Linux File Permission-reading, writing and executing
 ankita kumari
ankita kumariTable of contents

In this article we will explore about how Access Management works on linux operating system.
In the below image,
a user ankita cannot create a directory "doc" as the reason specified that "permission denied".
similarly user sagar cannot create a file "sample.txt" as the reason stated that "permission denied" .


why this is happening?🤔 Is something wrong?
Being a multi-user Operating System having limited file permissions is sometimes difficult and can be challenging for someone who is new to Linux/Unix operating systems.
Users and Groups in Linux
Before understanding permissions, we should understand the file ownerships.
In Linux file permissions system, there are three types of owners associated with a file or a directory.
Owner - owner referred as the user who created the file or a directory. Simply the owner has full privileges and permissions over the file, including the changing of mode(permissions) of a file or a directory.
Group - Every user is the part of some group(s). so the users belonging to that particular group of a file or a directory have permissions to perform actions on the file.
other - Other are everyone else!. Any users that are not part of the user or group classes belong to this class. The permissions indicate what action all other users can perform on the file.
Viewing the file permissions
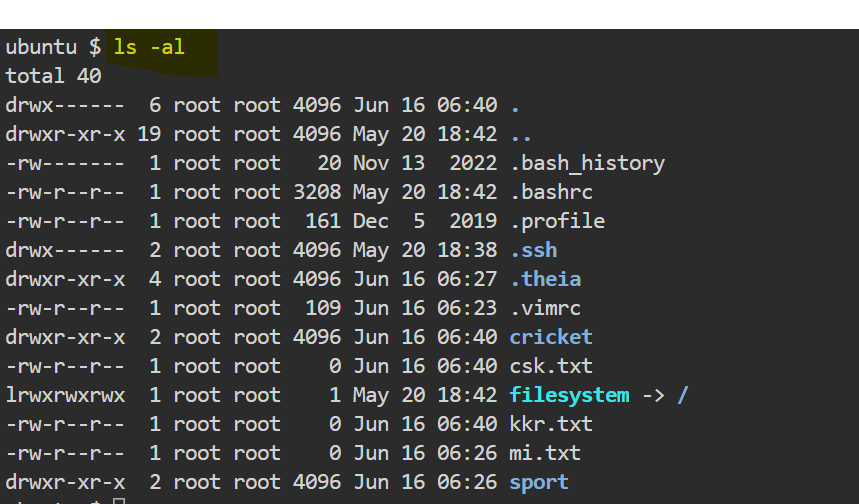
You can view the permissions of files and directories by using ls command with option -al .
Understanding the permission indicators
Here is how to understand the output of the ls -al command.
At the top,"Total 40 " represents the total number of files and directories present.
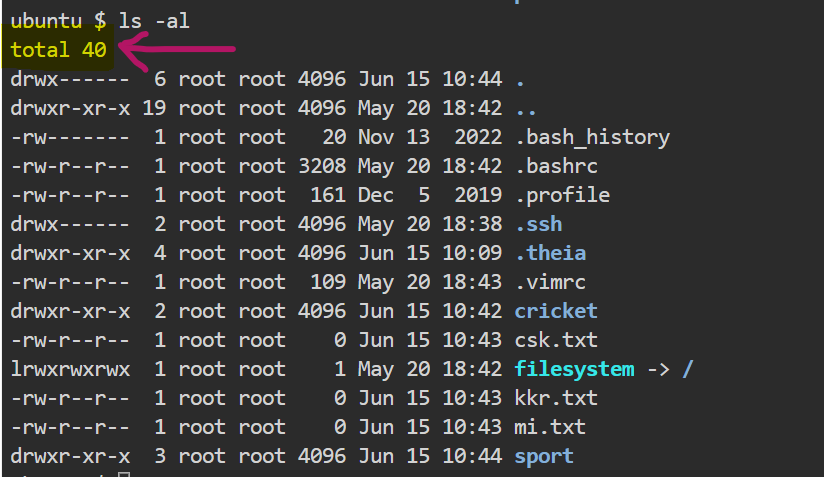
now coming down, there is symbolic representation using a combination of letters: d, r, w and x.
To understand this representation, let's start one by one.
📌File Type - The very first character indicates the file types.
Character | Type of file |
- | A regular file |
d | A directory |
l | A symbolic link. Its a file system object that points to another file system object. |
b | A block special file. This file type refers to a device that handles data in blocks such as hard drives, DVD. |
c | A character special file. This file type refers to a device that handles data as a stream of bytes at a time. |
📌Permissions - In the same column starting from second character there are total nine characters, three sets of characters either dash(-) or letters, three times, indicating permissions for owner, group and others.

