[CSS] Mastering Position Property
 Lim Woojae
Lim Woojae
Introduction
In this article, we will be discussing position property, which is one of the most important concepts you need to know.
The position property specifies the method used for arranging the HTML elements.
There are five methods:
static
relative
absolute
fixed
sticky
We will only be discussing the first FOUR(4) of them. If you want to find out more about position: sticky, you can have a look at this article:
position: static
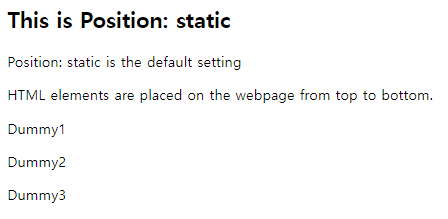
By default, all your HTML element has position: static if you do not set specific method, such as relative, absolute, fixed and sticky. This means that your element is rendered on the website as you intended. The order/sequence will be from top to bottom.
HTML code:
<h2>This is Position: static</h2>
<p>Position: static is the default setting</p>
<p>HTML elements are placed on the webpage from top to bottom.</p>
<p>Dummy1</p>
<p>Dummy2</p>
<p>Dummy3</p>
CSS code:
* {
position: static;
}
position: relative
position: relative is a bit different. It allows you to set where the elements are to be placed. If you want to move it a little bit left, you can do that.
The element is positioned relative to its original position, so if you set left: 20px, the element moves 20px to the right. If you want it to move to the left, you can do left: -20px. But you would mostly just do right: 20px instead of left: -20px.
My tip is just to think that the element moves from the direction you have set. If it is left: 20px, it is moving 20px from the left.
HTML code:
<h2>position: relative</h2>
<div class="relative">The element has moved 20px from the left and 80px from the right "relative" to its original position.</div>
CSS code:
.relative {
position: relative;
border: 1px solid red;
left: 20px;
top: 80px;
}

position: absolute
position: absolute might be the most confusing one because people think that it is related to the word "absolute". However, the element with position: absolute is positioned relative to its first position: relative parent. Therefore, it is similar to the position: relative, but the original position is the parent element.
HTML code:
<div class="relative"> <!-- parent of absolute -->
position: relative
<div class="static">
position: static
<div class="absolute">position: absolute</div>
</div>
</div>
CSS code:
.relative {
position: relative;
border: 3px solid green;
width: 400px;
height: 130px;
left: 50px;
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
border: 3px solid red;
top: 80px;
right: 10px;
width: 240px;
}
.static {
width: 350px;
border: 3px solid blue;
}

For the position: relative, it moved 50px from the left, relative to the the
<body>tag.For the position: absolute, it moved 60px from the left, but relative to the parent element.
position: fixed
In position: fixed, the HTML element stays stationary for all time. So, it is usually used for a navigation bar like this:
HTML code:
<h2 class="fixed">position: fixed</h2>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
<p>Dummy</p>
CSS code:
.fixed {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
border: 3px solid green;
}

If you try this out, the green box is stationary, which means it does not move. I have added some dummy texts using <p> tag to scroll down and see if it does not move.
Again, if you want to learn about the position: sticky (which is very interesting), check out this article:
Reference
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Lim Woojae directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Lim Woojae
Lim Woojae
Computer Science Enthusiast with a Drive for Excellence | Data Science | Web Development | Passionate About Tech & Innovation