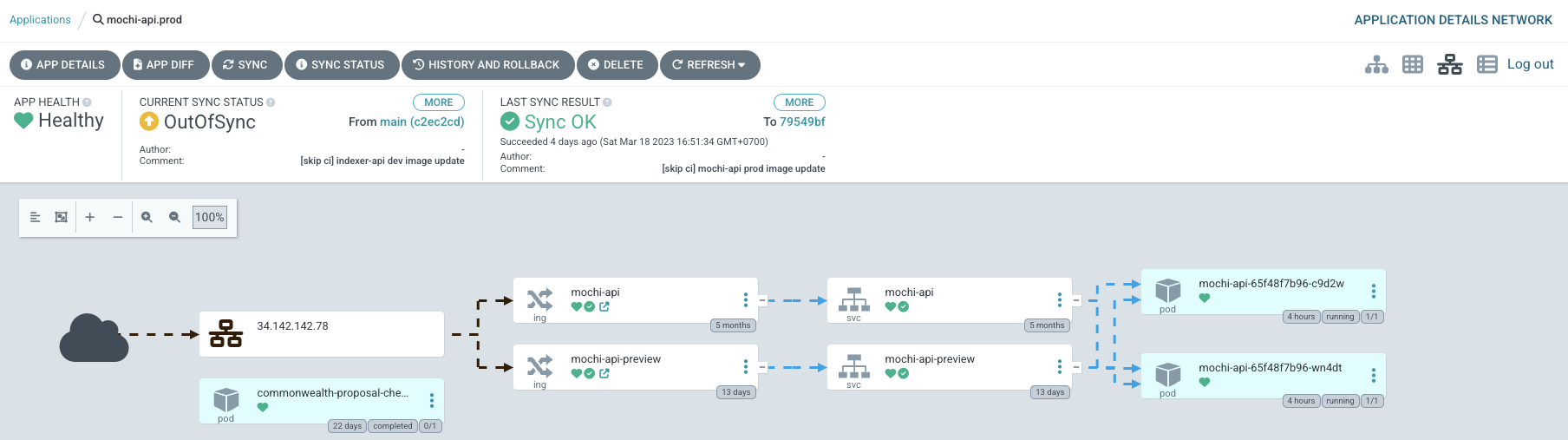
At Dwarves Foundation, our team has always faced some bit of friction when deploying apps for our clients. We’ve known about blue-green deployments for a while and were recently given the chance to evaluate and demonstrate them for one of our Discord bot projects.
Applying Blue-green deployment for Mochi Bot
Introducing Mochi Bot to the Web3 space, our team has developed a flexible and user-friendly product with features like NFT rarity queries, sales alerts on Discord and Twitter, and showing various tips. To enhance user experience and streamline deployment, we had the chance to implement blue-green deployment for the Mochi Bot application. Below is our case study that evaluates the cost and practicality of this deployment strategy in our current infrastructure.
Current Infrastructure & Implementation Plan
Mochi Bot runs on a Kubernetes infrastructure managed by ArgoCD, with two pods. By implementing blue-green deployment, we aim to eliminate downtime and ensure consistent updates across pods. To achieve this, we set up two identical production environments (blue and green) and followed these steps:
Evaluate current infrastructure and identify prerequisites.
Prepare Kubernetes manifests for blue and green environments.
Apply new configurations to clusters.
Test deployment process, including traffic switching and rollback procedures.
Preparation & Resource Definition
To implement blue-green deployment in Kubernetes, we needed to define the application resources and the rollout strategy. We defined the application resources using three YAML files:
.
└── app/
├── bluegreen-rollout.yaml
├── ingress.yaml
└── service.yaml
Before that, setting up Argo Rollouts is a prerequisite to enable blue-green deployment capability:
kubectl create namespace argo-rollouts
kubectl apply -n argo-rollouts -f <https://github.com/argoproj/argo-rollouts/releases/latest/download/install.yaml>
The blue-green update strategy is applied to define the release through the bluegreen-rollout.yaml file.
# bluegreen-rollout.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Rollout
metadata:
name: mochiapp
labels:
app: mochiapp
spec:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mochiapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mochiapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: argoproj/rollouts:blue
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080
strategy:
blueGreen:
autoPromotionEnabled: false
activeService: mochiapp
previewService: mochiapp-preview
The bluegreen-rollout.yaml file is structured similarly to a typical deployment file, but with the added strategy section. Here, we specified the activeService to update with the new template hash during promotion (required), and the previewService to update with the new template hash before (optional).
