Shardeum’s Innovative Approach to Achieve Atomic and Cross Shard Composability
 Shreya Bhardwaj
Shreya Bhardwaj
Title: Shardeum’s Innovative Approach to Achieve Atomic and Cross-Shard Composability
Introduction:
In the fast-evolving world of blockchain technology, scalability has always been a significant challenge. As the number of transactions on a blockchain network increases, the need for efficient processing becomes crucial. Shard-based architectures have emerged as a potential solution, aiming to enhance scalability by dividing the blockchain into smaller units called shards. One of the most promising advancements in this field is Shardeum's innovative approach to achieving atomic and cross-shard composability. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of atomic and cross-shard composability, delve into Shardeum's unique solution, and discuss its potential impact on the blockchain ecosystem.
Understanding Scalability Challenges in Blockchain:
Scalability has emerged as a significant challenge for blockchain technology, impeding its widespread adoption. As the number of users and transactions on a blockchain network grows, the system's capacity to handle increased workload becomes strained. This congestion leads to delays in transaction confirmation and higher transaction fees, limiting the network's efficiency and usability.
The inherent design of traditional blockchain architectures, such as Bitcoin, where each transaction is processed sequentially and added to a linear chain, poses limitations on scalability. With this approach, the network's capacity to process a large volume of transactions concurrently is limited.
To overcome these scalability challenges, various scaling solutions have been proposed and implemented. Off-chain solutions, such as payment channels and sidechains, aim to execute transactions outside the main blockchain, reducing the burden on the main network. These solutions allow for faster and more cost-effective transactions, as they occur off the main chain and are only settled periodically on the blockchain.
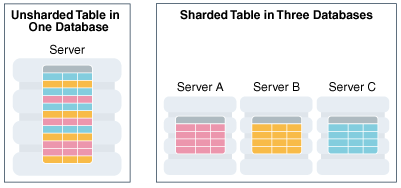
Another approach to scalability is the introduction of sharding, which involves dividing the blockchain into smaller units called shards. Each shard is responsible for processing a subset of transactions, enabling parallel processing and significantly increasing the network's capacity. Sharding improves scalability by distributing the workload across multiple shards, allowing for higher transaction throughput.
Layer 2 scaling solutions, such as state channels and Plasma, provide additional scalability by enabling the execution of smart contracts off-chain while ensuring the final settlement on the main blockchain. These solutions minimize the burden on the main blockchain, reducing congestion and improving scalability.
Furthermore, advancements in consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA), offer scalability benefits by reducing the computational requirements for validating transactions. These mechanisms allow for faster block confirmation times and increased transaction throughput compared to the energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) consensus used in early blockchain implementations.
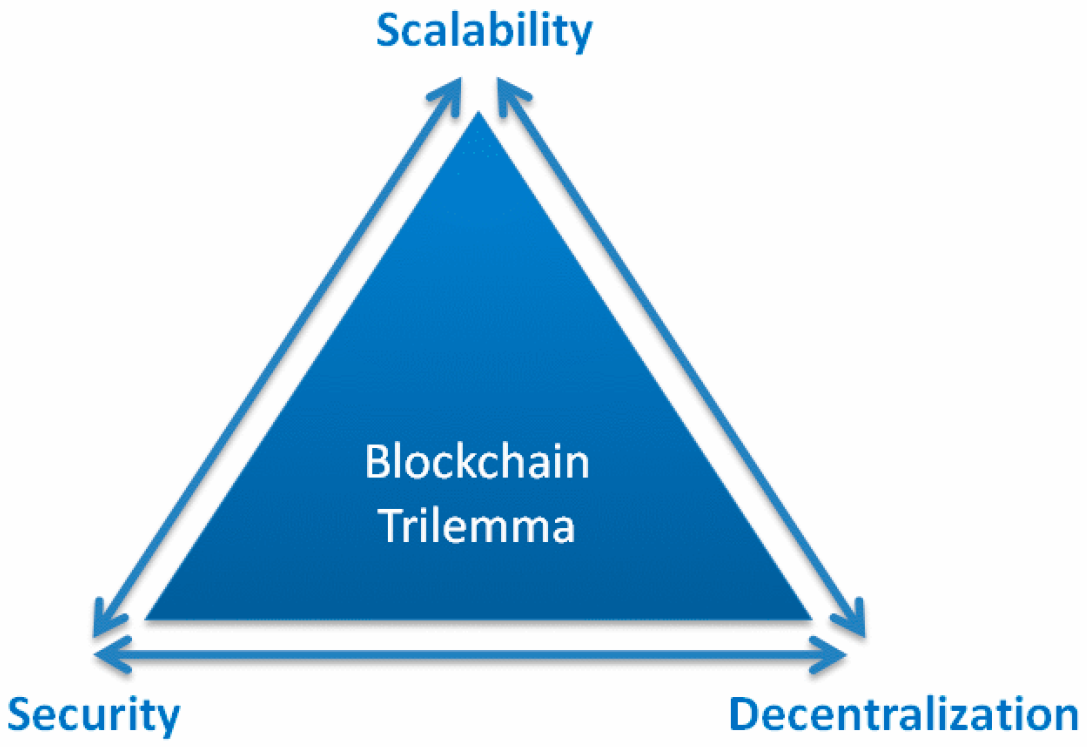
In summary, scalability challenges in blockchain arise due to the sequential processing of transactions, leading to congestion, delays, and higher fees. Scaling solutions, including off-chain mechanisms, sharding, Layer 2 solutions, and innovative consensus mechanisms, aim to address these challenges and unlock the full potential of blockchain technology.
