How to run Medusa on Gitpod
 Mark Tawanda Munyaka
Mark Tawanda Munyaka
Introduction
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install, run and test Medusa on Gitpod.
What is Medusa?
Medusa is an open source composable commerce engine for building ecommerce websites. A great alternative to Shopify with much more features.
It's a Node.js server built with Express and other tools that offer functionalities for managing events, caching, job queues, and more.
It is fully customizable and extensible through the use of commerce modules. You can build webshops, subscription services, digital products stores, ticketing systems, and any other ecommerce solutions.
Here is an architecture example of a full-fledged ecommerce app you can build using Medusa.

You could think of Medusa as a set of tools used to build digital commerce applications. If you want to know more about Medusa, check out their documentation.
What is Gitpod?
Gitpod is a cloud development environment. It allows developers to code and collaborate on projects in a browser-based workspace. You can code on the go with any device as long as there is internet access and a web browser.
It uses a Linux-based container in the cloud, with a code editor/ide of your choice. You can spin up a fresh dev environment within seconds. It comes with the most commonly used developer tools, especially for web developers.
For personal projects, I use Gitpod to test open source apps built by other developers, new technologies, and small projects. It can be very convenient if you are limited on compute power on your local machine.
Objective of Tutorial
This tutorial will show you how to install, run and test a Medusa-based project in a Gitpod workspace. We will use the default quickstart Next.js storefront provided by Medusa as a means to test the project. You will walk through the steps required to configure Gitpod to work with Medusa. By the end of this tutorial, you should have a working Medusa app running in your Gitpod workspace.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial you must have the following:
- Gitpod account: Sign up here
NOTE:
You must have anyone of the following accounts to sign up for Gitpod:
GitHub
GitLab
Bitbucket
Web browser of your choice
SSH client of your choice
Step 1 - Initialize Gitpod Workspace
Log in to your Gitpod account.
Start a new workspace by clicking on New Workspace or pressing Ctrl + O on your keyboard.
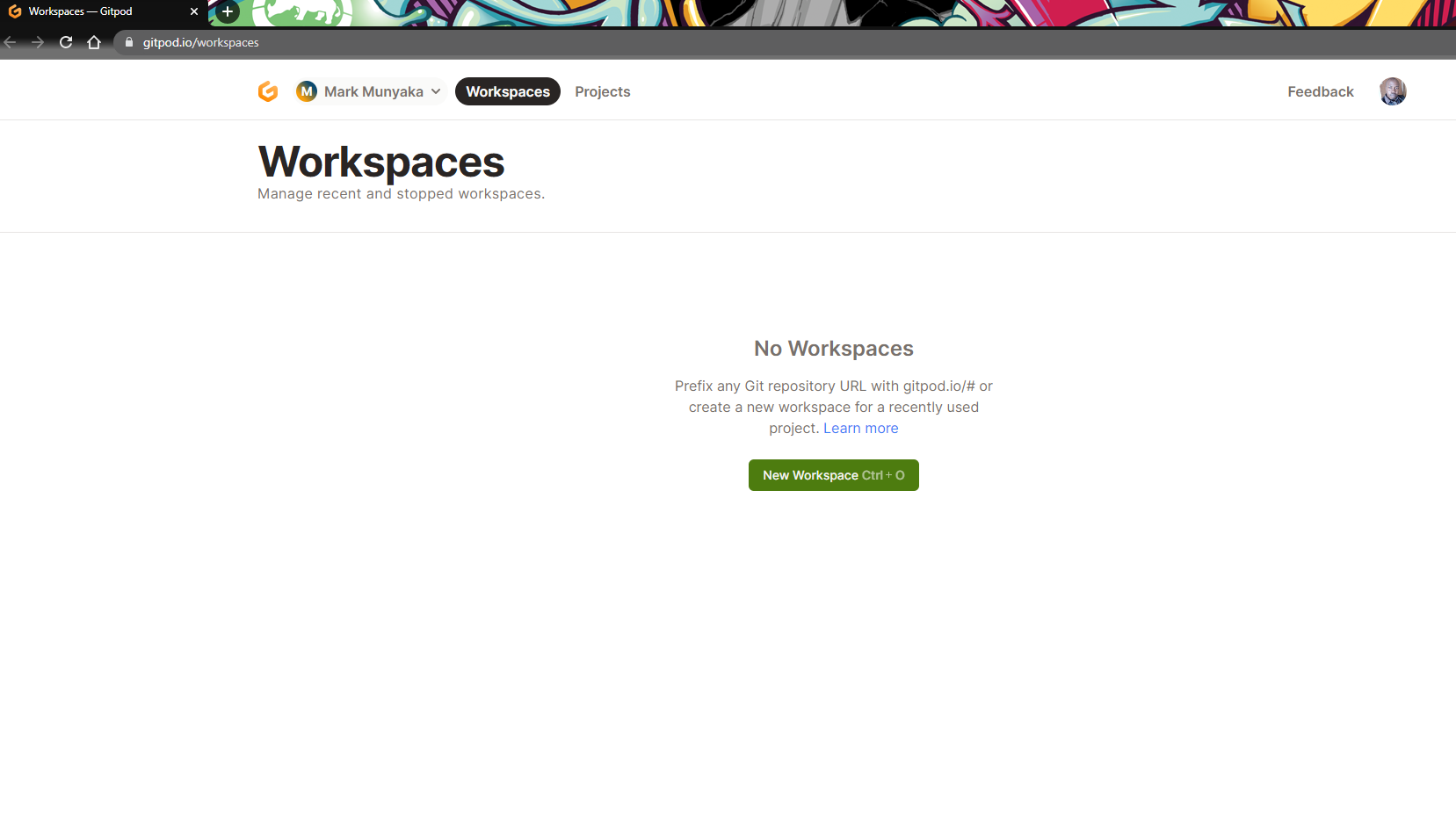
Select a repository from your GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket account and leave the Editor and Class options with the default values and click on New Workspace.
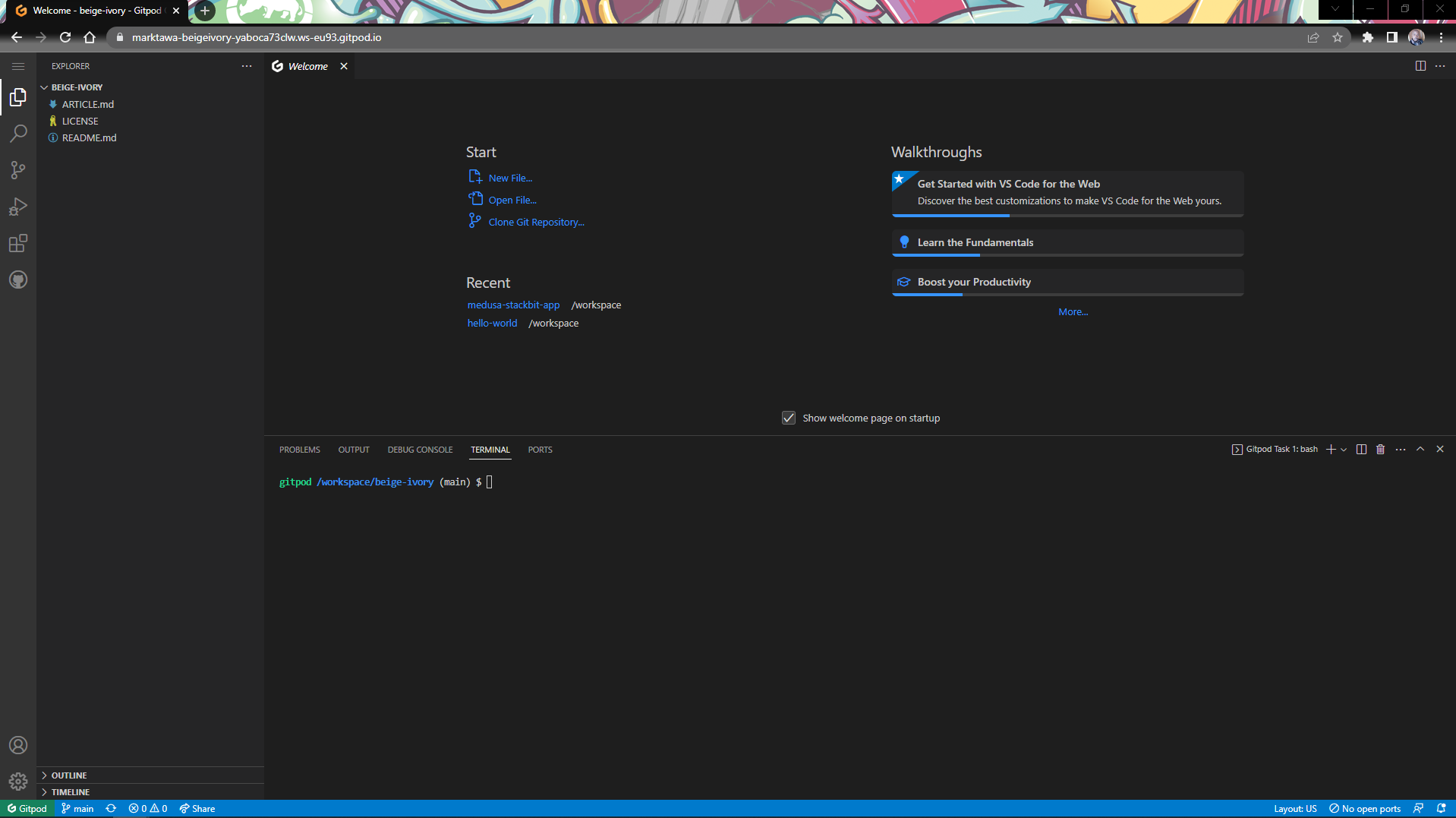
You should see VSCode in your browser, with a list of the files in your repository in the EXPLORER. This is your Gitpod workspace running.
Step 2 - Setup Medusa backend
Next, you will install a Medusa backend using the Quickstart guide.
The default Gitpod workspace comes pre-installed with node, npm and, yarn. These are the necessary tools required to install Medusa.
In the terminal window, install the Medusa CLI.
npm install @medusajs/medusa-cli -g
