Advance Git & GitHub for DevOps Engineers.
 Shifa Syed
Shifa SyedTable of contents
- Git Branching:
- Git Revert and Reset
- Git Rebase and Merge
- What Is Git Rebase?
- What Is Git Merge?
- Add a text file called version01.txt inside the Devops/Git/ with “This is first feature of our application” written inside. This should be in a branch coming from master switch to dev branch ( Make sure your commit message will reflect as "Added new feature")
- Add new commit in dev branch after adding below mentioned content in Devops/Git/version01.txt: While writing the file make sure you write these lines
- Restore the file to a previous version where the content should be “This is the bug fix in the development branch”
- Demonstrate the concept of branches with 2 or more branches with a screenshot
- Add some changes to dev branch and merge that branch in master
- As a practice try git rebase too, and see what difference you get.

Git Branching:
Use a branch to isolate development work without affecting other branches in the repository. Each repository has one default branch, and can have multiple other branches. You can merge a branch into another branch using a pull request.
Branches allow you to develop features, fix bugs, or safely experiment with new ideas in a contained area of your repository.
Git Revert and Reset
Two commonly used tools that git users will encounter are git reset and git revert. The benefit of both of these commands is that you can use them to remove or edit changes you’ve made in the code in previous commits.
Git Rebase and Merge
What Is Git Rebase?
Git rebase is a command that lets users integrate changes from one branch to another, and the logs are modified once the action is complete. Git rebase was developed to overcome merging’s shortcomings, specifically regarding logs.
What Is Git Merge?
Git merge is a command that allows developers to merge Git branches while the logs of commits on branches remain intact.
The merge wording can be confusing because we have two methods of merging branches and one of those ways is actually called “merge,” even though both procedures do essentially the same thing.
Add a text file called version01.txt inside the Devops/Git/ with “This is first feature of our application” written inside. This should be in a branch coming from master switch to dev branch ( Make sure your commit message will reflect as "Added new feature")
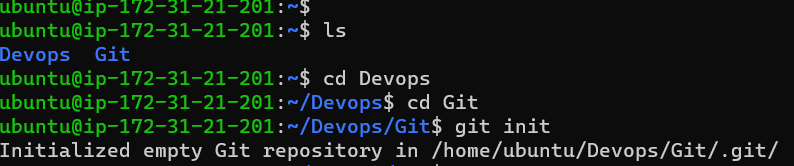
Open your terminal or command prompt and navigate to the desired directory where you want to create the repository.
Initialize a new Git repository
git initCreate a new file called
version01.txtwith the specified content:mkdir Devops mkdir Git cat>version01.txt

- Add the file to the staging area:
git add version01.txt
Create and switch to the
devbranch:git checkout -b dev

Commit the changes with the commit message "Added new feature":
git commit -m "Added new feature"
Push the
devbranch to the remote repository:before this, do remote login
git remote add origin <url>git push -u origin dev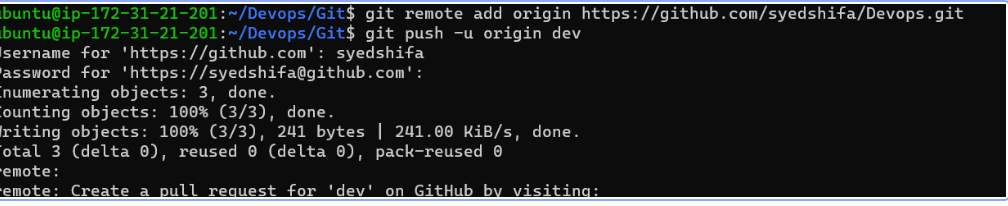

