Binary Trees Explained: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
 Tanmay Sarkar
Tanmay Sarkar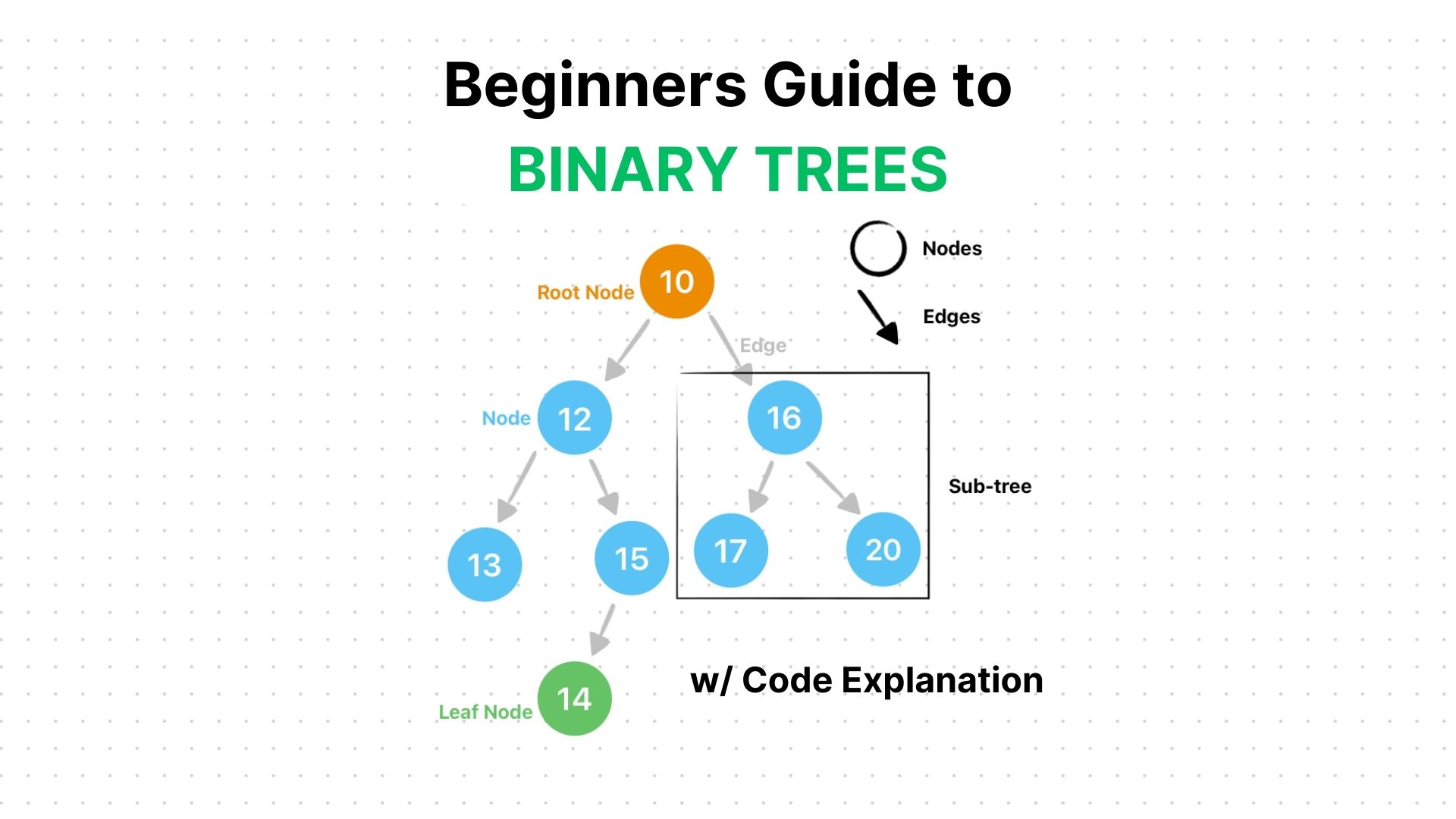
Introduction 🧑🏽💻
Welcome to the fascinating world of binary trees! If you're new to this topic or looking to reinforce your understanding, you're in the right place. In this tutorial, I'll take you on a step-by-step journey through the fundamentals of binary trees. By the end of this article, you'll have a solid understanding of binary trees and feel confident in your ability to tackle more advanced data structures.
