[CSS] Overflow - Explained with Examples.
 Lim Woojae
Lim Woojae
What is CSS Overflow?
CSS overflow is used when the size of the child element is larger than the parent element. Then, the overflow occurs because the content of the child element is bigger.
For example:
<div style="height: 200px; width: 250px; border: 3px solid green;">
<p>
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
</div>
This code causes this:
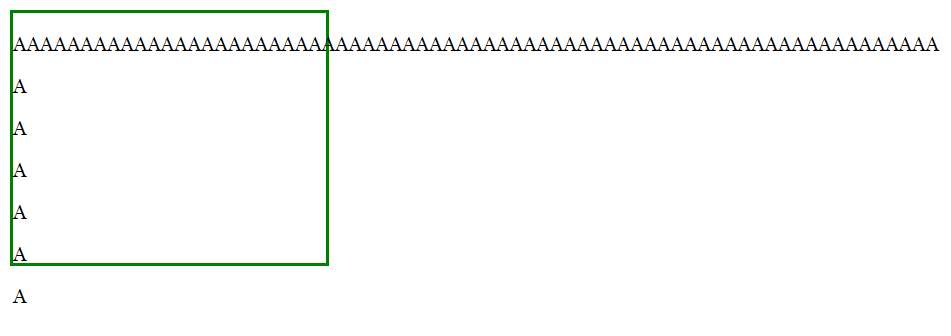
To prevent this or make the contents to be in the green box, you need a property called "overflow".
Overflow can have six(4) values:
visible - Default. Overflow is not clipped.
auto - Overflow is clipped. Scroll bars are made where the contents are overflown.
scroll - Overflow is clipped. Scroll bars appear on both x and y-axis.
hidden - Overflow is clipped. The overflew contents are not visible.
Overflow: visible
Overflow: visible is the default, which means the scroll bars will not appear.
HTML Code:
<div style="height: 200px; width: 250px; border: 3px solid green; overflow: visible;">
<p>
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
</div>

Overflow: auto
In overflow: auto, the scroll bars appear for the axis where the content is overflown.
HTML Code:
<div style="height: 200px; width: 250px; border: 3px solid green; overflow: auto;">
<p>AAAA</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
</div>

Do you notice that the scroll bar is only at the y-axis because we have added so many <p> tags in the y-axis?
Overflow: scroll
Overflow: scroll adds scroll bars on both x and y-axis regardless of how big or small the content size is. In the past, it was needed because of the browsers like internet explorer.
So, if you want to show the scroll bar every time, you can use overflow: scroll.
HTML Code:
<div style="height: 200px; width: 250px; border: 3px solid green; overflow: scroll;">
<p>AAAA</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
</div>

You would notice that the scroll bars are there even though the texts are not still in the box.
Overflow: hidden
Overflow: hidden only shows the content that is placed inside the parent element. The scroll bars are not generated.
HTML Code:
<div style="height: 200px; width: 250px; border: 3px solid green; overflow: hidden;">
<p>
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
<p>A</p>
</div>

As you can see, the scroll bars do not exist; however, the texts are not overflown. Only the texts in the green box are visible to the users.
* Additional Note. If you want the text to be shown in a straight line (or a single line), you can add this style:
CSS Code:
p {
white-space: nowrap;
}
Overflow-x and Overflow-y
Overflow-x and overflow-y are not so different from overflow property. They just allow you to select which axis you do not want the content to be overflown.
For overflow-x, it will prevent the overflow in the x-axis
For overflow-y, it will prevent the overflow in the y-axis.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Lim Woojae directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Lim Woojae
Lim Woojae
Computer Science Enthusiast with a Drive for Excellence | Data Science | Web Development | Passionate About Tech & Innovation