Volley with Compose Kotlin
 Rhytham Negi
Rhytham Negi
Important Features of Volley
Automatic scheduling of network requests.
Multiple concurrent network connections.
Transparent disk and memory response caching with standard HTTP cache coherence.
Support for request prioritization.
Cancellation request API. You can cancel a single request, or you can set blocks or scopes of requests to cancel.
Ease of customization, for example, for retry and backoff.
Strong ordering makes it easy to correctly populate your UI with data fetched asynchronously from the network.
Debugging and tracing tools.
Built-in support for
Raw strings
Images
JSON
Benefits of using Volley
Eases networking for Android apps.
Makes networking faster.
Integrates easily with any protocol.
Provides built-in support for features you need.
Limitations of Volley
Not suitable for large download or streaming operations, due to holding all responses in memory during parsing.
Consider using an alternative like Download Manager for large download operations.
Getting Started with Volley
The easiest way to add Volley to your project is to add the following dependency to your app’s build.gradle file:
Installation
dependencies {
implementation 'com.android.volley:volley:1.2.1'
// For Json representation
implementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.9'
}
You need to internet permission add <user-permission> with android.permission.INTERNET
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"> </uses-permission>
Let's Code our Simple request
Here, we send Request to thee URL https://random-data-api.com/api/v2/credit_cards that returns a random Credit card detail. JSON response:
{
"id": 6185,
"uid": "09db6100-4847-401f-b224-244b761d3b46",
"credit_card_number": "1234-2121-1221-1211",
"credit_card_expiry_date": "2027-04-15",
"credit_card_type": "switch"
}
Note: The credit card detail provided by API does not belong to any real user data.
Create a function call simpleRequest() that receive context as argument and initiate a new RequestQueue using Volley.newRequestQueue
fun simpleRequest(context: Context):String {
val queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(context)
val url = "https://random-data-api.com/api/v2/credit_cards"
var response = ""
val stringRequest = StringRequest(Request.Method.GET,
url, {
// Handling Success
Log.d("Success", "simpleRequest:${it}")
response = it
}, {
// Handling Error
Log.d("Error", "simpleRequest:${it}")
response = "Error"
})
queue.add(stringRequest)
return response
}
StringRequest uses 4 param:
method – the request
Request.Methodto use (GET,POST)URL – URL to fetch the string
listener - Listener to receive the String response
errorListener– Error listener, or null to ignore errors
Logcat Response:
2023-04-16 15:44:03.272 11586-11586 Success com.rhytham.volleyincompose D simpleRequest:{"id":9485,"uid":"00b429e3-7ae6-45fc-9b9a-d0c1dc84a895","credit_card_number":"1228-1221-1221-1431","credit_card_expiry_date":"2026-04-15","credit_card_type":"mastercard"}
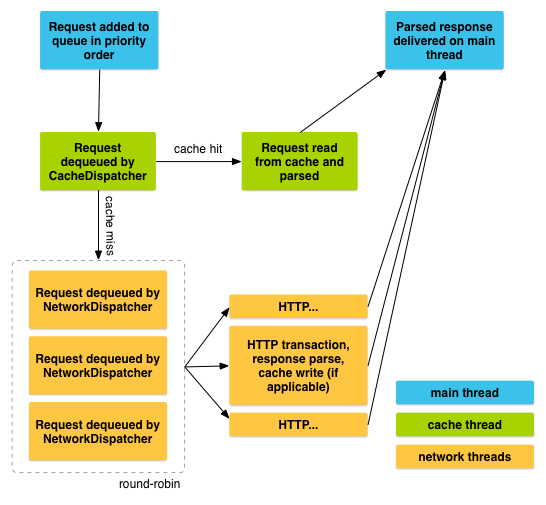
Life Cycle of Request
To send a request, you simply construct one and add it to the RequestQueue with add(), as shown above. Once you add the request it moves through the pipeline, gets serviced, and has its raw response parsed and delivered.
When you call add(), Volley runs one cache processing thread and a pool of network dispatch threads. When you add a request to the queue, it is picked up by the cache thread and triaged: if the request can be serviced from cache, the cache response is parsed on the cache thread and the parsed response is delivered on the main thread. If the request cannot be serviced from cache, it is placed on the network queue. The first available network thread takes the request from the queue, performs the HTTP transaction, parses the response on the worker thread, writes the response to cache, and posts the parsed response back to the main thread for delivery.