Create a new Medusa project for your backend and seed it with some data.
medusa new my-medusa-store --seed
Start your Medusa backend server
cd my-medusa-store
medusa develop
Your Medusa server should start running on port 9000. Test it, in a new terminal tab.
curl localhost:9000/store/products
The beginning of the JSON response should be similar to this:
{
"products": [
{
"id": "prod_01GWTHY98VZ3BHWFJX9DNXJ6PY",
"title": "Medusa Coffee Mug",
"subtitle": null,
"status": "published",
"external_id": null,
"description": "Every programmer's best friend.",
"handle": "coffee-mug",
"is_giftcard": false,
"discountable": true,
"thumbnail": "https://medusa-public-images.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/coffee-mug.png",
"profile_id": "sp_01GWTHY89ZKN791N6H948SVA38",
"collection_id": null,
"type_id": null,
"weight": 400,
"length": null,
"height": null,
"width": null,
"hs_code": null,
"origin_country": null,
"mid_code": null,
"material": null,
Step 3 - Setup Next.js storefront
Next, you will install the Next.js starter storefront to view the products from the server using the Next.js Storefront Quickstart Guide in the Medusa Documentation.
In a new terminal tab, create a new Next.js project using the Medusa starter template:
npx create-next-app -e https://github.com/medusajs/nextjs-starter-medusa my-medusa-storefront
Set up environment variables for your Next.js storefront:
cd my-medusa-storefront
mv .env.template .env.local
Make sure the Medusa backend server is running and then run the Next.js app:
npm run dev
Your Next.js storefront should start running on port 8000.