Introduction to Shard-based Architectures:
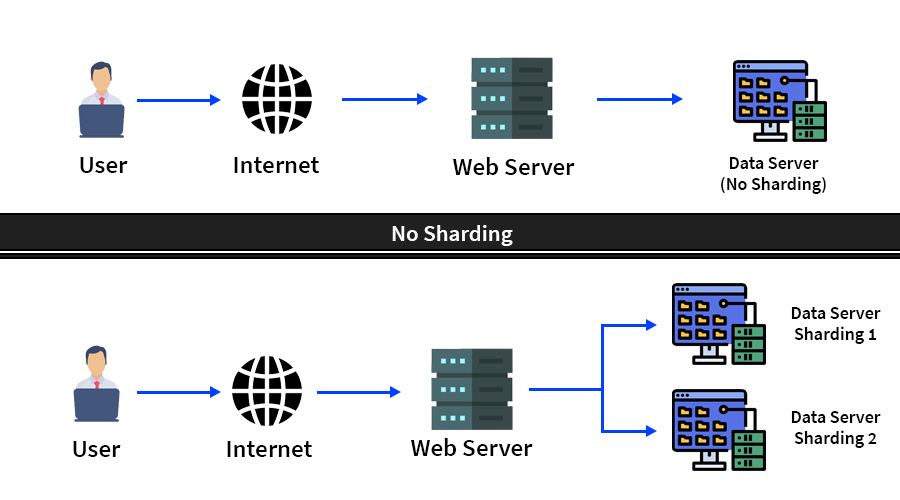
Shard-based architectures offer a solution to the scalability limitations of blockchain networks by dividing the blockchain into smaller units called shards. Each shard processes a subset of transactions, enabling parallel transaction processing and improved scalability.
However, achieving atomic and cross-shard composability within this framework poses challenges. Atomic composability ensures that transactions within a shard are either fully executed or completely rolled back, maintaining consistency. Cross-shard composability allows operations spanning multiple shards, enabling seamless value transfer and complex transactions.
Coordinating transactions across shards while preserving atomicity requires innovative approaches and careful design considerations. Inter-shard communication protocols must facilitate consistent and atomic state updates. Overcoming these challenges involves developing novel consensus mechanisms and smart contract frameworks.
By addressing these hurdles, shard-based architectures enhance scalability while maintaining the reliability and integrity of blockchain networks. Platforms like Shardeum provide solutions to enable atomic and cross-shard composability, unlocking the full potential of blockchain scalability.
The Concept of Atomic Composability:

4.1 Atomicity and Its Significance:
Atomicity is a fundamental property of transactions in a blockchain network. It refers to the indivisible nature of a transaction, where either all the operations within the transaction succeed, or none of them do. This all-or-nothing characteristic ensures consistency and integrity in the blockchain system.
The significance of atomicity lies in its ability to maintain the reliability and security of blockchain networks. If a transaction is not atomic and can be partially executed or reversed, it can lead to inconsistent states and compromise the integrity of the system. Atomicity guarantees that the effects of a transaction are applied as a whole, preventing incomplete or inconsistent updates to the blockchain.
