Digital Signatures on Ethereum Blockchain
 Adeogo Favour
Adeogo FavourOverview
In today's digital world, where information is transmitted and exchanged across networks and devices, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents is crucial. Digital signatures are one such mechanism that provides this security and authenticity for electronic documents.
Ethereum on its own is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables the creation and execution of smart contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps). One of the key features that make Ethereum a secure and trustworthy platform is digital signatures. In this blog, we will explore what Ethereum digital signatures are, how they are made, how they work, and their significance to the Ethereum ecosystem.
What are Digital Signatures?
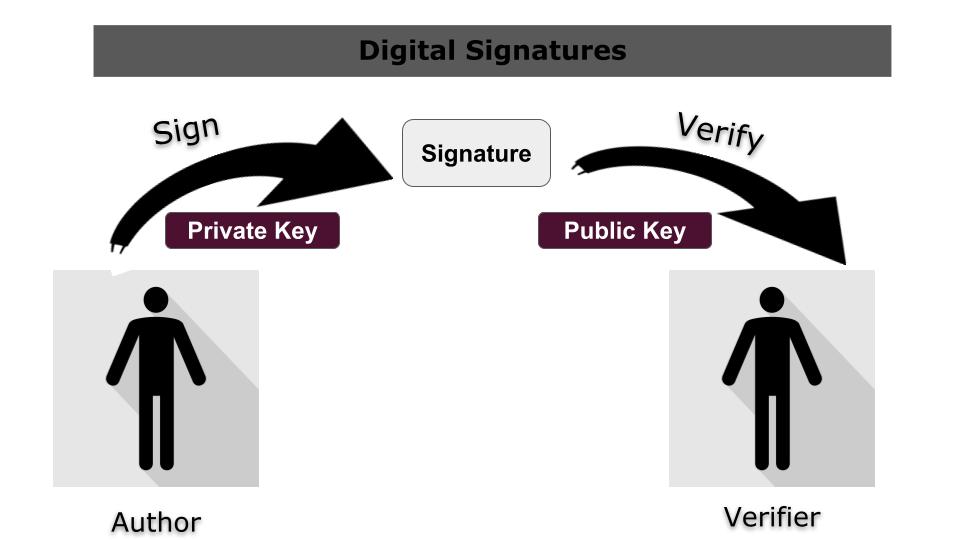
Digital signatures are cryptographic tools that allow users to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital documents, messages, and transactions. They are based on public-key cryptography, which uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The private key is used to sign a message, while the public key is used to verify the signature. Digital signatures are essential for secure communication, online transactions, and electronic contracts.
Digital Signatures in Ethereum
Ethereum uses digital signatures to verify the identity of users and to authenticate transactions on its blockchain. Suppose Dami creates a transaction on the Ethereum network, he has to use his private key to sign the transaction to prove that he is the rightful owner of the private key and that the transaction is legitimate . The transaction is then broadcasted to the network, and his signature is verified by other nodes on the network using his public key(address in layman's terms).
Ethereum uses a specific type of digital signature called the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), which is based on the mathematics of elliptic curves. ECDSA is a widely used digital signature algorithm that is known for its efficiency and security. It is used in many blockchain platforms, including Bitcoin and Ethereum.
ECDSA signatures consist of two numbers (integers): r and s. Ethereum also uses an additional v (recovery identifier) variable. The signature can be notated as {r, s, v}. We will understand more about it as we go on.
How to make a Digital Signature
Here, we are going to be using Solidity to show how digital signatures are made.
For you to learn about Solidity you can check it out here. Generally, Solidity is an object-oriented, high-level language for implementing smart contracts.
So we dive straight into it.
Step 1: Create a new file in your RemixIDE
Create a new file digitalSignature.sol and since I'll be using a compiler version of 0.7 and above I'll enter the following.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;
Step 2: Create a contract
contract digitalSignature{
}
Step 3: Create a function to Verify Signatures
function verifySig(address signer, string memory message, bytes memory sig)
external pure returns (bool){
bytes32 messageHash = getMessageHash(message);
bytes32 ethSignedMessageHash = getEthSignedMessageHash(messageHash);
return recover(ethSignedMessageHash, sig) == signer;
}
Note: We still have to make a getMessageHash , ethSignedMessageHash recover functions to hash whatever message we enter and get a signed message and recover whatever signed message.
Step 4: Write the getMessageHash function to hash the message
function getMessageHash(string memory message)
public pure returns(bytes32){
return keccak256(abi.encodePacked(message));
}
Step 5: Write the recover function
function recover(bytes32 ethSignedMessageHash, bytes memory sig)
public pure returns(address){
(bytes32 r, bytes32 s, uint8 v) = _split(sig);
return ecrecover(ethSignedMessageHash,v,r,s);
}
To verify a message, we need the original message, the address of the private key it was signed with, and the signature {r, s, v} itself
From the recover function, we have a _split function that uses assembly
function _split(bytes memory sig)
internal pure returns(bytes32 r, bytes32 s, uint8 v){
require(sig.length == 65, "invalid signature length");
assembly{
r:=mload(add(sig,32))
s:=mload(add(sig,64))
v:=byte(0,mload(add(sig,96)))
}
In assembly, the First 32 bytes store the length of the signature add(sig, 32) = pointer of sig + 32 effectively, skips the first 32 bytes of signature mload(p) loads the next 32 bytes starting at the memory address p into memory.
