Exploring the World of Decentralized Finance: Part 1
 Kairav Thakkar
Kairav Thakkar
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving financial landscape, a new paradigm has emerged that promises to revolutionize the way we transact, invest, and access financial services. Welcome to the world of Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, where traditional intermediaries are replaced by smart contracts and blockchain technology to create a transparent, inclusive, and decentralized financial ecosystem. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of DeFi, exploring its significance, core features, challenges, and its potential to reshape the financial landscape as we know it.
Understanding the Basics of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
What is DeFi ?

DeFi refers to a new wave of financial applications and protocols built on decentralized blockchain networks, such as Ethereum. Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on centralized intermediaries like banks and exchanges, DeFi operates in a trustless and permissionless manner. This means that anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet can participate in the DeFi ecosystem without the need for intermediaries or the traditional financial infrastructure.
The significance of DeFi lies in its potential to democratize finance and provide financial services to the unbanked and underbanked populations around the world. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi offers transparency, security, and accessibility, empowering individuals to take control of their financial lives.
The principles behind DeFi
DeFi is built upon three key principles: decentralization, transparency, and financial inclusivity.
Decentralization:
Decentralization is at the core of DeFi. Unlike centralized systems where a single entity has control over financial transactions and data, DeFi protocols operate on a decentralized network of computers, ensuring that no single point of failure exists. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of censorship, manipulation, and systemic failures.
Transparency:
Transparency is another fundamental aspect of DeFi. All transactions and operations within the DeFi ecosystem are recorded on the blockchain, making them publicly visible and auditable. This level of transparency enhances accountability, minimizes fraud, and builds trust among participants.
Financial Inclusivity:
One of the most powerful aspects of DeFi is its ability to promote financial inclusivity. By removing barriers to entry and enabling anyone with an internet connection to access financial services, DeFi has the potential to empower billions of people who are currently underserved by the traditional financial system. Whether it's access to savings accounts, loans, or investment opportunities, DeFi opens up a world of possibilities for those who have been excluded from the traditional banking system.
The Rise of DeFi
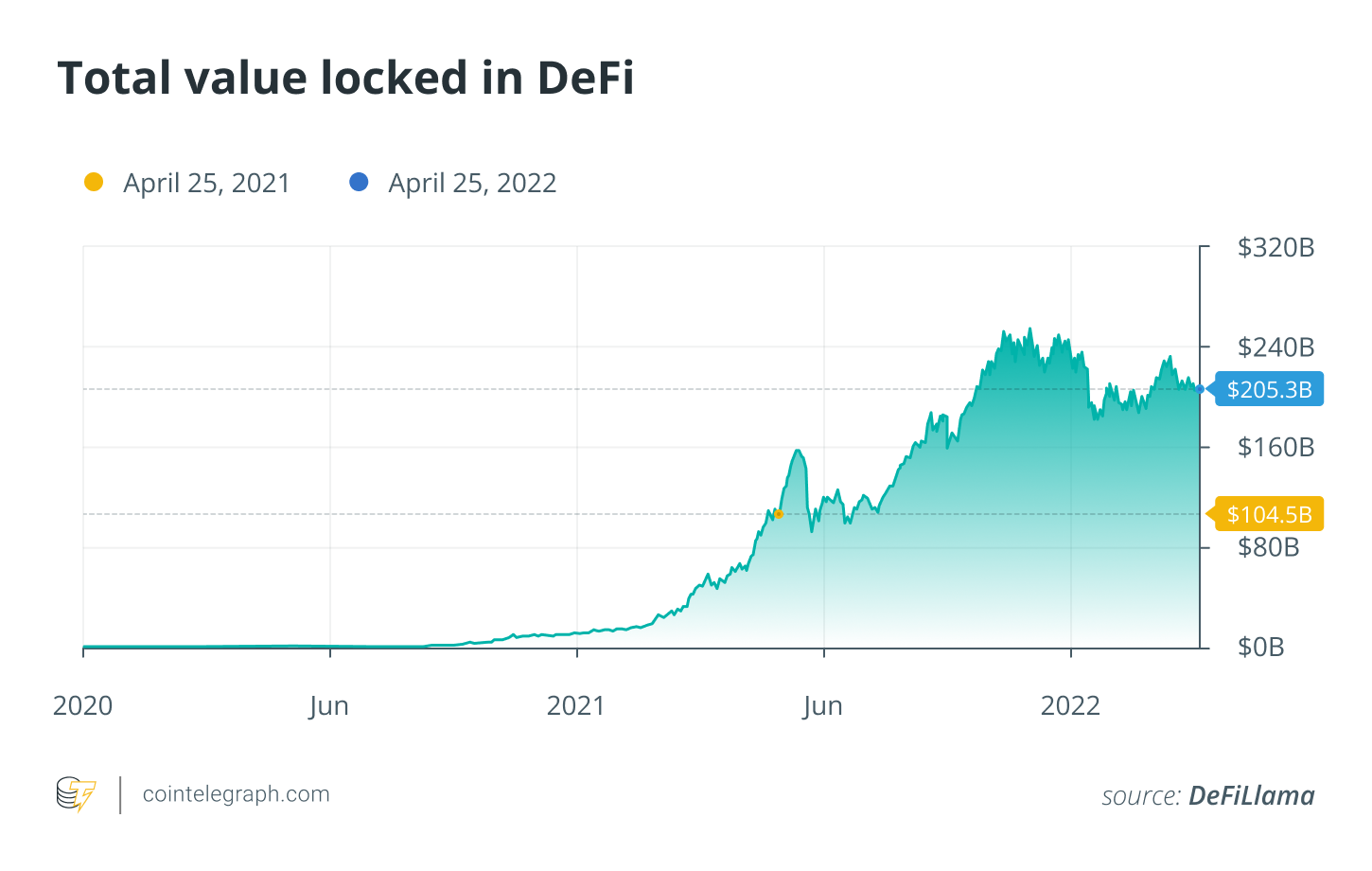
Exploring the exponential growth of the DeFi ecosystem.
Over the past few years, the DeFi ecosystem has experienced remarkable growth, with an explosion of new projects, protocols, and innovations. According to industry reports, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi protocols has surpassed billions of dollars, reflecting the increasing adoption and interest in decentralized finance.
The growth of DeFi can be attributed to several factors, including the rising demand for alternative financial services, the potential for higher yields compared to traditional investments, and the increasing recognition of the benefits offered by blockchain technology.
Factors contributing to the surge in popularity
Several key factors have contributed to the surge in popularity of DeFi:
Liquidity and Yield Opportunities: DeFi protocols offer attractive yields and liquidity incentives for users who provide their assets as collateral or liquidity to the ecosystem. This has attracted investors and traders seeking higher returns compared to traditional financial products.
Open and Permissionless Innovation: DeFi allows anyone to build and deploy financial applications without requiring permission from centralized authorities. This permissionless nature has fostered a culture of innovation and experimentation, leading to a wide range of novel DeFi protocols and products.
Global Accessibility: DeFi eliminates geographic barriers and enables individuals from around the world to access financial services. This has been particularly impactful for the unbanked and underbanked populations who were previously excluded from traditional financial systems.
Interoperability: DeFi protocols can interact and integrate with each other, allowing for composability and the creation of complex financial products. This interoperability has fueled the growth of the DeFi ecosystem by facilitating collaboration and expanding the range of available services.