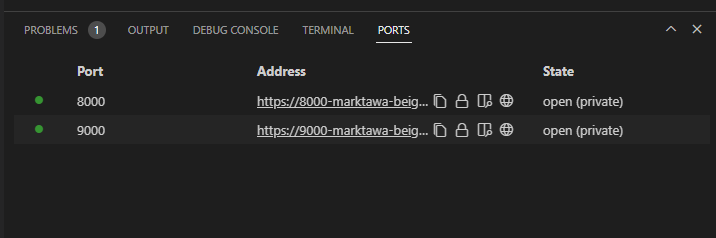
Gitpod will automatically create a preview link based on the port which is running. If you don't see it click on the PORTS tab and should see a list of ports available for preview. Select the preview link for port 8000.
A new tab with the URL of the preview link to the storefront will open. Here's the storefront.
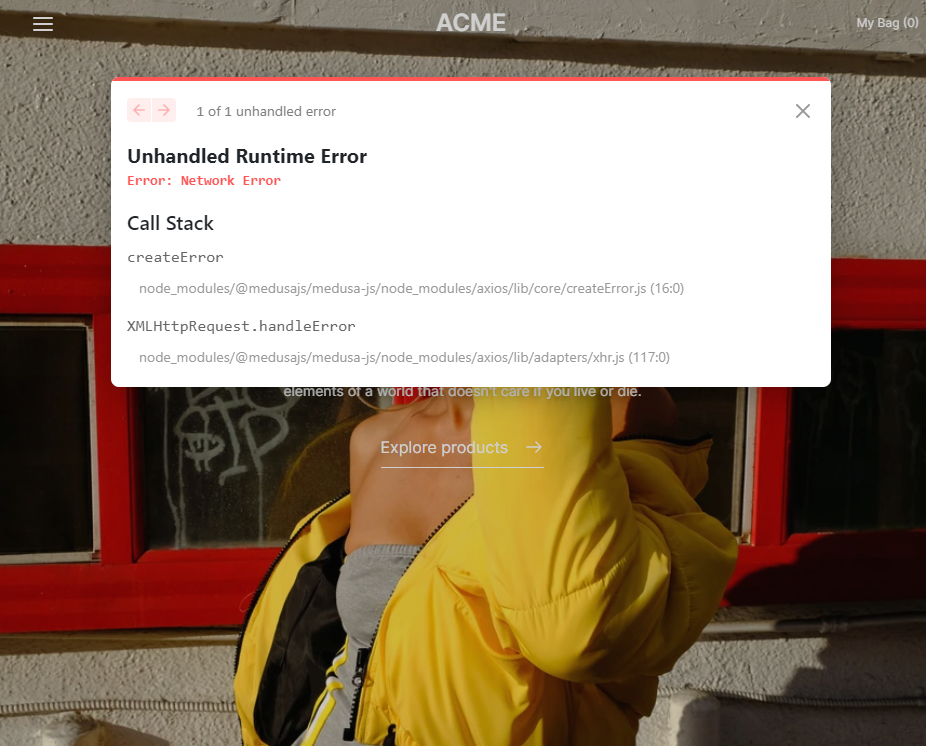
The storefront loads but the products from the backend server do not appear. This is due to a Network Error due to some CORS issue.
To get around this we will use port forwarding to preview the storefront.
Step 4 - Setup SSH port forwarding
In this step, we will use SSH port forwarding to preview the storefront in your browser. If you want to know more about SSH port forwarding please check out this article.
Make sure you have an SSH client installed on your computer before you proceed with this step. I used OpenSSH, but the instructions work for other SSH clients too.
In a new browser tab, go to your Gitpod Workspaces Dashboard. Click on the Actions icon for your Medusa project workspace. Select Connect via SSH.