Next, we created the ingress.yaml and service.yaml files, which contained the respective configurations for ingress and service resources:
# ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: mochiapp
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- mochiapp.bluegreen.domain
secretName: mochiapp.bluegreen.domain-tls
rules:
- host: mochiapp.bluegreen.xyz
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: mochiapp
port:
name: http
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: mochiapp-preview
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- preview.mochiapp.xyz
secretName: preview-mochiapp.bluegreen.domain-tls
rules:
- host: preview-mochiapp.bluegreen.domain
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: mochiapp-preview
port:
name: http
# service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mochiapp
labels:
app: mochiapp
spec:
selector:
app: mochiapp
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: http
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mochiapp-preview
labels:
app: mochiapp
spec:
selector:
app: mochiapp
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: http
type: ClusterIP
Applying Resources to the Cluster and Testing
We applied the resource files to the Kubernetes cluster using kubectl apply commands. The application was deployed to the active environment and could be viewed on the production domain - mochiapp.bluegreen.domain.
kubectl apply -f app/bluegreen-rollout.yaml
kubectl apply -f app/service.yaml
kubectl apply -f app/ingress.yaml

When releasing a new version, we changed the image of the application and applied the changes to the cluster. Argo rollouts created a new ReplicaSet with the new image and initiated the rollout of the updated version in the preview environment, accessible at the preview domain - preview-mochiapp.bluegreen.domain.
# bluegreen-rollout.yaml
containers:
- name: myapp
image: argoproj/rollouts-demo:green
kubectl apply -f app/bluegreen-rollout.yaml
Once the updated application version was thoroughly tested, we promoted it to the active environment using a specific command. The updated application was then accessible on the active environment in the blue domain.