Key Components of DeFi
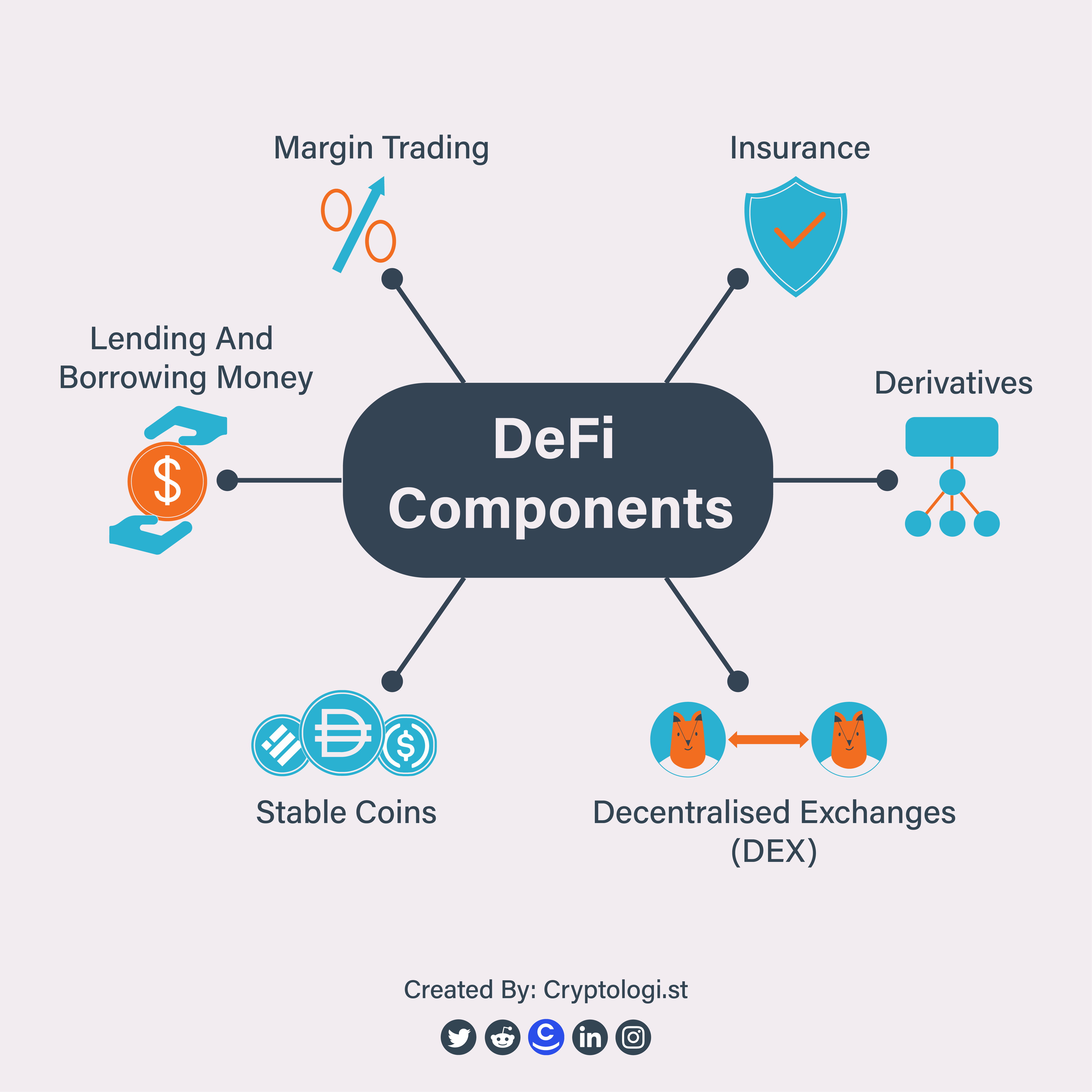
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized Exchanges, or DEXs, have gained significant traction within the DeFi ecosystem as alternatives to centralized exchanges. DEXs enable users to trade digital assets directly from their wallets without relying on intermediaries. Here's how DEXs work:
Peer-to-Peer Trading: DEXs facilitate peer-to-peer trading by connecting buyers and sellers directly. Users retain control over their funds throughout the trading process, eliminating the need for a centralized custodian.
Smart Contract Integration: DEXs rely on smart contracts to automate trade execution and settlement. These smart contracts act as self-executing agreements, ensuring that trades occur only when predefined conditions are met.
Liquidity Providers: DEXs utilize liquidity pools provided by users who deposit their assets into the pool. These liquidity providers earn a share of the trading fees generated by the DEX, incentivizing liquidity provision.
Elimination of Central Order Books: Unlike traditional exchanges that rely on central order books, DEXs use automated market-making algorithms to match buy and sell orders. This enables seamless trading without the need for a centralized authority to manage the order book.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
DeFi lending and borrowing platforms provide decentralized solutions for users to lend and borrow digital assets. These platforms leverage smart contracts to automate loan agreements, interest rates, and collateralization. By removing the need for traditional banks or lending institutions, DeFi lending platforms offer more accessible and flexible borrowing options. Examples of prominent DeFi lending platforms include Hashstack, Compound, Aave, and MakerDAO.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins play a vital role in DeFi by offering digital assets with a stable value, typically pegged to a fiat currency like the US Dollar. Stablecoins provide stability within the volatile cryptocurrency market and enable users to mitigate price fluctuations when interacting with DeFi protocols. Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Dai are popular examples of stablecoins used in the DeFi ecosystem.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Yield farming and liquidity mining are mechanisms through which users can earn passive income by providing liquidity to DeFi protocols. Users can lock their digital assets in liquidity pools and receive rewards in the form of additional tokens or fees generated by the protocol. Yield farming and liquidity mining incentivize users to contribute liquidity and participate in decentralized governance, fostering community involvement and growth within DeFi projects.