Step 6: We compile our deploy it
Deployment
Now to deploy our code,
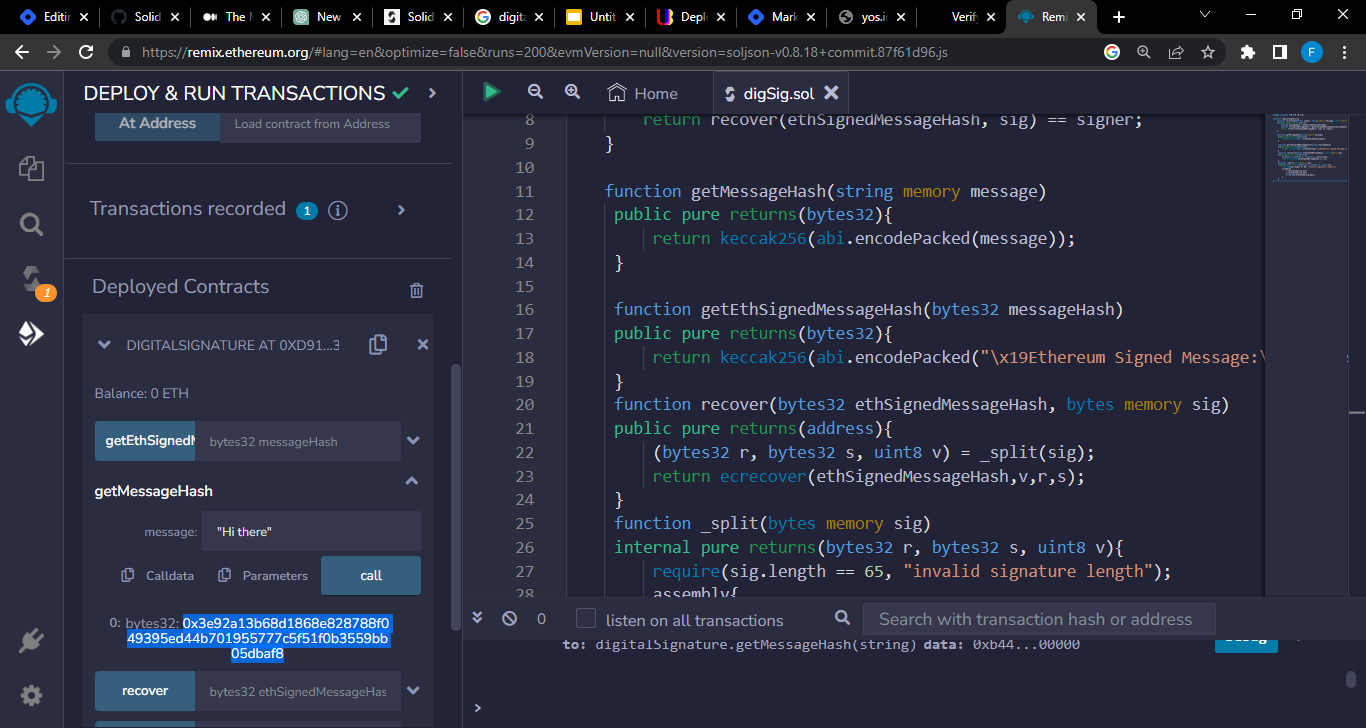
Step 1: We enter a message and get the hash
Step 2: Open the console and enable Ethereum by using the ethereum.enable
Step 3: We need to get our Account public key using the code
await ethereum.request({
method: 'eth_requestAccounts',
})
Then we get the public key and save it in a notepad
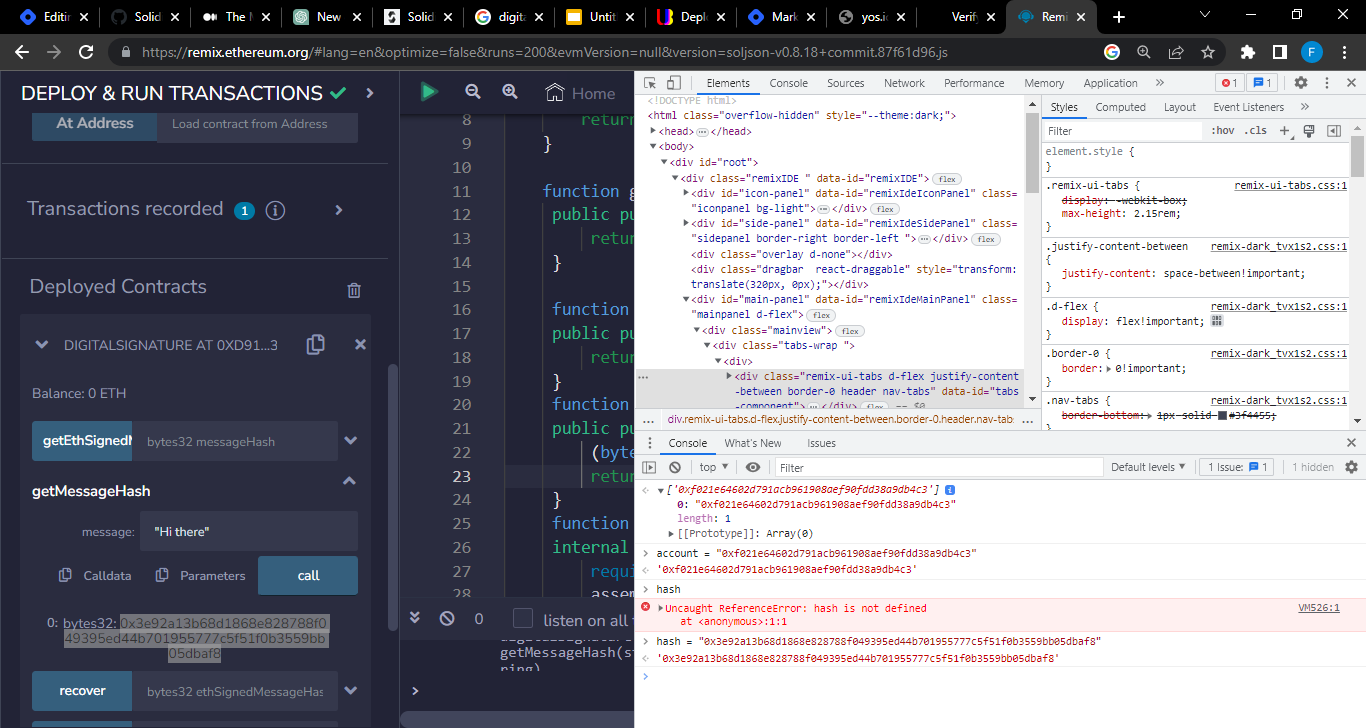
Step 4: We then save the account and message hash as constants
account = "0x----"
hash = ""
Step 5: Enter the code which returns a promise
ethereum.request({method:"personal_sign", params:[account, hash]})
This also returns a request to sign the message
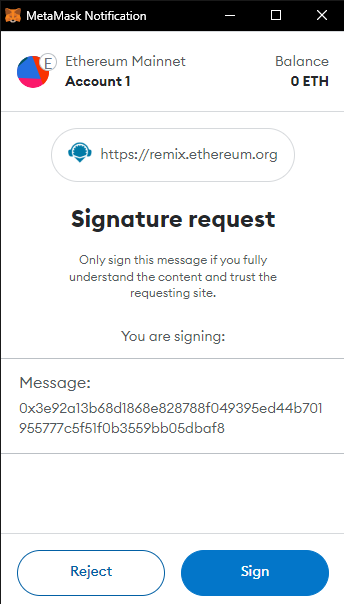
Now, you have signed your message, you can now go on to recover the hashes and verify that you posted the message.
Conclusion
Digital signatures are an essential component of the Ethereum platform. They provide security, privacy, and trust for users and enable decentralized transactions and smart contracts. Understanding how digital signatures work and their significance for the Ethereum ecosystem is essential for anyone interested in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space. As Ethereum continues to grow and evolve, digital signatures will remain a critical tool for ensuring the security and integrity of the platform.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Adeogo Favour directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Adeogo Favour
Adeogo Favour