Understanding Binary Trees 🎄
Let's start by demystifying binary trees. Don't worry if you're unfamiliar with the concept – I'll break it down for you. Binary trees consist of nodes connected by edges, forming a hierarchical structure. Imagine it as a tree with branches spreading out, where each node can have up to two children. Simple, right? We'll illustrate this with easy-to-understand diagrams to make it crystal clear.
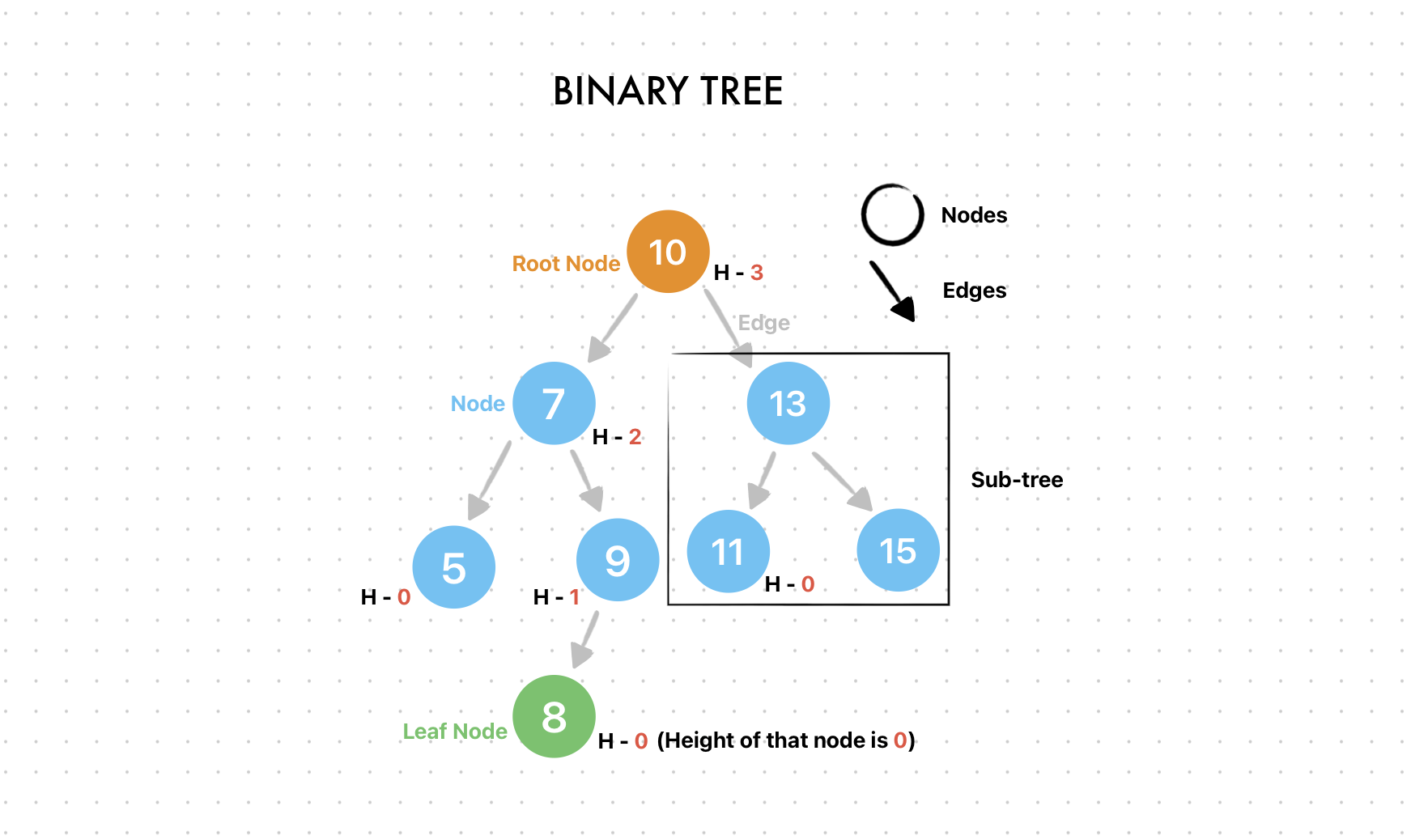
A binary tree is a hierarchical structure composed of nodes. Each node can have at most two children: a left child and a right child. The topmost node is called the root, and it serves as the starting point of the tree. The nodes below the root are referred to as internal nodes, while those at the bottom without any children are called leaf nodes.