Decentralized Insurance
Decentralized insurance protocols within the DeFi space aim to provide coverage against smart contract failures, hacks, or other risks. These protocols allow users to purchase insurance policies and protect their assets within the decentralized ecosystem. DeFi insurance platforms bring transparency and trust to the insurance industry by leveraging blockchain technology for policy creation, premium payments, and claims management. Examples of DeFi insurance platforms include Nexus Mutual and Cover Protocol.
Decentralized Asset Management
Decentralized asset management platforms enable users to manage their digital assets and portfolios autonomously. These platforms often utilize algorithmic trading strategies and automated portfolio rebalancing to optimize returns for users. DeFi asset management protocols offer users greater control, transparency, and lower costs compared to traditional asset management services. Examples of decentralized asset management platforms include Yearn.finance and Balancer.
The key components of DeFi work in synergy to create a financial ecosystem that empowers individuals with greater control over their assets, access to financial services, and opportunities for financial growth. By eliminating intermediaries, promoting transparency, and leveraging decentralized technologies, DeFi is redefining the way we think about and interact with finance.
Core Features and Benefits of DeFi
Eliminating intermediaries
One of the key features of DeFi is its ability to eliminate intermediaries that traditionally play a role in financial transactions. Instead, DeFi relies on smart contracts and decentralized protocols to automate and execute transactions. This brings several benefits:
Reduced Costs: By removing intermediaries, DeFi eliminates the fees and costs associated with traditional financial services. Users can transact directly with one another, resulting in lower transaction fees and increased cost-efficiency.
Faster Transactions: DeFi transactions are executed instantly and do not require manual processing or approval from intermediaries. This enables faster settlement times and reduces the friction associated with traditional financial systems.
Increased Security: DeFi protocols leverage blockchain technology, which offers enhanced security and immutability. Smart contracts ensure that transactions are executed as programmed, reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Enhanced Privacy: DeFi transactions can provide a higher level of privacy compared to traditional financial systems. While transactions are visible on the blockchain, users' identities can be kept anonymous, protecting their financial privacy.
Transparency and security
Blockchain technology is a foundational pillar of DeFi, providing transparency, immutability, and enhanced security. Here's how blockchain contributes to the core features of DeFi:
Transparency: All transactions recorded on the blockchain are visible to the public, creating a transparent ecosystem where every transaction can be audited and verified. This transparency reduces the potential for fraud and fosters trust among participants.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes immutable and cannot be altered or tampered with. This ensures the integrity of financial transactions and prevents unauthorized changes.
Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology employs cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions and user assets. Decentralized consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, provide additional layers of security by preventing malicious actors from gaining control over the network.
Smart Contract Auditing: Smart contracts, the backbone of DeFi, can be audited and verified by security experts to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that they operate as intended. This helps mitigate the risk of smart contract exploits and enhances the overall security of DeFi protocols.
Financial inclusivity
One of the most transformative aspects of DeFi is its potential to promote financial inclusivity by providing access to financial services for the unbanked and underbanked populations worldwide. Here's how DeFi enables financial inclusivity:
No Geographic Restrictions: DeFi protocols are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, eliminating the need for physical infrastructure and geographical limitations. This allows individuals in underserved regions to participate in the global financial ecosystem.
Lower Entry Barriers: Traditional financial systems often require individuals to meet certain criteria or provide extensive documentation to access services. DeFi removes many of these barriers, enabling individuals to participate with minimal requirements, such as a digital wallet and an internet connection.
Microfinance Opportunities: DeFi protocols allow for microtransactions, enabling individuals to access small loans or investment opportunities that were previously unattainable. This empowers individuals to improve their financial situations and build economic resilience.
Decentralized Identity Solutions: DeFi has the potential to leverage decentralized identity solutions, where individuals maintain control over their personal data. This allows individuals to prove their identity and access financial services without relying on traditional identity verification processes.