Favour Adeogo is a seasoned technical writer with a passion for elucidating the intricacies of backend development in scalable applications. With a semi-robust background in software engineering, Favour brings a unique blend of technical expertise and communication skills to his writing endeavors. Specializing in the .NET ecosystem, Favour has honed his craft in documenting the backend architecture of scalable applications built on the .NET framework. His in-depth understanding of technologies such as C#, ASP.NET, and SQL Server enables her to articulate complex concepts in a clear and concise manner, catering to both novice developers and seasoned professionals alike. Throughout his career, Favour has collaborated closely with development teams to capture the nuances of backend implementation, ensuring that his documentation remains relevant and up-to-date in rapidly evolving technological landscapes. His meticulous attention to detail and commitment to accuracy have earned him recognition for producing high-quality technical content that serves as a valuable resource for developers worldwide. In addition to his technical prowess, Favour possesses excellent research skills, allowing him to stay abreast of the latest advancements in backend development methodologies and best practices. He is adept at distilling vast amounts of technical information into comprehensive guides, tutorials, and API documentation that empower developers to leverage the full potential of the .NET stack in building scalable and robust applications. Favour's dedication to his craft, coupled with his passion for empowering developers through clear and concise documentation, makes him a trusted resource in the tech community. Whether he's crafting tutorials, writing API guides, or documenting architectural patterns, Favour remains committed to fostering a deeper understanding of backend development with dotNET, thereby empowering developers to build innovative and scalable solutions with confidence.