Now, let's break down the components of a binary tree:
Root: The topmost node of the tree, serving as the starting point.
Internal Node: Nodes other than the root and leaf nodes, having both a left and right child.
Leaf Node: Nodes at the bottom of the tree without any children.
Left Child: The node directly below and to the left of another node.
Right Child: The node directly below and to the right of another node.
Parent: The node above and connected to another node.
Subtree: A smaller binary tree within the main binary tree, having its root.
The time complexity of binary tree operations is typically determined by the height in balanced trees, while it is determined by the number of nodes in unbalanced trees. A well-balanced binary tree, such as an AVL tree or Red-Black tree, ensures that the height remains logarithmic. This balance leads to efficient operations, such as insertion, deletion, and searching, all of which have a time complexity of O(logN) in balanced trees.
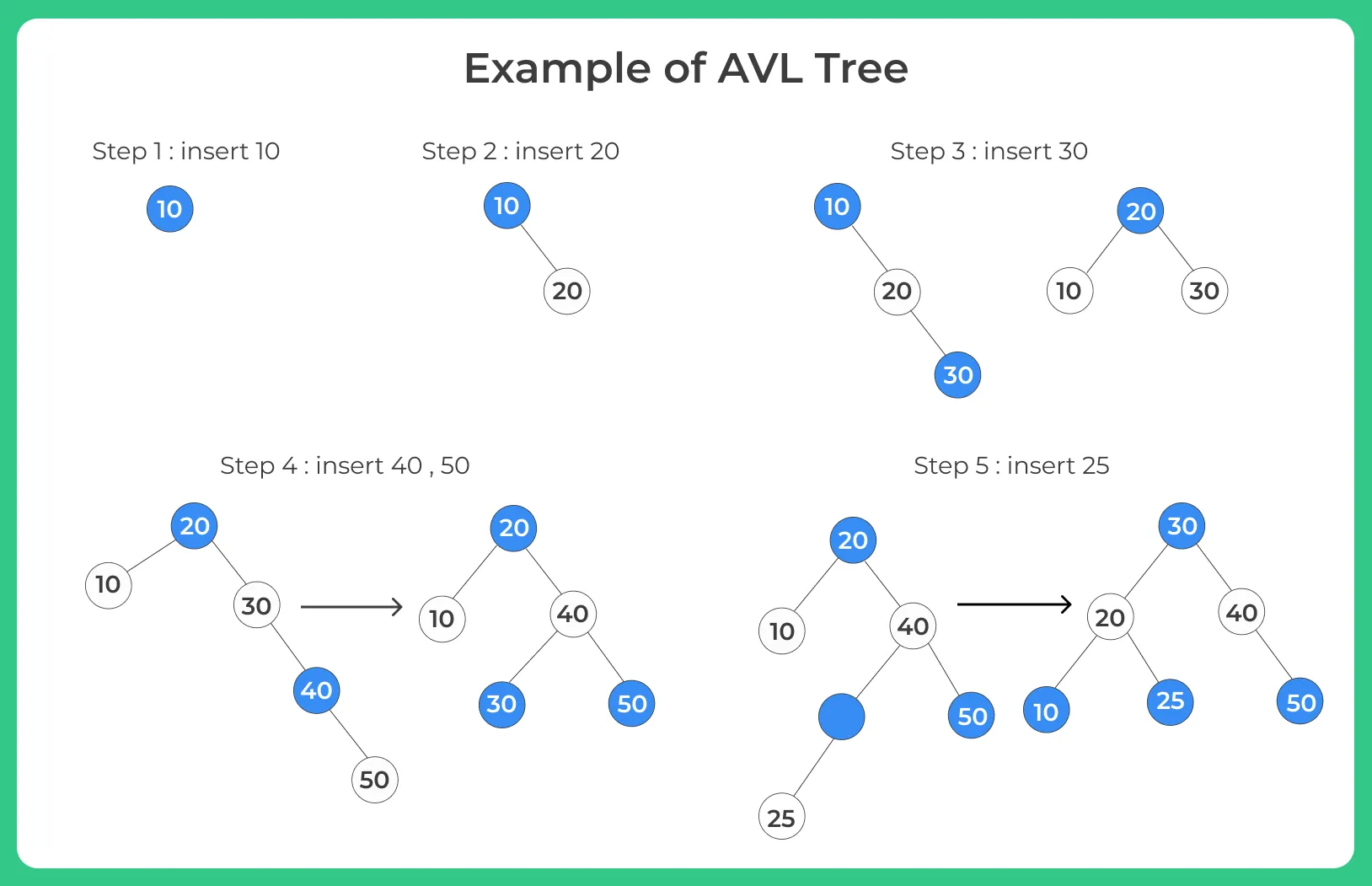
Now a question arises, Why should one use binary trees over other data structures?
Binary trees excel in scenarios that require efficient searching, sorting, and hierarchical organization. They provide a balance between ordered structure and fast access, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Compared to linear structures like Linked Lists or Arrays, Binary trees reduce the search space significantly, resulting in faster operations. Additionally, binary trees can handle dynamic data effectively, allowing for efficient insertion and removal of elements.
Use cases of Binary Trees ⏯️
Prepare to be amazed by the countless applications of binary trees! From efficient searching with binary search trees to evaluating mathematical expressions with expression trees, and even data compression with Huffman coding. All these is being possible by Binary Trees.
Let's explore some common use cases where binary trees shine.
Searching and Sorting: One of the primary applications of binary trees is in searching and sorting algorithms. Binary Search Trees (BST), a specific type of binary tree, enable efficient searching for a particular value. They maintain an order where the left child of a node is smaller, and the right child is greater. This property allows for quick comparisons and reduces the search space, resulting in logarithmic time complexity O(logN) for searching operations.
