Mastering the basics: The Data Science Hierarchy of Needs
 Warui Wanjiru
Warui Wanjiru
Welcome back to our data engineering series! In our previous blogs, we explored the fascinating world of data engineering and its crucial role in shaping data-driven organizations. Today, we embark on a thrilling journey to unravel the secrets of the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs, inspired by Abraham Maslow's renowned theory on human motivation.
Maslow's theory, introduced in his 1943 paper titled "A Theory of Human Motivation," proposed a hierarchy of needs in which humans must satisfy foundational needs before progressing to higher levels of development. While Maslow's theory primarily focuses on human psychology, its structure can be adapted to various contexts. In the realm of data science, the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs serves as a framework that outlines the essential stages organizations must traverse to fully leverage the power of data.
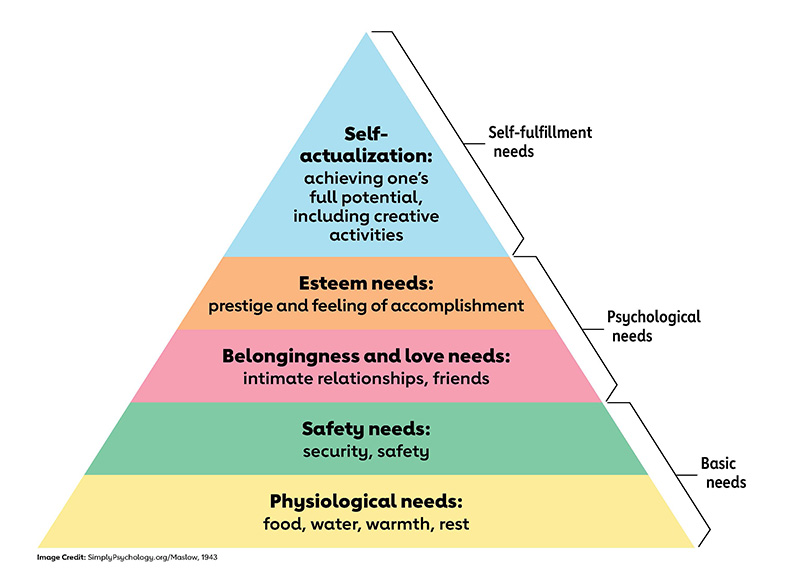
Similar to Maslow's pyramid, the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs illustrates a layered approach, with each stage building upon the previous one. It begins with the foundational elements and gradually progresses toward more advanced capabilities.
What is the data science hierarchy of needs?
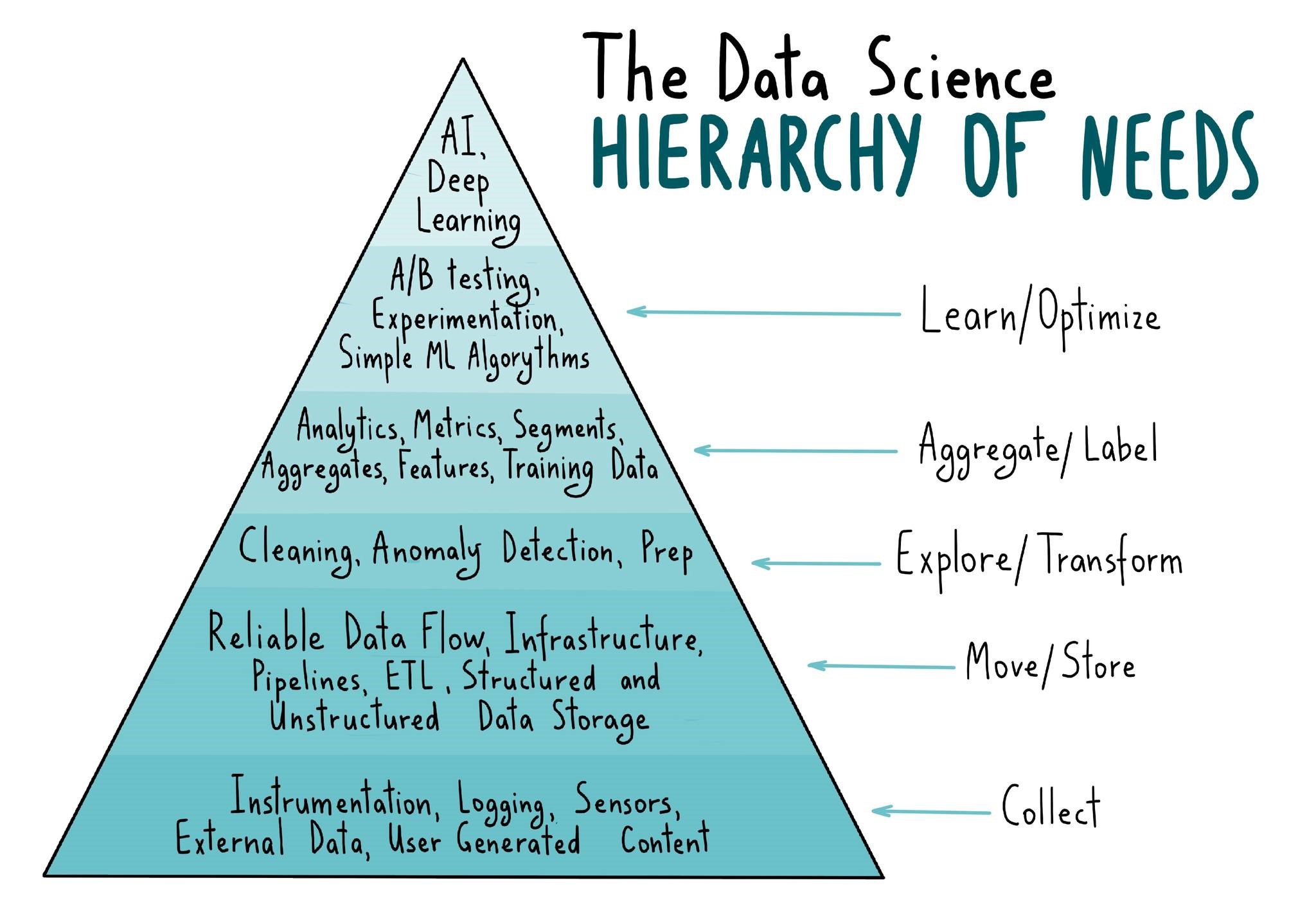
The Data Science Hierarchy of Needs is a conceptual framework that outlines the stages organizations must navigate to fully leverage the power of data. Similar to Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs, this framework emphasizes the importance of building a strong foundation before progressing to higher levels of data-driven excellence. Let's explore each stage of the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs in detail:
1. Collection:
The collection stage is the bedrock of the hierarchy, focusing on acquiring and gathering data from various sources. This includes instrumentation, which involves implementing tools and systems to capture data, logging user interactions, and leveraging sensors to collect relevant information. External data sources and user-generated content also play a crucial role in enriching the dataset, providing valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and more.
2. Move/Store:
Once data is collected, it needs to be efficiently moved, organized, and stored. This stage involves establishing a reliable dataflow infrastructure, including pipelines for data ingestion, transformation, and extraction (ETL). Structured and unstructured data storage solutions are implemented to ensure scalability, accessibility, and security. Robust data management practices are crucial to maintaining data integrity and enabling seamless data processing throughout the organization.
3. Explore/Transform:
In the explore/transform stage, data is prepared for analysis by undergoing cleaning and transformation processes. Anomaly detection techniques are applied to identify and handle irregularities or inconsistencies in the data. Data preparation involves removing duplicates, handling missing values, and standardizing formats. This stage lays the groundwork for subsequent analysis and enables the generation of accurate insights.
4. Aggregate/Label:
In the aggregate/label stage, data is aggregated and organized into meaningful segments. Analytics and metrics are derived to measure performance, identify trends, and evaluate key performance indicators (KPIs). Segmentation allows for the creation of targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer experiences. Features are extracted to feed machine learning algorithms, and training data is labeled for supervised learning models.
5. Learn/Optimize:
The learn/optimize stage focuses on experimentation and optimization. A/B testing and experimentation frameworks are utilized to evaluate different approaches and measure their impact on key metrics. Simple machine learning algorithms are employed to generate predictive insights, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions. This stage helps refine models, improve accuracy, and optimize strategies based on insights gained from data analysis.
6. AI/Deep Learning:
The pinnacle of the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs is the AI/Deep Learning stage. At this level, organizations leverage advanced techniques like artificial intelligence and deep learning to extract high-level patterns, perform complex tasks, and automate processes. With a well-structured dataset, proper instrumentation, dashboards, and good measurement, organizations can scale up the use of machine learning models. AI and deep learning enable automation, predictive analytics, and the extraction of valuable insights from big data.
What benefits, then, does the data science hierarchy of needs offer to organizations?