Note that expensive operations like blocking I/O and parsing/decoding are done on worker threads. You can add a request from any thread, but responses are always delivered on the main thread.
Create @Composable function to hold the Card Details :
@Composable
fun CreditCardM3(
cardNumber: String,
cardHolderName: String,
cardExpiry: String )
{
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.height(height = 200.dp)
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(all = 10.dp),
elevation = CardDefaults.elevatedCardElevation()
) {
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.visa_logo),
contentDescription = " Visa logo",
modifier = Modifier
.height(height = 38.dp)
.padding(all = 6.dp),
alignment = Alignment.TopStart
)
Text(
modifier = Modifier.padding(start = 8.dp),
text = "Credit card",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.labelSmall
)
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.chip),
contentDescription = " Visa logo",
modifier = Modifier
.height(height = 50.dp)
.padding(all = 6.dp),
alignment = Alignment.TopStart
)
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(start = 10.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
text = cardNumber,//XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall,
fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold
)
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(end = 10.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
text = "Expiry Date: $cardExpiry", //2026-04-14
textAlign = TextAlign.End,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.labelSmall
)
Text(
modifier = Modifier.padding(start = 10.dp),
text = cardHolderName,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyLarge,
fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold
)
}
}
Check out GitHub repo for Assets: VolleyInComposeExample at (github.com)

StringRequest with Custom Header/s
Volley provides the following classes for JSON requests:
JsonArrayRequest: A request for retrieving aJSONArrayresponse body at a given URL.JsonObjectRequest: A request for retrieving aJSONObjectresponse body at a given URL, allowing for an optionalJSONObjectto be passed in as part of the request body.
Both classes are based on the common base class JsonRequest.
For an example: Let's take sample URL with an Authorization Token and returns aJson as response. Create a variable
val URL = "https://data.example.com/api/database/table/1jhsdhshskj"
response: [Example]
{
"count": 1,
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"id": "4weA2aCKFmCx7hq1c",
"order": "1.00000000000000000000",
"nid": "829379381",
"title": "Test Title",
"description": "This is the actual notes",
"Created on": "2023-04-16T14:52:04.178089Z",
"owner_id": [
{
"id": "4dPp17S92SVQbjMVpy",
"value": "1"
}
]
}
]
}
Next task is to get Data from results Json Object which returns JSONArray. For store the JsonArray. Create a variable data of type JSONArray
var data: JSONArray
Now, the main part of Request is to get the data from API. There are lots of ways to do with Volley, for now we use StringRequest to get Json in plain String and parse that String to JSONObject / JSONArray
val jsonResponse: StringRequest = object : StringRequest(
Method.GET,
URL,
{ response ->
// Parse the response JSON object
val it = JSONObject(response)
// Get the "results" array from the JSON object
data = it.getJSONArray("results")
Log.d("Success", data.toString())
},
{ Log.d("Failure", "Error is here") }
) {
// Override the getHeaders method to include an authorization token in the headers
override fun getHeaders(): MutableMap<String, String> {
return mutableMapOf("Authorization" to "Token 15DWDFG6CdfU46D9WshfA4s")
}
}
queue.Add(jsonResponse)
Final code: fun simpleStringRequest(context: Context)
fun simpleStringRequest(context: Context){
val URL = "https://data.example.com/api/database/table/1jhsdhshskj"
var data: JSONArray
val jsonResponse: StringRequest = object :StringRequest(Method.GET,URL,
{ response ->
// Parse the response JSON object
val it = JSONObject(response)
// Get the "results" array from the JSON object
data = it.getJSONArray("results")
Log.d("Success", data.toString())
},
{ Log.d("Failure", "Error is here") }
) {
// Override the getHeaders method to include an authorization token in the headers
override fun getHeaders(): MutableMap<String, String> {
return mutableMapOf("Authorization" to "Token 15DWDFG6CdfU46D9WshfA4s")
}
}
}
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned how to use Volley library in Kotlin Android to make network requests. We have seen how to create a simple request and a string request with header parameters. Volley is a powerful and easy-to-use library that simplifies the network operations in Android applications. It provides features such as automatic scheduling, caching, prioritization, and cancellation of requests. It also supports different types of requests such as JSON, image, and RAW String requests. Volley is a great choice for developers who want to perform network operations efficiently and reliably in their Kotlin Android applications.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rhytham Negi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