the r represents the read permissions.
the w represents the write permissions.
the x represents the execution permissions.
the - represents explicitly no permissions .
let's understand these three triplets by taking one example of our directory cricket .

here
The first three characters belongs to owner. In our case it sets to
rwxthat means the owner has full permissions to read, write and execute.The next three characters after the owner triad belongs to group. Here it sets to
r-xwhich implies that the users belonging to that group will have read and execute permissions.The final three characters after the group triad belongs to other. Here it sets to
r-xwhich means that all other users on the system has read and write permission over that directory.
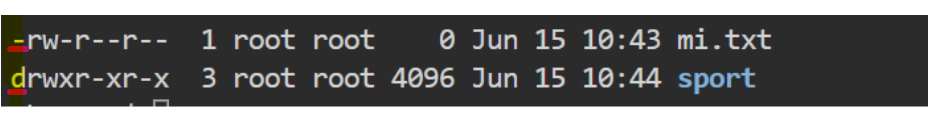
📌Link count - Second column belongs to the number of hard links to that file or directory. For e.g. file mi.txt having 1 hardlink and directory sport is having 2 hardlink. let's find out link information for demo_file as ls output shows it as

📌Owner - Third column belongs to owner who owns the file or directory. For eg - for file mi.txt the owner is root and similarly for directory sport also the owner is root only.

📌Group - And fourth column belongs to Group, the members of that group only will have the access to this file or directory. Only one group can be the owner of a file or directory at a time.
For eg - the root's group has the permission to access the file mi.txt which implies the users of the group "root" are the owner for file.

📌File size - Fifth column belongs to file size. Here size of files is described in bytes.

📌Modification Time/Date - Sixth column belongs to Time/Date. It shows the last modified date and time of that file or directory.

📌Filename - Obviously, the name of that file or directory.

