Understanding Ad-hoc commands in Ansible
 Dhwarika Jha
Dhwarika JhaTable of contents
- Ansible ad hoc ping command to ping 3 servers from the inventory file
- Write an ansible ad hoc command to check uptime
- Ansible ad hoc command to check the free memory or memory usage of hosts
- ad-hoc command to get physical memory allocated to the host
- To check the disk space on all hosts in an inventory file

Ansible ad hoc commands are one-liners designed to achieve a very specific task they are like quick snippets and your compact Swiss army knife when you want to do a quick task across multiple machines.
To put simply, Ansible ad hoc commands are one-liner Linux shell commands and playbooks are like a shell script, a collective of many commands with logic.
Ansible ad hoc commands come in handy when you want to perform a quick task.
Ansible ad hoc ping command to ping 3 servers from the inventory file
Ansible ad hoc command to ping a host:
ansible -i /path/to/inventory/file server1:server2:server3 -m ping
This command uses the ansible command with the following options:
-i /path/to/inventory/file: specifies the path to the inventory file containing the servers we want to ping. /etc/ansible/hosts are by default paths of the inventory file. there is no need to write a path in the ansible ad hoc command. If your inventory file is at a different location then you need to write the path of the inventory file in ad hoc command.
server1:server2:server3: specifies the list of servers to ping, separated by colons.
-m ping: specifies that we want to use the ping module to ping the servers.
In my case I have added the naming convention as Ansible-Server1 in the /etc/ansible/hosts file, that is why I used the command as shown below
ansible Server1:Server2 -m ping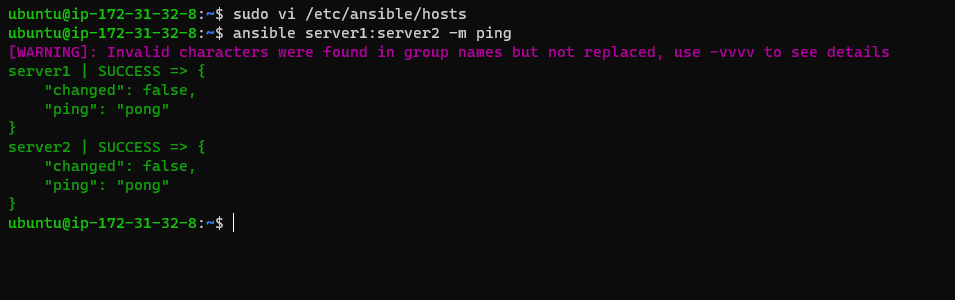
Write an ansible ad hoc command to check uptime
ansible -i /path/to/inventory/file all -m command -a uptime
This command uses the ansible command with the following options:
-m command: specifies that we want to use the command module to execute the uptime command on the remote servers.
-a uptime: specifies the arguments to pass to the command module, which in this case is simply the uptime command.
ansible all -m command -a uptime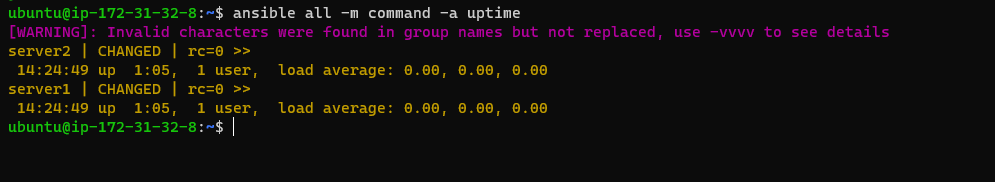
Ansible ad hoc command to check the free memory or memory usage of hosts
ansible -i /path/to/inventory/file all -a "free -m"
-a "free -m": the -a option specifies the arguments to pass to the command to be executed on the remote hosts. In this case, the free -m command is executed to show the memory usage on each host.

ad-hoc command to get physical memory allocated to the host
ansible all -m shell -a "cat /proc/meminfo|head -2"
-m shell: the -m option specifies the module to use to execute the command on the remote hosts. In this case, the shell module is used to execute the command.
-a "cat /proc/meminfo|head -2": the -a option specifies the arguments to pass to the module to execute the command on the remote hosts. In this case, the cat /proc/meminfo|head -2 command is executed to display the first two lines of the /proc/meminfo file on each host.

To check the disk space on all hosts in an inventory file
ansible -i inventory_file all -m shell -a 'df -h'
This command uses the df command to show the disk space usage on each host in the inventory file.
The -m shell option is used to execute the command on the remote hosts using the shell.

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dhwarika Jha directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
