Kubernetes Flask App end to end Deployment With Microservices
 Subho Dey
Subho Dey
Introduction:-
Kubernetes is a powerful container orchestration tool that enables developers to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications. While Kubernetes is designed to be easy to use, it's not without its challenges, and troubleshooting is a critical skill that all Kubernetes users must possess. In this blog, we'll explore some common Kubernetes troubleshooting techniques that you can use to diagnose and fix issues with your Kubernetes clusters.
Prerequisites for deployment-
- Update the system and install docker:
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install docker.io -y
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
- Kubeadm installation:
sudo curl -fsSLo /usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install kubeadm=1.20.0-00 kubectl=1.20.0-00 kubelet=1.20.0-00 -y
- To connect with the cluster(for the master node):
sudo su
kubeadm init
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/weaveworks/weave/releases/download/v2.8.1/weave-daemonset-k8s.yaml
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
- To connect with the cluster(for the Worker node):
sudo su
kubeadm reset pre-flight checks
(*Paste the Join command on worker node and append `--v=5` at end*)
(*kubeadm token create --print-join-command*)
- To verify cluster connection:-
kubectl get nodes
Let's dive into our deployment------>
Clone the repo:-
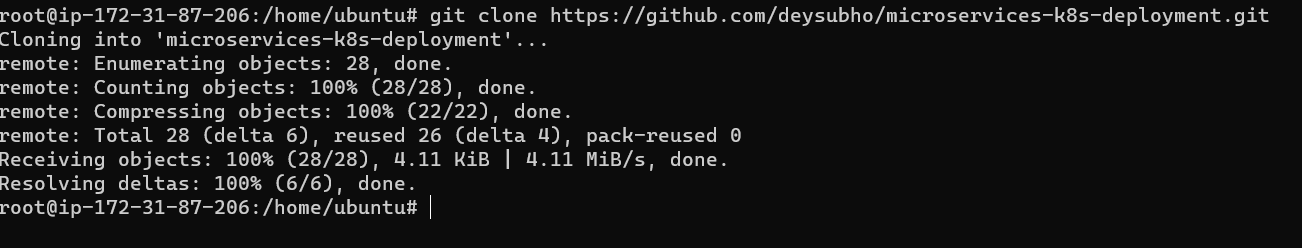
create the docker file
vim Dockerfile- configuration of the docker file
FROM python:alpine3.7
COPY . /app
WORKDIR /app
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
ENV PORT 5000
EXPOSE 5000
ENTRYPOINT [ "python" ]
CMD [ "app.py" ]
3. Now we will make a new file vim taskmaster.yml
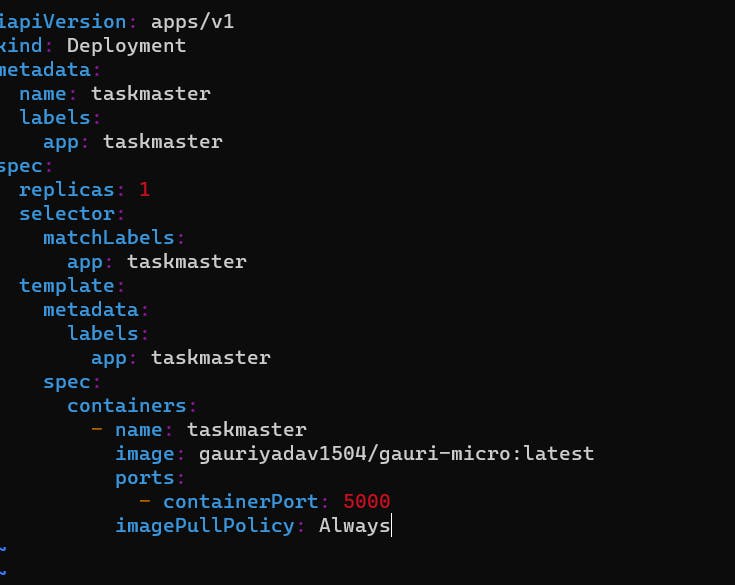
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: taskmaster
labels:
app: taskmaster
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: taskmaster
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: taskmaster
spec:
containers:
- name: taskmaster
image: gauriyadav1504/gauri-micro:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
imagePullPolicy: Always
Check whether the nodes are ready or not!!
sudo kubectl get nodes
5. Check whether the pod is running or not: -
sudo kubectl get pods
6. Run the taskmaster yml file:-

- 7 . Scale the taskmaster:-

8 . make taskmaster service vim taskmaster-svc.yml
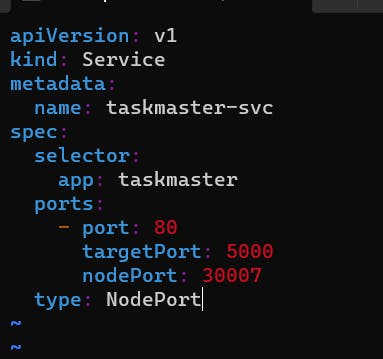
kind: Service metadata: name: taskmaster-svc spec: selector: app: taskmaster ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 5000 nodePort: 30007 type: NodePort9 . Run the taskmaster service file:-

- 10 . Run the Mongo persistent volume file:-

- 11 . Claim persistent volume:-

- 12 . Run the Mongo yml file:-

- 13 . Run the Mongo svc file:-

- 14 . Check whether the clusters are running or not:-
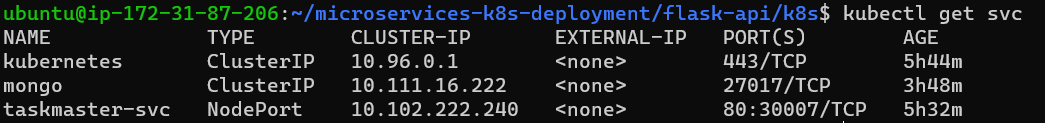
- 15 . Change the inbound rules:-

Finally, just copy the public IP of the worker node and check in Postman whether it's running on not!
!!!!!!!!!YOU DID IT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Thank you!
Follow for more!
HAPPY TO HELP IN DM ON LINKEDIN
Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/in/subhodey/

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Subho Dey directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Subho Dey
Subho Dey
"DevOps engineer with a passion for continuous improvement and a drive to build better software, faster. I'm a strong believer in the power of collaboration, automation, and agile methodologies to transform the world of software development and delivery. My expertise includes continuous integration and delivery, infrastructure as code, Docker, Kubernetes, and configuration management. Follow along as I share my insights and experiences on Hashnode and let's build better software, together!"