Reading, writing and Executing
File permissions have a different meaning depending on the file type. The combinations of following character have different effects, depending on whether they are set to a file or to a directory.
|
|
|
| Allows a file to be opened and read. User's can't modify the file. | allows the user to read the directory contents without any modification in the directory. |
| Allows a file to be written to or modified, but does not allows a file to be deleted or renamed. | allows the directory contents to be modified, (You can create new files; rename or delete existing files and directory) if only if the executes permissions is also set otherwise the permissions has no effect. |
| allows a file to be treated as program and executed. | allows a directory to access details about files in the directory. Directory contents can be accessed with cd . |
Examples of Permissions in Linux
Now we understand file permissions. Let's see some examples.
|
|
|
|
|
|
How do I change the permissions?
There is a command named chmod in Linux which is used to change the permissions of file or a directory. Only the file's owner and superuser can change the mode(permissions) of a file or a directory.
There are two methods of changing file permissions using chmod.
1.Octal number representation
2.Symbolic representation
Octal number representation
Each permission is assigned a value as the following table show, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set.
Number | Octal permission representation | Set |
| 0 | No permission | --- |
| 1 | Execute permission | --x |
| 2 | write permission | -w- |
| 3 | Execute and write permission; 1 (execute) + 2 (write) = 3 | -wx |
| 4 | Read permission | r-- |
| 5 | Read and execute permission; 4 (read) + 1 (execute) = 5 | r-x |
| 6 | Read and write permission; 4 (read) + 2 (write) = 6 | rw- |
| 7 | All permission ; 4 (read) + 2 (write) + 1 (execute) = 7 | rwx |
The syntax :-
$ chmod <number> <file or directory>
let understand the permissions by taking an example of file sample.txt. Running ls -l on the sample.txt shows the file's permission as below,
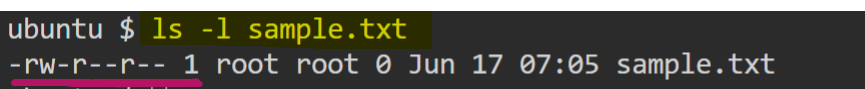
here sample.txt is a regular file, having read + write permissions for owner, read permission for group and read permission for other.
- Assign
read + write + executepermissions toowner,read + writepermissions togroupandread + executepermissions toothersonsample.txt.
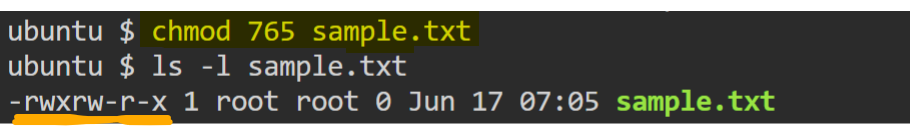
- Assign
read + write + executepermissions toowner,writepermissions togroupandno permissionpermissions toothersonsample.txt.
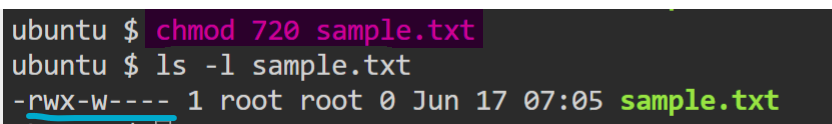
Symbolic Representation
The easiest way for a beginner to modify file or directory permission is to use the symbolic mode.
To specify who is affected, a combination of the characters u, g, o, and a is used.
symbol | representation |
u | stands for "user" but represents the owner of file or a directory. |
g | stands for "group", represents the members of that specified group only. |
o | stands for "others" except user and group |
a | stands for "all", represent the combination of u, g and o. |