In a blockchain ecosystem, where trust and immutability are paramount, atomicity ensures that the state of the blockchain accurately reflects the intended changes made by transactions. It provides a level of assurance that transactions are executed reliably and consistently, establishing the foundation for reliable and secure blockchain applications.
4.2 Challenges in Achieving Atomic Composability:
Implementing atomic composability in a shard-based architecture is challenging due to the decentralized nature of blockchains. Coordinating transactions across multiple shards while preserving atomicity requires innovative approaches and careful design considerations.
One of the challenges is ensuring transaction isolation. In a shard-based architecture, each shard operates independently and processes a subset of the overall transactions. Ensuring transaction isolation and preventing interference between different transactions executing concurrently on different shards is crucial for maintaining atomicity. Mechanisms such as locking or optimistic concurrency control may be employed to achieve transaction isolation.
Another challenge is cross-shard validation. When transactions span multiple shards, validating the consistency and integrity of the entire transaction becomes a challenge. Ensuring that all the shards involved in a transaction reach a consistent state and that the transaction satisfies the necessary conditions before being committed is essential for preserving atomicity. Coordinating the validation process across shards without introducing centralized points of failure requires innovative consensus mechanisms and inter-shard communication protocols.
Rollback and recovery mechanisms also play a vital role in achieving atomic composability. In case of a failure or error during the execution of a transaction, ensuring the ability to roll back and recover the system to a consistent state is crucial. Atomic composability requires mechanisms for aborting or rolling back the entire transaction and reverting any changes made across shards if necessary.
Scalability and performance considerations also arise when aiming for atomic composability. As the number of shards and transactions increase, achieving atomic composability at scale introduces additional challenges. Efficiently coordinating and validating transactions across shards without sacrificing speed and throughput is a critical consideration in achieving atomic composability.
Addressing these challenges involves the development of innovative protocols, consensus mechanisms, and smart contract frameworks specifically designed to support atomic composability within a shard-based architecture. Solutions like Shardeum tackle these challenges by introducing novel approaches to transaction coordination, validation, and rollback mechanisms, ensuring atomicity across shards and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain network. By overcoming these challenges, atomic composability enables the reliable and secure execution of complex operations across shards, enhancing the overall functionality and potential of blockchain systems.
The Concept of Cross Shard Composability:
5.1 The Need for Cross-Shard Composability:
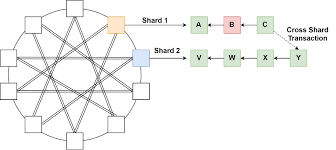
Cross-shard composability is essential to fully leverage the benefits of sharding in a blockchain network. Sharding divides the blockchain into smaller units or shards, allowing for parallel transaction processing and improved scalability. However, without cross-shard composability, transactions are limited to individual shards, hindering the seamless flow of value and reducing the overall scalability potential of the network.
In a decentralized ecosystem, users and applications often require interactions that span multiple shards. For example, a decentralized exchange may need to execute a trade involving assets from different shards, or a decentralized application may need to access and update data distributed across multiple shards. Cross-shard composability enables these types of operations, facilitating the efficient exchange of assets, data, and value across shards and enhancing the versatility and usability of the blockchain network.
5.2 Challenges in Achieving Cross-Shard Composability:
Enabling cross-shard composability presents several challenges due to the decentralized nature of blockchain networks and the need to coordinate transactions across different shards. Some of the key challenges include:
a) Coordinated Transaction Execution: To achieve cross-shard composability, transactions involving multiple shards must be executed in a coordinated and synchronized manner. This requires establishing mechanisms for inter-shard communication and coordination, ensuring that all relevant shards involved in a transaction reach a consistent and agreed-upon state.
b) Consistent State Updates: As transactions interact with different shards, ensuring consistent state updates across shards becomes crucial. All affected shards must accurately reflect the changes resulting from a transaction to maintain data integrity and prevent inconsistencies.
c) Conflict Resolution: Conflicts can arise when multiple transactions attempt to modify the same data or assets across different shards simultaneously. Resolving conflicts fairly and securely is essential to maintain the integrity of the blockchain network. Conflict resolution mechanisms need to be designed and implemented to ensure consistent and reliable outcomes.
d) Scalability Considerations: Implementing cross-shard composability at scale introduces additional scalability challenges. As the number of shards and the volume of transactions increase, the network must efficiently handle the coordination, synchronization, and validation of transactions across shards without compromising performance.
