Part 3-Advance Git & GitHub for DevOps Engineers.
 Ritul Gupta
Ritul Gupta
Types of Repositories
Github:- Bare Repositories (Central Repo)
Store and Share only.
All Central Repositories are Bare Repo.
Git:- Non-Bare Repositories (Local Repo)
Where we can modify the files.
All local Repositories are Non-Bare Repositories.
Git Merge
Git merge is a command that allows developers to merge Git branches while the logs of commits on branches remain intact.
You can't merge branches of different Repositories
We use the Pulling Mechanism to merge Branches.
git merge <branch name>
Git Conflict
When some files have different content in different branches if you do merge, conflict occurs (Resolve conflict then add and commit).
Conflict occurs when you merge branches
Git Stashing
Suppose you are implementing a new feature for your product, your code is in progress and suddenly a customer escalation comes. Because of this, you have to keep aside your new feature work for a few hours.
You cannot commit your partial code and also cannot throw away your changes. So you need some temporary storage, when you can store your partial changes and later on commit it.
To stash an item (Only applies modified files, not new files).
To stash on Item
git stash
To see stashed items
git stash list
To apply stashed items
git stash apply stash @ {0}
Then you can add and commit
To clear the stash items
git stash clear
Git Reset
git Reset is a Powerful command that is used to undo local changes to the state of a git repo.
To reset the staging area
git reset <Filename>
git reset .
To reset the changes from both the staging area and the working directory at a time.
git reset --hard
Git Revert
The revert command helps you undo an existing commit.
It does not delete any data in this process instead Rather git creates a new commit with the included files reverted to their previous state. So, your version control history moves forward while the state of your file moves backward.
NOTE :
Reset- Before commit
Revert- After commit
How to remove untracked files
git clean -n (dry clean)
git clean -f (forcefully)
Git Rebase
Git rebase is a command that lets users integrate changes from one branch to another, and the logs are modified once the action is complete. Git rebase was developed to overcome merging’s shortcomings, specifically regarding logs.