With symbolic permission you can add, delete or specify the Permissions you want by using operators in the following table;
operator | specifications |
+ | Add the specified permissions to a file or directory |
- | Remove the specified permissions to a file or directory |
= | Sets the specified current permissions to a file or directory. |
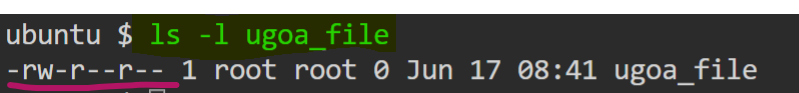
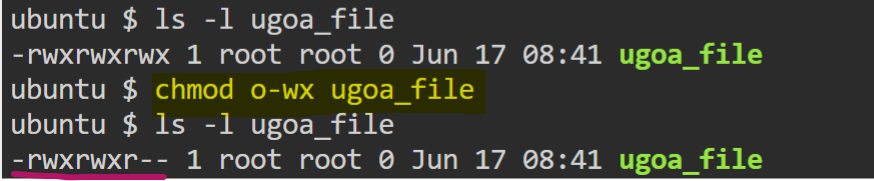
let understand the permissions by taking an example of file ugoa_file. Running ls -l on the ugoa_file shows the file's permission as below,
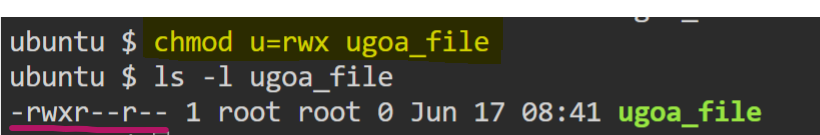
- Assign
read + write + executepermissions toowner.
- Remove
write + executepermissions fromothers.
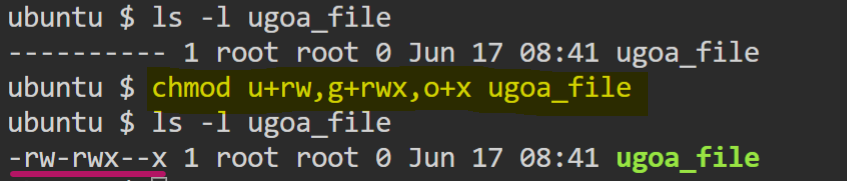
here you can give permissions to u, g and o iby combining the operators in single line,
- Assign
read + writepermissions to owner,read + write + executepermissions togroupandexecutepermissions toothers.
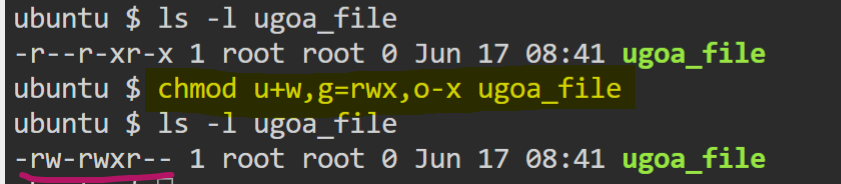
- Assign
writepermissions to owner,read + write + executepermissions togroupand removeexecutepermissions fromothers.
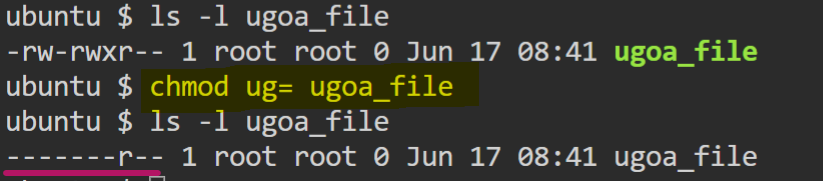
- If no permission input is given after
"="then all the permission will be removed for that class.
Changing Ownership and Groups
while creating an account in Linux, it assigns a owner ID, group ID and groups to each user.
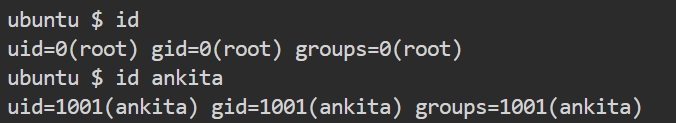
chown
The chown command stands for "change owner" used to change the owner and group owner of a file or directory. Superuser privileges are required to use this command.
The syntax of chown are as follows:
$ chown <owner>:<group> file/directory
- How do I change the owner associated with
samplefile?
$ chown <username> <filename>
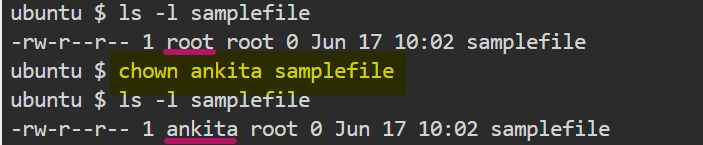
Earlier the owner of "samplefile" was "root" now its changes to user "ankita".
- How do I change the group associated with
samplefile?
$ chown :<groupname> <filename>
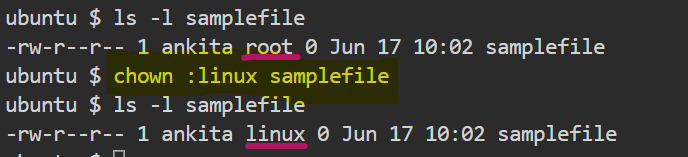
similarly samplefile ,the group owner was "root" but now changes to "linux" .
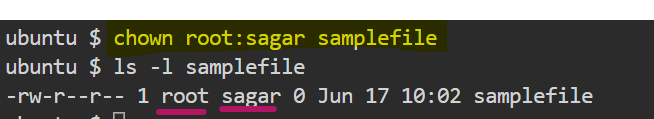
- How do I change the owner and group at the same time for
samplefile?
$ chown <username>:<groupname> <filename>
chgrp
In older versions of Unix, the chown command changed only file ownership, not group ownership. A specific command, chgrp was used for changing group owner of a file or directory.
The syntax are as follows:
$ chgrp <groupname> <filename>
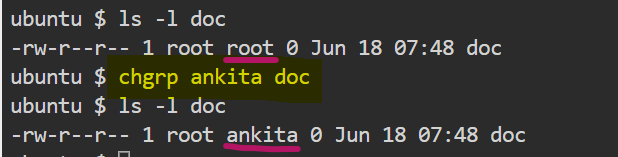
I prefer to memorize single command chown as it applicable to both user and group changing ownerships rather to memorize chown for the user and chgrp for the group.
🦋Conclusion
Though we came to end of this article, I hope this article has helped you to understand how Linux file permissions work and how can we change permissions.
Hope you like this article. So Stay Tuned for the next article .
Thank you. Happy learning!📍
And also don't forget to like and share this article.😎
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ankita kumari directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

ankita kumari
ankita kumari
Multi-Tasker