Challenges and limitations in the Defi Space

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has gained significant traction in recent years, offering promising solutions to many of the challenges faced by traditional financial systems. However, the DeFi space is not without its own set of challenges. Here are some of the key obstacles faced by the DeFi industry:
Security vulnerabilities: DeFi platforms often rely on smart contracts, which are code-based agreements that execute transactions automatically. While smart contracts provide efficiency and transparency, they are susceptible to bugs and vulnerabilities. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to significant financial losses for users. The decentralized nature of DeFi also means that there is no central authority to oversee and mitigate these risks, making security a critical challenge.
Regulatory uncertainty: DeFi operates on a global scale, which brings challenges related to regulatory compliance. Different jurisdictions have varying regulations and policies regarding cryptocurrencies, tokens, and financial services. The lack of clear guidelines and regulatory frameworks creates uncertainty for DeFi projects and inhibits their ability to scale and attract institutional investors.
Scalability and speed: The scalability of DeFi protocols is a significant challenge. As more users engage with DeFi platforms, network congestion and high transaction fees become common issues. The limited throughput of blockchain networks like Ethereum, which is widely used in the DeFi ecosystem, poses scalability challenges. Improving the scalability and transaction speed without compromising security is a crucial hurdle for DeFi to overcome.
User experience and accessibility: DeFi applications often require users to interact with complex interfaces, manage private keys, and understand various protocols. This can be intimidating and confusing for non-technical users, hindering the mass adoption of DeFi. Improving user experience, making the applications more intuitive, and enhancing accessibility are vital for DeFi to attract a broader user base.
Price volatility and market manipulation: Cryptocurrencies, which are integral to DeFi platforms, are known for their price volatility. This volatility poses risks for users who rely on stablecoins or participate in lending and borrowing activities. Additionally, the lack of regulatory oversight and the presence of decentralized exchanges can create opportunities for market manipulation, further exacerbating price volatility concerns.
Liquidity fragmentation: DeFi protocols operate on decentralized exchanges (DEXs), which often suffer from fragmented liquidity. This means that there may be insufficient liquidity for certain tokens or trading pairs, leading to slippage and suboptimal trading experiences. Solving the liquidity fragmentation challenge is crucial for DeFi to provide robust and efficient trading environments.
Integration with traditional finance: While DeFi aims to disrupt and replace traditional financial systems, integrating with legacy systems poses challenges. Bridging the gap between DeFi and traditional finance requires seamless interoperability, regulatory compliance, and trust-building measures. Overcoming this challenge is essential to unlock the full potential of DeFi and enable smooth transitions from traditional financial systems.
Despite these challenges, the DeFi space continues to innovate and evolve rapidly. Developers, researchers, and industry participants are actively working on solutions to address these obstacles and propel the growth and adoption of DeFi. As the industry matures and technologies advance, it is expected that many of these challenges will be mitigated, paving the way for a more robust and accessible decentralized financial ecosystem.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the decentralized finance (DeFi) space holds immense potential to revolutionize the financial industry by offering transparent, efficient, and inclusive solutions. However, it faces several challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption and long-term success.
Security vulnerabilities in smart contracts, regulatory uncertainties, scalability limitations, user experience issues, price volatility, liquidity fragmentation, and integration with traditional finance are among the key obstacles that the DeFi industry must overcome.
Fortunately, the DeFi ecosystem is dynamic and resilient, with passionate developers and stakeholders continuously striving to tackle these challenges head-on. Efforts are being made to enhance security measures, establish regulatory frameworks, improve scalability solutions, enhance user interfaces, mitigate price volatility risks, address liquidity fragmentation, and foster interoperability with traditional finance.
As technology advances and industry knowledge expands, the DeFi space is likely to evolve and mature, paving the way for a more robust and accessible financial ecosystem. Collaboration between industry participants, regulators, and innovators will play a crucial role in creating a sustainable and trustworthy DeFi landscape.
While the challenges are real, the potential benefits of DeFi cannot be ignored. Empowering individuals with greater financial control, expanding access to financial services for the unbanked, and driving financial innovation are among the promises that DeFi holds.
With continued innovation, research, and collaborative efforts, the DeFi space has the potential to reshape the global financial landscape, offering greater financial inclusion, efficiency, and transparency for all.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Kairav Thakkar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Kairav Thakkar
Kairav Thakkar
Currently working as an AI prompt engineer, I possess skills in blockchain engineering, data analysis, generative AI research, and :) you guessed it- prompt engineering. I am passionate about blockchain data analysis and business applications of prompt engineering.