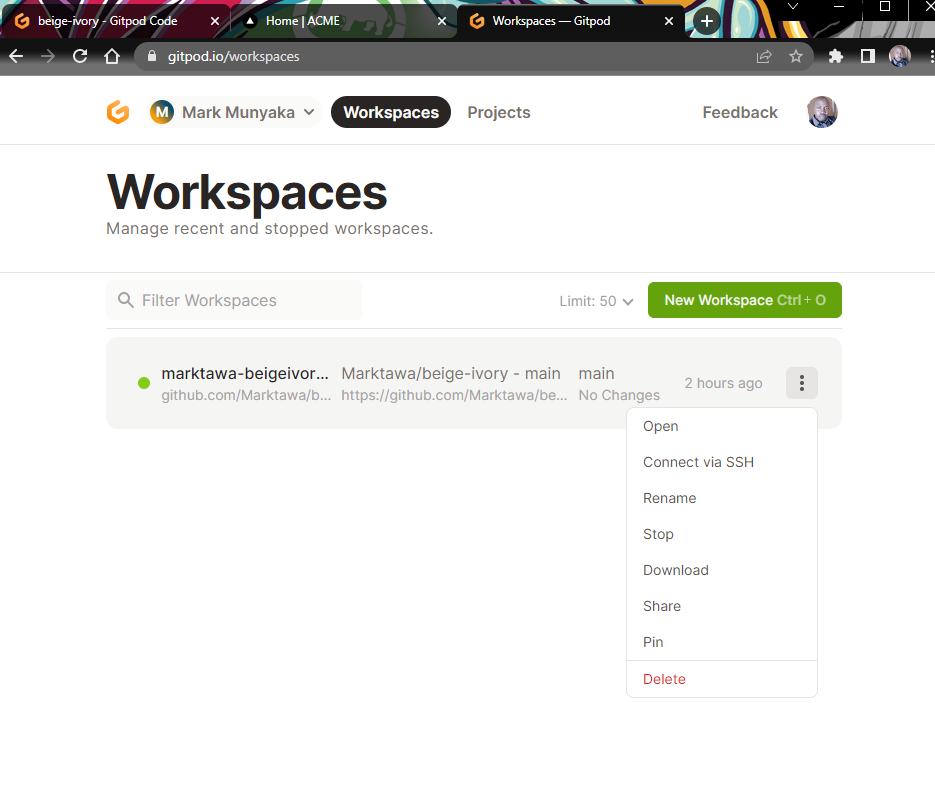
In the Connect via SSH modal select the Access Token tab and copy the link given.

In a terminal application on your local computer paste the link for your SSH Access token and edit the command to forward port 9000 using SSH.
ssh -L 9000:localhost:9000 marktawa-beigeivory-yaboca73clw#4jTE-2J-BNzJpS48OOaP0deLZsANtY-L@marktawa-beigeivory-yaboca73clw.ssh.ws-eu93.gitpod.io
Replace the link <marktawa-beig...\> with the specific link for your workspace.
If all works well port 9000 from the remote Gitpod workspace should be available on your local machine you can test using curl localhost:9000/store/products and you should see the list of products.
Next forward port 8000 for the storefront. Copy the previous command and replace 9000 with 8000.
ssh -L 8000:localhost:8000 marktawa-beigeivory-yaboca73clw#4jTE-2J-BNzJpS48OOaP0deLZsANtY-L@marktawa-beigeivory-yaboca73clw.ssh.ws-eu93.gitpod.io
Step 5 - Preview Next.js Starter Storefront
Open a new tab and go to localhost:8000 in your browser. You should see the Next.js starter storefront once again.
