Tree Data Structure
 Nisha Yadav
Nisha Yadav2 min read
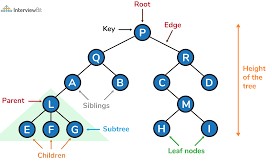
A tree is a type of data structure with many children for each node. The time complexity for creating a tree is O(1). And the time complexity for searching, inserting, or deleting a node which depends on the height of the tree h, so the worst time complexity is O(h).
For e.g., P is the root of the given tree.
Code Implementation:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Tree {
static Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
public static TreeNode<Integer> takeinput(){
System.out.println("enter next node data: ");
int n = s.nextInt();
TreeNode<Integer> root = new TreeNode<Integer>(n);
System.out.println("enter the number of children for"+n);
int children_number = s.nextInt();
for(int i =0; i< children_number; i++){
TreeNode<Integer> child = takeinput();
root.children.add(child);
}
return root;
}
public static void print(TreeNode<Integer> root){
String s = root.data + ":";
for(int i =0; i<root.children.size(); i++){
s = s + root.children.get(i).data + ",";
}
System.out.println(s);
for(int i =0; i<root.children.size(); i++){
print(root.children.get(i));
}
}
public static TreeNode<Integer> takeinputrecursive(){
System.out.println("enter root data");
int rootData = s.nextInt();
if(rootData == -1){
return null;
}
TreeNode<Integer> root = new TreeNode<Integer>(rootData);
System.out.println("enter number of children for "+rootData);
int children_num = s.nextInt();
while(children_num>0){
TreeNode<Integer> child = takeinputrecursive();
root.children.add(child);
children_num--;
}
return root;
}
public static void main(Str[] args) {
// TreeNode<Integer> rootinput = takeinput();
// print(rootinput);
TreeNode<Integer> rootrecursive = takeinputrecursive();
print(rootrecursive);
}
// that will be the input from user:
// enter next node data:
// 4
// enter the number of children for4
//3
// enter next node data:
// 2
// enter the number of children for2
//0
// enter next node data:
// 3
// enter the number of children for3
//1
// enter next node data:
// 6
// enter the number of children for6
//0
// enter next node data:
// 5
// enter the number of children for5
//0
// that is the output of user
// 4:2,3,5,
// 2:
// 3:6,
// 5:
// 6:
}
Here the implementation of code is simple or recursive.
0
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nisha Yadav directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nisha Yadav
Nisha Yadav
hey everyone, I am a student of Computer Science Engineering, I am an active learner & knowledge of programming, data structure, and algorithm. And presently I am learning web development(Html,css,javascript)