Embracing the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs offers numerous benefits to organizations that seek to harness the power of data effectively. By following this framework, companies can achieve the following advantages:
First and foremost, the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs ensures a systematic and structured approach to data utilization. It provides a clear roadmap for organizations to navigate the various stages of data processing, from collection to advanced analytics. This structured approach eliminates guesswork and promotes efficiency, enabling companies to make the most of their data resources.
Furthermore, by prioritizing the foundational stages of data collection, movement, and storage, organizations can establish a robust infrastructure capable of handling large volumes of data. This infrastructure provides the necessary groundwork for more advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence applications. A solid foundation ensures data reliability, accessibility, and scalability, facilitating better decision-making and enabling organizations to derive valuable insights from their data assets.
Another significant benefit is the focus on data quality and preparation. The Data Science Hierarchy of Needs emphasizes the importance of cleaning and transforming data before analysis. By addressing data anomalies, removing duplicates, and standardizing formats, organizations can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their insights. This attention to data quality fosters trust in the analysis outcomes and enables organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
Moreover, the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs promotes a culture of experimentation and optimization. By incorporating A/B testing and experimentation frameworks, organizations can iteratively improve their models and strategies. This iterative approach minimizes the risk of making decisions based on flawed assumptions and helps organizations fine-tune their data-driven initiatives. It also encourages a continuous learning mindset, allowing organizations to adapt to evolving market conditions and customer preferences.
Conclusion:
As we conclude our exploration of the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs, it's essential to highlight the distinctions between data analysts, data scientists, and data engineers. While these roles are interconnected and collaborate closely, they possess unique skill sets and responsibilities within the data ecosystem.
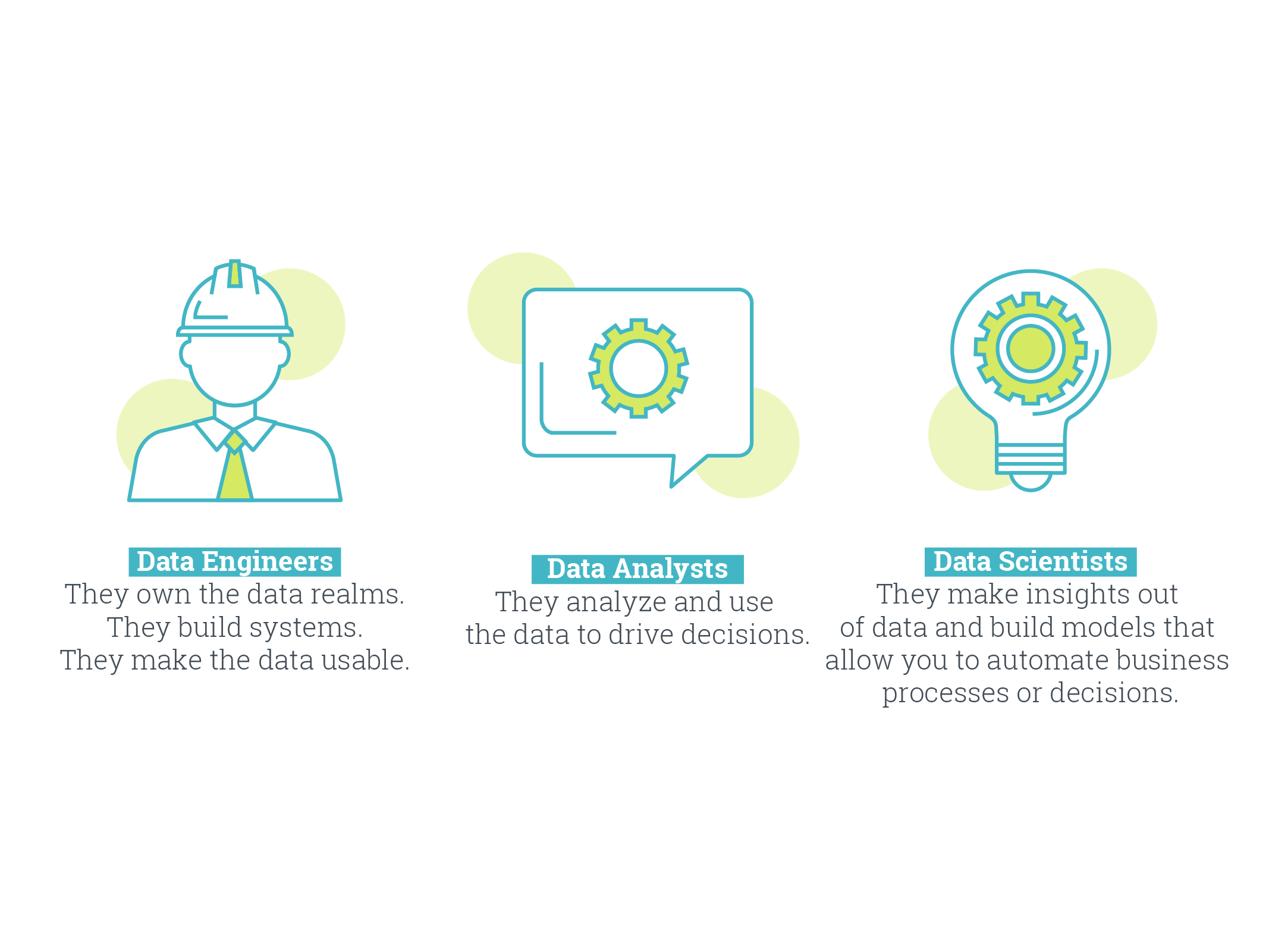
Data analysts are experts in extracting insights from data and translating them into actionable recommendations. They excel at data visualization, statistical analysis, and storytelling. Their role primarily revolves around examining historical data, identifying trends, and generating reports that inform decision-making. Data analysts play a critical role in interpreting data and bridging the gap between raw data and business insights.