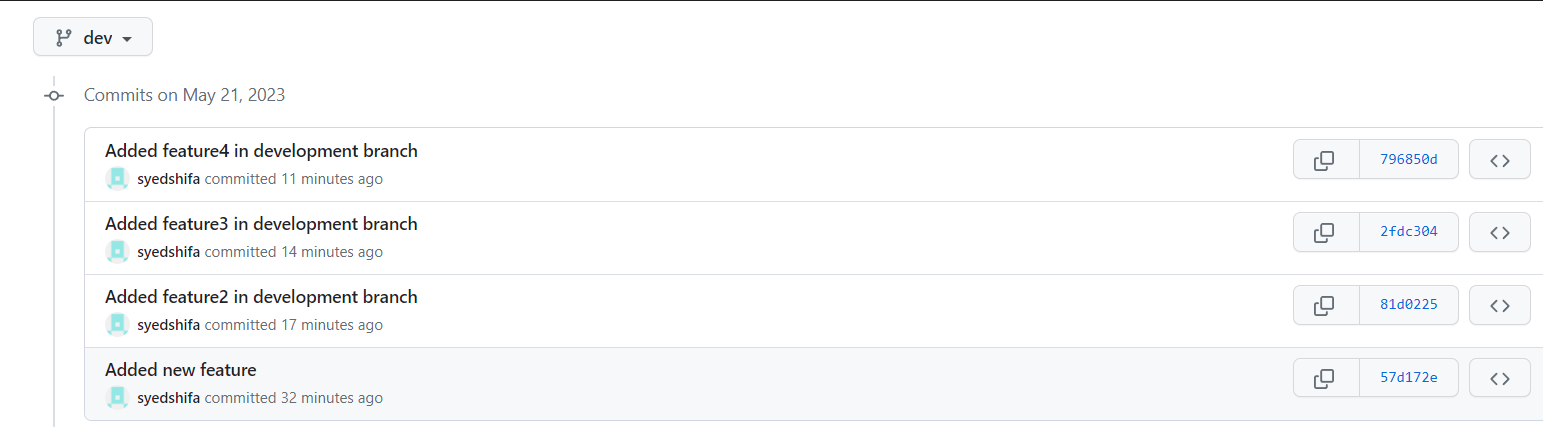
Add new commit in dev branch after adding below mentioned content in Devops/Git/version01.txt: While writing the file make sure you write these lines
1st line>> This is the bug fix in development branch
Commit this with message “ Added feature2 in development branch”
cat>>version01.txt
This is the bug fix in development branch
git add version01.txt
git commit -m "Added feature2 in development branch"
git push -u origin dev
2nd line>> This is gadbad code
Commit this with message “ Added feature3 in development branch
echo "This is gadbad code" >> version01.txt
git add version01.txt
git commit -m "Added feature3 in development branch"
3rd line>> This feature will gadbad everything from now.
Commit with message “ Added feature4 in development branch"
echo "This feature will gadbad everything from now." >> version01.txt
git add version01.txt
git commit -m "Added feature4 in development branch"
git push -u origin dev
Restore the file to a previous version where the content should be “This is the bug fix in the development branch”
restore the file to a previous version, you can use git revert command. Find the commit hash of the previous version (e.g., using git log, git log --oneline) and then run the following command:
git revert <commit_hash>
This will create a new commit that undoes the changes made in the specified commit.
Alternatively, if you want to completely reset the file to a previous version and discard the commits, you can use git reset command. Again, find the commit hash of the previous version and run the following command:
git reset <commit_hash> --hard
This will move the dev branch pointer to the specified commit, discarding any commits made after that point.
Please note that performing a reset or revert operation can be destructive, so make sure to double-check the commit hashes and the impact of these commands before executing them.
Demonstrate the concept of branches with 2 or more branches with a screenshot
In Git, branches are used to isolate work on different features, bug fixes, or tasks within a repository. They allow multiple parallel lines of development to coexist, making it easier to manage and organize changes. Each branch represents an independent line of development with its own set of commits.
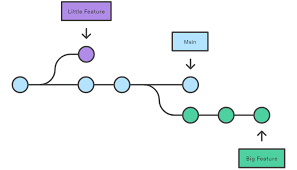
To demonstrate this concept, let's consider a scenario where we have a project with a master branch and two branches: main and dev.
Start with the
masterbranch:Initialize a new Git repository if you haven't already:
git init.Create and modify files according to your project requirements.
Commit the initial changes to the
masterbranch:git commit -m "Initial commit".
Create the
mainbranch:Create a new branch called
mainthat branches off frommaster:git checkout -b main.Make changes specific to
mainin your project files.Commit the changes to the
mainbranch:git commit -m "Added feature 1".
Create the
devbranch:Switch back to the
masterbranch:git checkout master.Create a new branch called
devthat branches off fromdev:git checkout -b feature2.Make changes specific to
devin your project files.Commit the changes to the
devbranch:git commit -m "Added feature 2".
At this point, you have three branches: master, main, and dev. Each branch represents a distinct line of development with its own set of commits. The master branch holds the initial version of your project, while main and dev branches contain changes specific to their respective features.
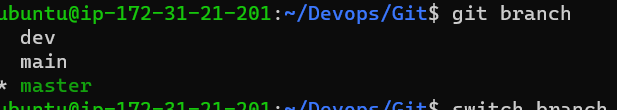
Add some changes to dev branch and merge that branch in master
- Ensure you are on the
devbranch:
git checkout dev
Make the desired changes to your project files.
Stage the changes:
git add .
- Commit the changes with an appropriate commit message:
git commit -m "Added changes to dev branch"
- Switch back to the
masterbranch:
git checkout master
- Merge the
devbranch intomaster:
git merge dev
Resolve any merge conflicts if they occur. Git will guide you through the process.
Commit the merge changes:
git commit -m "Merged dev branch into master"
- Push the changes to the remote repository:
git push origin master
By following these steps, you will have added changes to the dev branch and merged it into the master branch, ensuring that the changes made in the dev branch are now incorporated into the master branch.
Please note that it's important to handle merge conflicts, if any, during the merge process. Additionally, adjust the branch names (dev and master) according to your specific branch names.
As a practice try git rebase too, and see what difference you get.
git switch dev
vim version01.txt
git add .
git commit -m "trying git rebase"
git switch master
git rebase dev

\===========================================================
Devops#devops,#90daysofDevOps #Day10
https://www.linkedin.com/in/shifa-syed-49014b229/
Thank you for reading!! I hope you find this article helpful!!
if any queries or any corrections to be done to this blog please let me know.
Happy Learning!!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shifa Syed directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