6.1 Sharding for Scalability:
Shardeum tackles scalability challenges by adopting a shard-based architecture. This approach involves dividing the blockchain into multiple shards, each capable of independent transaction processing. By distributing the workload across shards, Shardeum significantly improves the network's throughput and overall performance. With sharding, the blockchain can handle a higher volume of transactions in parallel, enhancing scalability and accommodating the growing demands of decentralized applications.
6.2 Achieving Atomic Composability:
Shardeum implements a unique consensus mechanism and smart contract framework to ensure atomic composability within individual shards. Atomicity is a crucial property that guarantees transactions within a shard either succeed entirely or fail. Shardeum's consensus mechanism validates and confirms the atomicity of transactions, ensuring that the blockchain state remains consistent and reliable. By achieving atomic composability, Shardeum enhances the reliability and integrity of the blockchain network, mitigating the risks of incomplete or inconsistent transaction execution.
6.3 Enabling Cross Shard Composability:
To enable cross-shard composability, Shardeum introduces a sophisticated inter-shard communication protocol. This protocol establishes a seamless and secure channel for transactions to be coordinated across different shards. By facilitating communication and data exchange between shards, Shardeum enables the transfer of assets and the execution of complex operations that span multiple shards. This capability opens up new possibilities for decentralized applications, allowing them to leverage the combined power of multiple shards and enabling efficient collaboration between different parts of the blockchain network.
The inter-shard communication protocol ensures that transactions involving multiple shards are validated and executed in a coordinated and synchronized manner. It addresses challenges such as transaction isolation, cross-shard validation, and conflict resolution, ensuring consistent state updates and maintaining the atomicity of operations across shards. Through cross-shard composability, Shardeum enhances the versatility and functionality of blockchain networks, enabling efficient value transfer, decentralized financial activities, and other use cases that require interactions between different shards.
By combining sharding for scalability, atomic composability within shards, and enabling cross-shard composability, Shardeum's innovative approach paves the way for a highly scalable and efficient blockchain ecosystem. It addresses the limitations of traditional blockchain architectures and opens up new possibilities for decentralized applications, driving the adoption and advancement of blockchain technology across industries.
Potential Impact on the Blockchain Ecosystem:
Shardeum's approach to achieving atomic and cross-shard composability has the potential to revolutionize the blockchain ecosystem. Here are some key impacts of their solution:
Enhanced Scalability: Shardeum's shard-based architecture improves scalability by distributing transaction processing across multiple shards, leading to higher throughput and improved network performance.
Seamless Value Transfer: Cross-shard composability enables the smooth transfer of value and assets across different shards, allowing for efficient token swaps and decentralized financial activities.
Complex Operations Across Shards: Shardeum enables complex operations that involve multiple shards, empowering decentralized applications to leverage the power of multiple shards simultaneously.
Interoperability and Collaboration: Shardeum's solution promotes interoperability between different blockchain networks, facilitating secure and trustworthy assets and data exchange.
Industry Adoption and Advancement: Shardeum's innovation drives blockchain adoption across industries, providing enhanced scalability, faster transactions, and increased composability for real-world use cases.
Conclusion
Shardeum's innovative approach to achieving atomic and cross-shard composability represents a significant advancement in the field of blockchain scalability. By combining sharding, atomic composability, and cross-shard communication, Shardeum offers a powerful solution that enhances transaction throughput, ensures data integrity, and enables complex operations across shards. With the potential to transform the blockchain ecosystem, Shardeum brings us closer to a decentralized future where scalability is no longer a bottleneck.
To learn more about Shardeum's groundbreaking approach, visit their official website: Shardeum.org. Additionally, for a more in-depth understanding of atomic and cross-shard composability, refer to their detailed blog post on the topic: Shardeum - Atomic and Cross-Shard Composability. Stay updated with Shardeum's latest developments and join the conversation by following them on social media platforms like Twitter, Telegram, and Discord. Also, do follow the amazing founders of Shardeum Nischal Shetty and Omar Syed , also don't forget to follow the content writer and committer at Shardeum who is also a moderator of the "Shardeum is Borderless v2 Program" Subbu.
Embrace the exciting possibilities of Shardeum's innovative solution and witness the future of blockchain scalability unfold before your eyes.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shreya Bhardwaj directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Shreya Bhardwaj
Shreya Bhardwaj
I am a senior year, CS engineering student, who's determined to learn and deep dive in the world of latest tech.