On the other hand, data scientists possess a broader skill set and a deep understanding of advanced statistical modeling, machine learning, and predictive analytics. They are adept at developing complex algorithms, building predictive models, and uncovering hidden patterns in large datasets. Data scientists focus on solving complex problems, developing innovative solutions, and driving predictive and prescriptive analytics initiatives. They work closely with data engineers to ensure data availability, reliability, and scalability for their modeling and analysis needs.
Lastly, data engineers are responsible for the foundational infrastructure that enables data collection, storage, and processing. They design and implement robust data pipelines, ensuring data quality, integrity, and security. Data engineers are skilled in database management, data integration, and data architecture. They collaborate with both data analysts and data scientists to ensure the availability of clean, structured data for analysis and modeling.
In the hierarchy of needs, data engineers lay the groundwork by building the infrastructure, data analysts provide insights to drive decision-making, and data scientists take it a step further by leveraging advanced techniques to uncover predictive insights and drive innovation. Together, these roles form a cohesive data ecosystem, each playing a vital part in the success of data-driven organizations.
In conclusion, the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs offers a comprehensive framework for organizations to unlock the true potential of data. By following the hierarchy's stages, companies can establish a solid foundation, deepen their understanding of data, optimize operations, and embrace advanced analytics and AI. Furthermore, recognizing the distinctions between data analysts, data scientists, and data engineers allows organizations to harness the strengths of each role and foster collaboration, leading to more robust data-driven solutions and outcomes.
Embracing the Data Science Hierarchy of Needs and leveraging the expertise of data analysts, data scientists, and data engineers sets organizations on a path toward data-driven excellence. The power of data is immense, and with the right framework and skilled professionals, businesses can harness its potential to gain a competitive edge, drive innovation, and make informed decisions that shape their success in the rapidly evolving digital landscape. So, embark on your data-driven journey, ascend the hierarchy, and unlock the transformative power of data. The possibilities are endless, and the rewards are waiting to be reaped!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Warui Wanjiru directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Warui Wanjiru
Warui Wanjiru
I am a passionate and highly motivated Junior Data Engineer, driven by my curiosity and eagerness to explore the vast world of data. With a solid foundation in data analytics, programming, and database management, I thrive on the challenge of extracting, cleaning, transforming, and visualizing data to uncover valuable insights. My journey in the realm of data engineering has exposed me to various programming languages and tools, including Python, SQL, and Tableau. However, I don't stop there—I am constantly seeking new knowledge and skills to stay ahead of the curve. Currently, I am immersing myself in the world of Rust, harnessing its speed and efficiency prowess. Embracing this new language allows me to tackle complex data engineering tasks with even greater efficiency and effectiveness. What truly sets me apart is my genuine enthusiasm for learning and taking on new challenges. I thrive in dynamic environments that push me to think creatively and find innovative solutions. With a solid understanding of data structures and algorithms, I relish the opportunity to dive into complex datasets, unearthing patterns and unlocking actionable insights. Above all, I am dedicated to making a real impact through data engineering. I believe in the power of data to drive transformative change and improve decision-making processes. By harnessing the power of data, I strive to empower organizations to make informed choices and achieve tangible results. Let's embark on this exciting journey together, where I can contribute my authentic enthusiasm, my thirst for knowledge, and my unwavering commitment to delivering exceptional data solutions.