kubectl argo rollouts promote mochi
With the deployment complete, the updated application was accessible on the active environment in the blue domain - mochiapp.bluegreen.domain.
An alternative would be to utilize the ArgoCD UI for the promotion, as it could prove to be exceptionally helpful for those who may not be able to operate the CLI, including QC, during the release rollout. Additionally, any issues that may arise can quickly be reverted with just the click of the "Rollback" button.
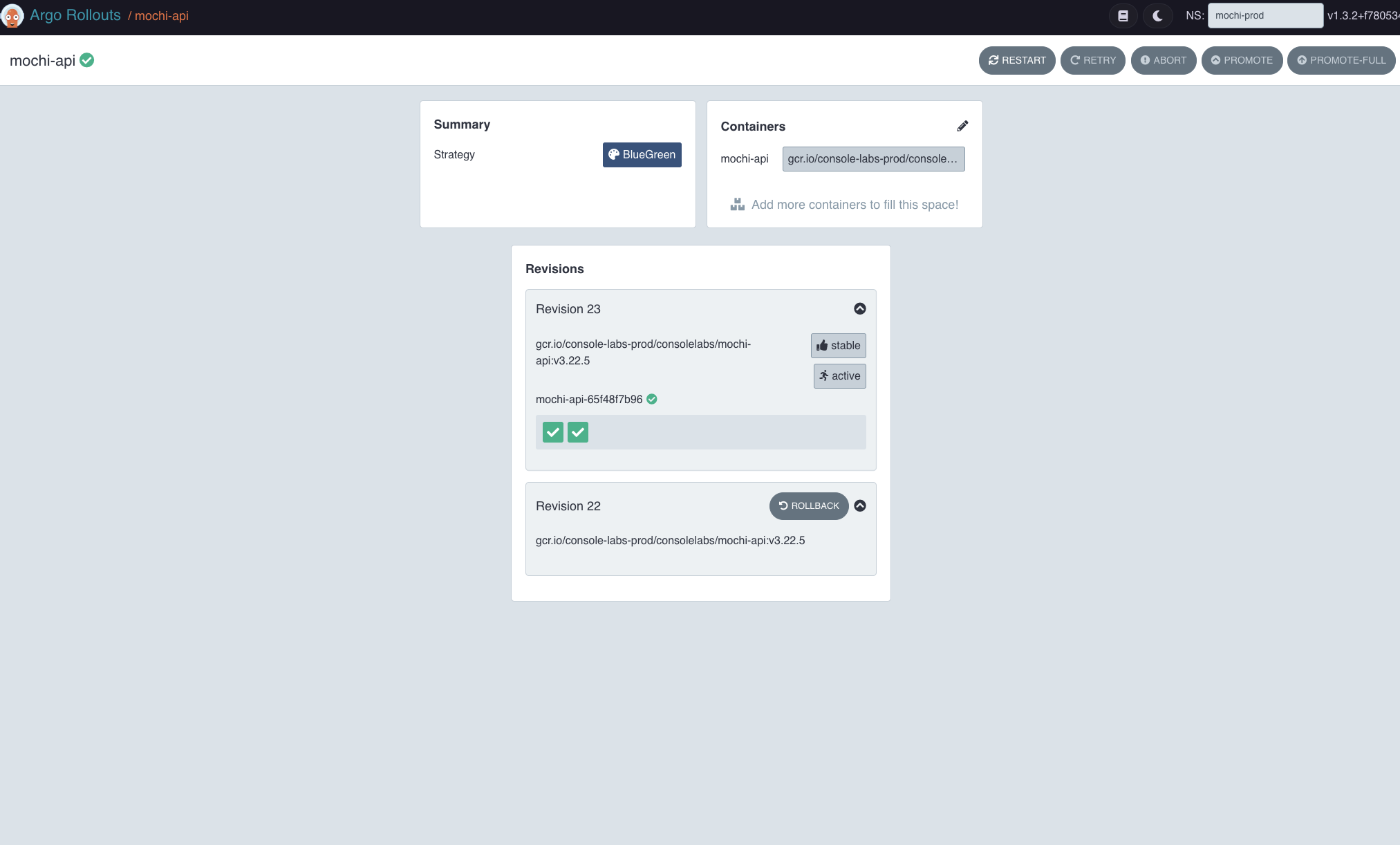
ArgoCD rollout dashboard to manage blue-green applications
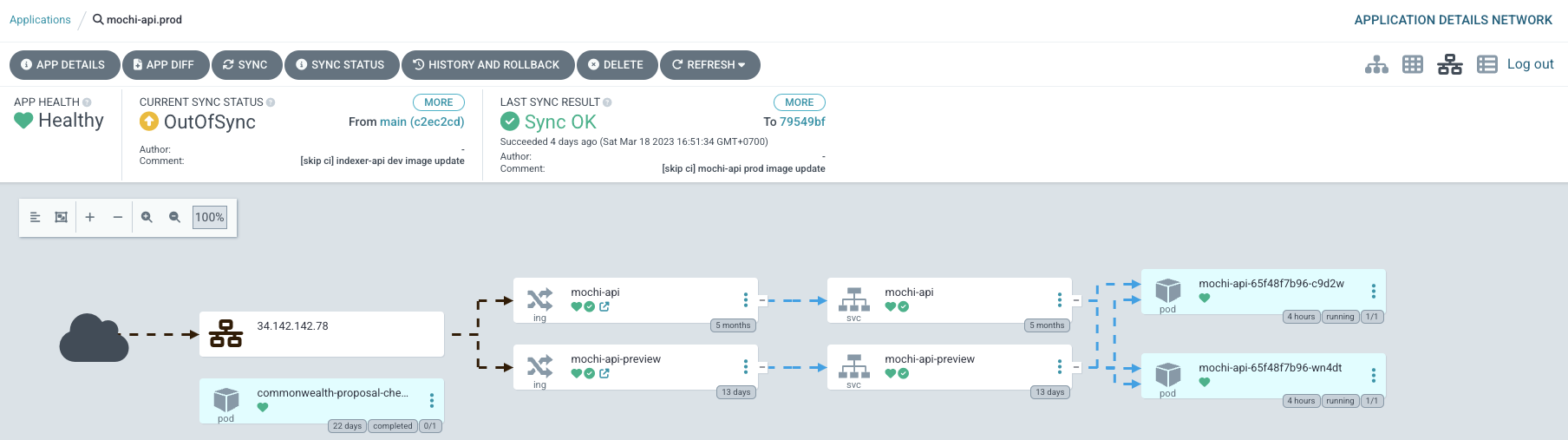
ArgoCD service Mochi API
Conclusion
This case study helped us demonstrate the value of blue-green deployment in reducing downtime, improving user experience, and streamlining the update process for applications like Mochi Bot.
Implementing a blue-green deployment strategy for Mochi Bot proved to be a smooth and hassle-free process. It provided an immediate benefit by eliminating inconsistencies between pod updates during deployment. Thankfully, as a result, the user experience remained seamless and uninterrupted during application updates.
Moving forward, our team plans to integrate K6 for API testing to improve the performance and reliability of Mochi Bot. We aim to establish a quality gate for the green version to ensure that only thoroughly tested and stable releases are deployed to the live environment.
Contributing
At Dwarves, we encourage our people to read, write, share what we learn with others, and contributing to the Brainery is an important part of our learning culture. For visitors, you are welcome to read them, contribute to them, and suggest additions. We maintain a monthly pool of $1500 to reward contributors who support our journey of lifelong growth in knowledge and network.
Love what we are doing?
Check out our products
Hire us to build your software
Join us, we are also hiring
Visit our Discord Learning Site
Visit our GitHub
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Quang Le directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