Task 1
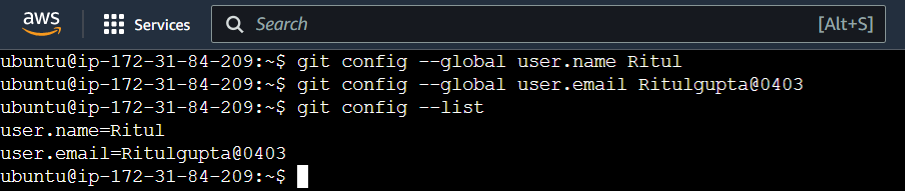
Set your user name and email address, which will be associated with your commits.
To set the user name and email address, use these commands:git config --global user.name "<username>" git config --global user.email "<email-id>"
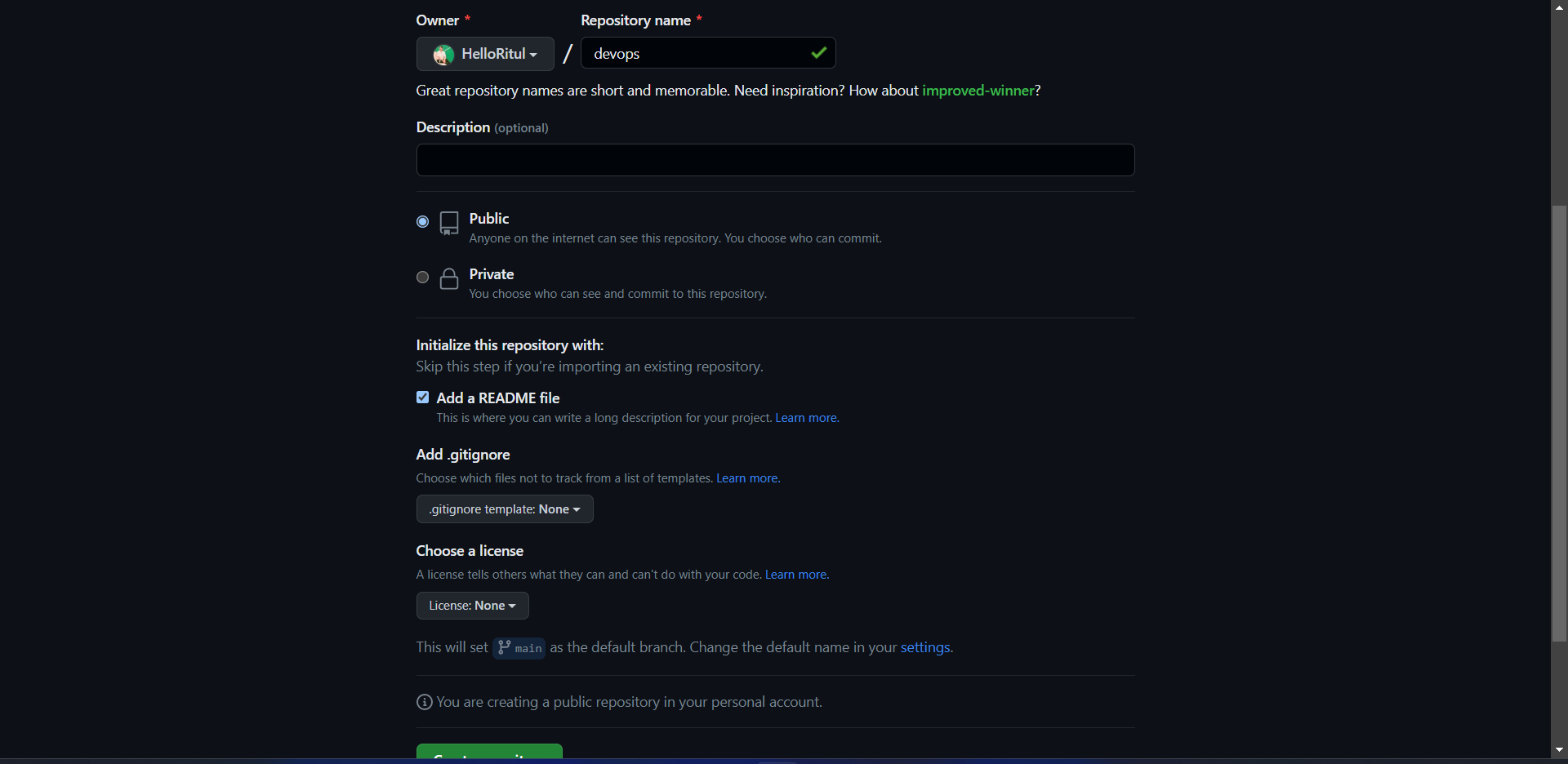
Task 2
- Create a repository named "devops" on GitHub
Connect your local repository to the repository on GitHub.
The git init command changes the current directory into a Git repository
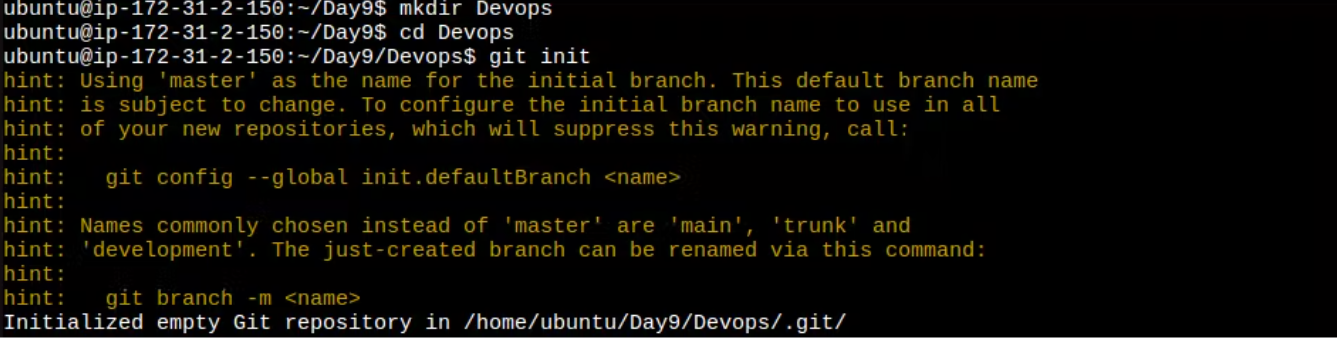
We can use this command to connect the local repository to the GitHub repository
git remote add origin <GitHub_repository_url>
Create a new file in Devops/Git/day-2.txt & add some content to it
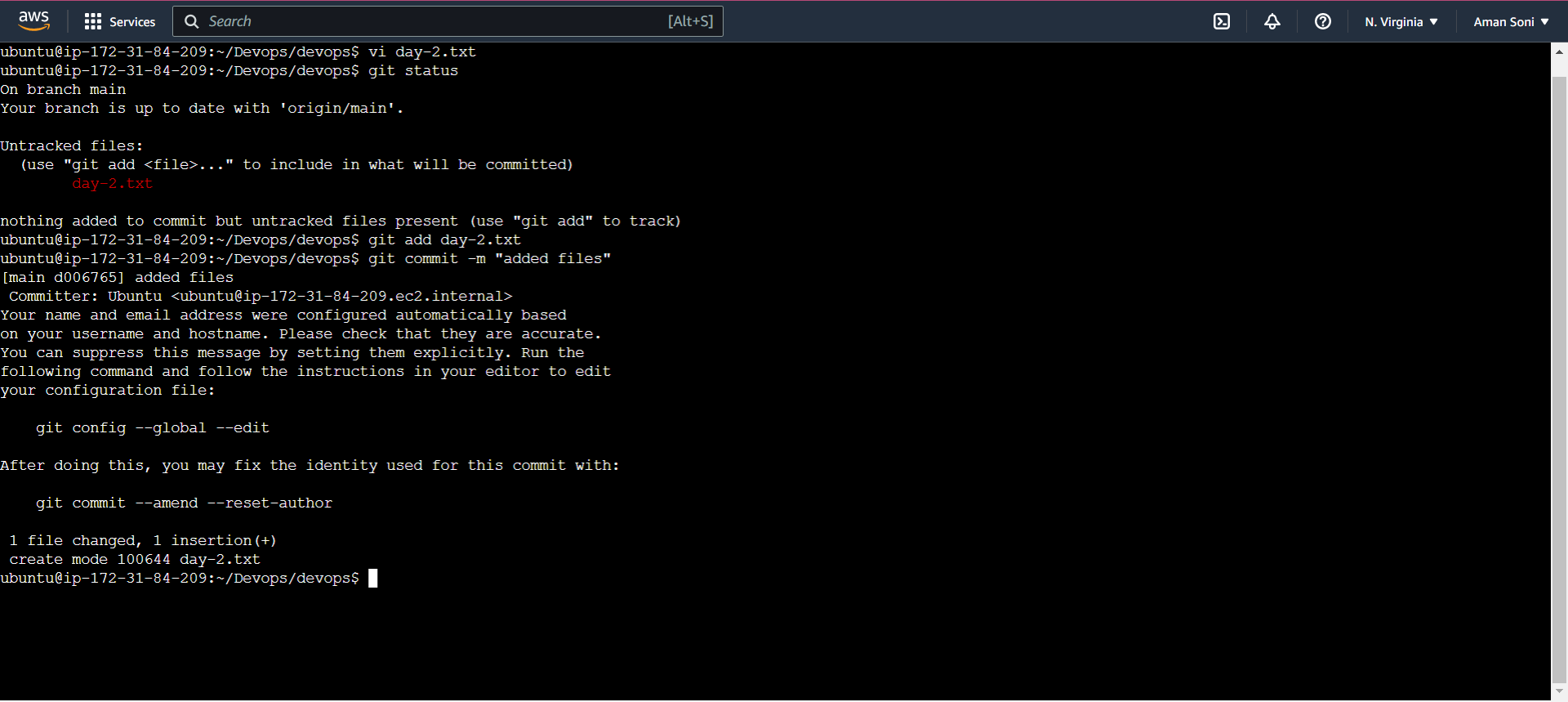
- Push your local commits to the repository on GitHub

Let's complete the git in the next blog, for that you will have to watch Part-4!!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ritul Gupta directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ritul Gupta
Ritul Gupta
Packaged App Development Associate @ Accenture | Infrastructure Engineering | Exploring Cloud & Security