Exploring Multi-Way Search Trees: A Comprehensive Overview
 Rahul Bhatt
Rahul Bhatt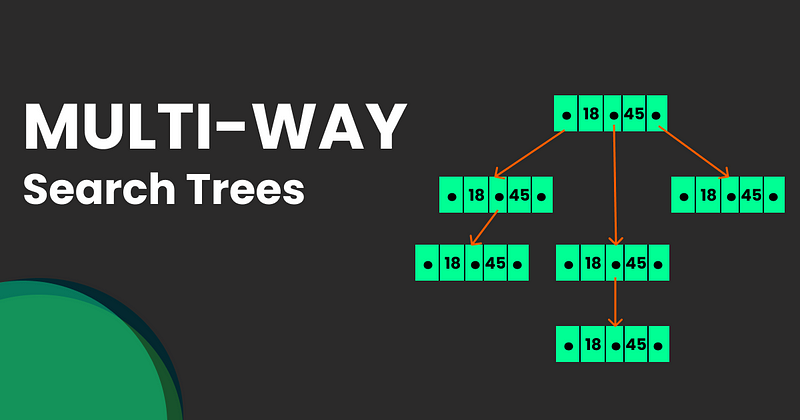
The data structure that is used in database
A M-way search tree has similar concept of that of binary tree and has M-1 values per nodes and M-sub trees. In this type of tree, M is called the degree of the tree.

Fig.1. Structure of M-Way Search Tree
In the above structure, P0, P1 …, Pn are the pointers to the node’s sub-trees and K0, k1, …, Kn-1 are the key values of the node. All the key values are stored in ascending order.
The basic properties of M-way search trees:
- Key vales in the sub tree pointed by P0 < key value K0. Similar pattern for the rest of the P’s and K’s.
- Key values in the sub-tree pointed by P1 > key value K0. Similar pattern for the rest of the P’s and K’s.
B-TREES
A B-Tree is a specialized M-way tree which is widely used for disk access. It is designed to store sorted data and allows operations like search, insertion and deletion. Along with the basic properties of M-way trees, B-Trees has several more properties:
- Every node in B-Tree has at most (maximum) m children.
- Every node in B-Tree except the root node and leaf nodes has at least m/2 children.
- The root node has at least two children if it is not a leaf node.
- All leaf nodes are at the same level.
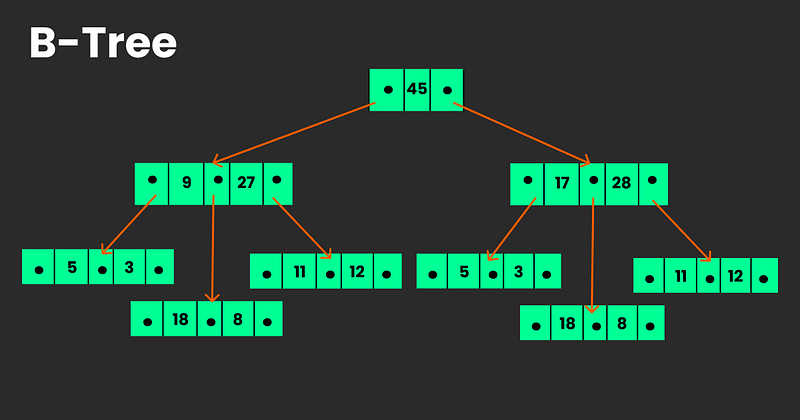
Fig.2. B Tree of order 4
Applications of B-Trees
B Trees are used for disk access because the indexing of the pointers help to access the data faster. Imagine it would require 1,000,000 comparisons if there would be a search for a single key on a set of one millions keys. Now with B-Tree indexing of order 10 would only require 114 comparisons in the worst case. Typically, we would use M-way search trees of 127–511 keys and 128–512 pointers. Thus, this way we can fetch large amount of data in one disk access.
B+ TREES
A B+ Tree is a better version of B Tree when it comes to efficient insertion, retrieval, and removal of records, each of which is identified by a key. A B+ Tree has following advantages to that of B Tree:
- Keys are used for indexing.
- It supports both sequential and random access to records.
- The height of the tree is balanced and less.
- The records can be fetched in equal number of disk accesses.
- Leaf nodes are linked to the nodes at the upper level.
B+ Tree properties compared to B Tree are as follows:
- B+ Trees stores redundant keys, while B Tree has search keys that do not repeat.
- In B+ Tree the data is stored only inside leaf nodes, while in B Tree data can be stored in internal as well as leaf nodes.
- In B+ Trees, searching operation is faster compared to B Tree because the data is only stored in leaf node.
- In B+ Tree, leaf node data are ordered using sequential linked lists, while in B Tree leaf nodes cannot be stored using linked lists.
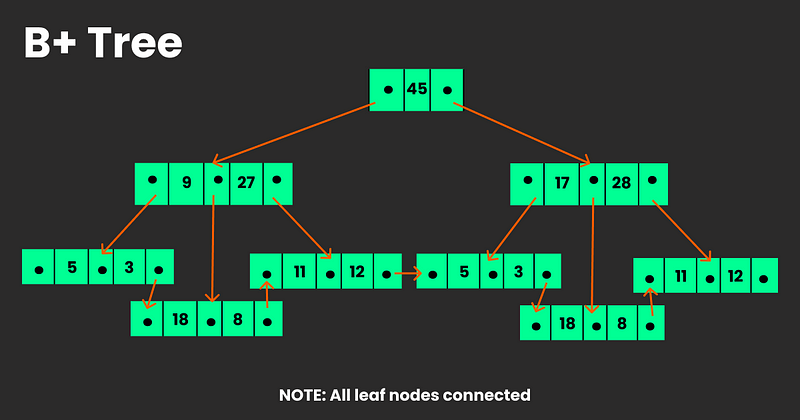
Fig.2. B+ Tree of order 3
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rahul Bhatt directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