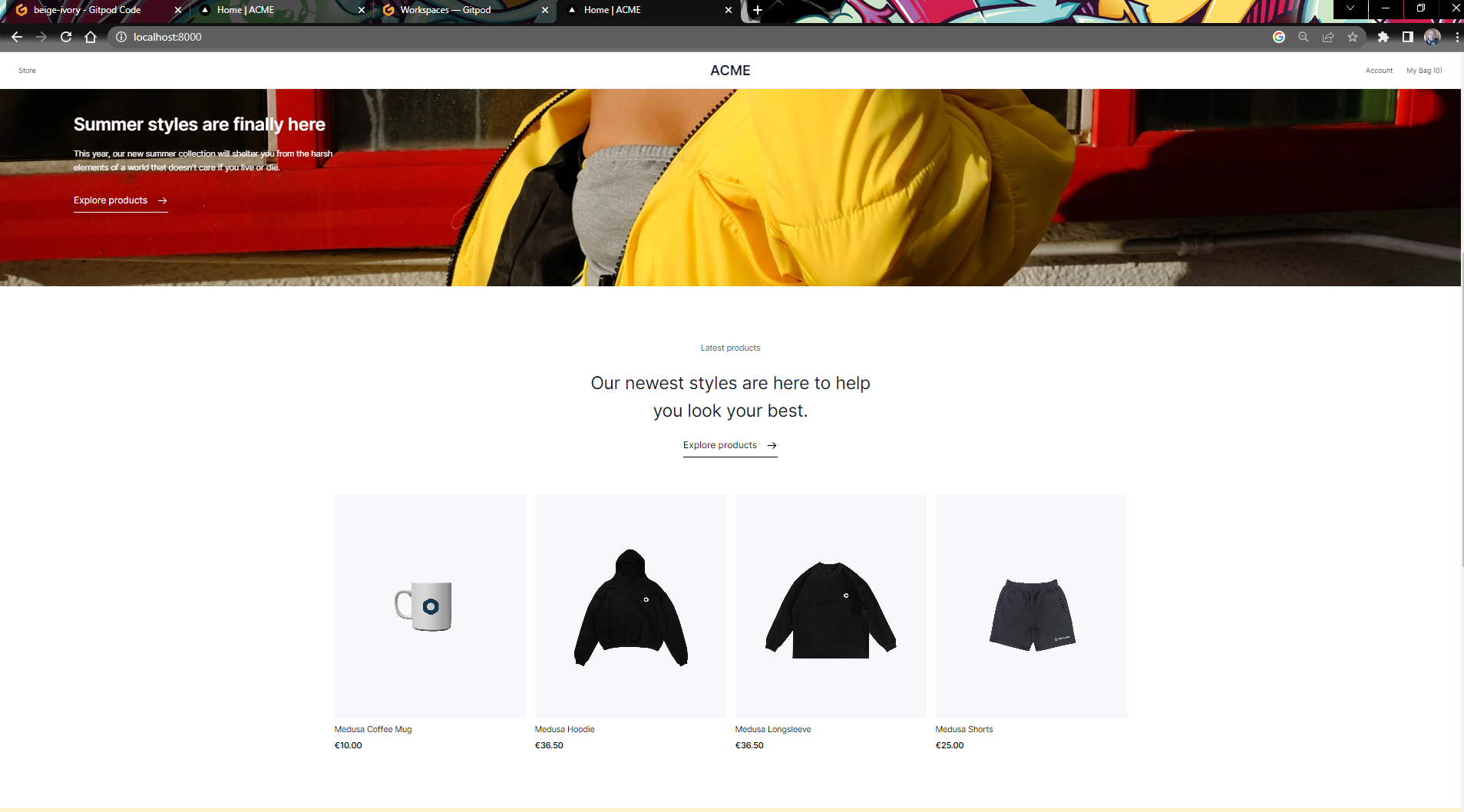
The difference now is that the products load and there is no network error. With that done, you have successfully run and tested your storefront.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully set up a Medusa backend with a Next.js storefront on an online development environment provided by Gitpod.
You also learned how to use SSH port forwarding to preview the storefront without any network errors.
This tutorial has helped you gain a solid understanding of how to use Medusa and Gitpod to build ecommerce applications efficiently. You can now continue to customize and build upon this foundation to create an e-commerce application that meets your specific needs. Keep exploring and have fun building!
Useful Links
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mark Tawanda Munyaka directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mark Tawanda Munyaka
Mark Tawanda Munyaka
I am a freelance developer and technical writer from Zimbabwe currently based in Lusaka, Zambia. I enjoy coding, reading, and outdoor sports. I love testing out new technologies (web, desktop, mobile) that can help me build cool apps. I am currently dabbling with the JAMStack ecosystem.