Hierarchical Structures: Binary trees are ideal for representing hierarchical relationships. File systems, organization charts, and family trees can all be efficiently modelled using binary trees. The parent-child relationship between nodes simplifies the navigation and management of hierarchical data.
Expression Evaluation: Expression trees utilize binary tree structures to represent mathematical expressions. Operators reside in internal nodes, while operands reside in leaf nodes. Expression trees allow for efficient evaluation of complex expressions by performing operations in a specific order, guided by the tree structure.
Huffman Coding: Binary trees are central to Huffman coding, a compression technique widely used in data compression algorithms. Huffman trees are constructed based on the frequency of characters in a text, with frequent characters occupying shorter paths in the tree. This results in optimal compression, reducing file sizes while maintaining data integrity.
Decision Trees: Binary trees are instrumental in decision tree algorithms used for classification and regression tasks in machine learning. Decision trees divide data based on features at each node, ultimately leading to leaf nodes representing specific classes or regression values. Decision trees are interpretable and enable efficient data classification and prediction.
Game Trees: Binary trees serve as the backbone for game trees, used in game theory and artificial intelligence. Game trees represent the possible moves and outcomes in games, facilitating decision-making and strategy development for both players and intelligent agents.
Implementation of Binary Tree 🌱
Let's roll up our sleeves and build our very own binary tree. I'll guide you through the process, step by step. You'll be constructing binary trees like a pro in no time!
In the above Replit code, I coded everything you need to know to get started using Trees. I wrote explanations also with the code itself, you must take a look at it to understand Binary Tree implementation completely.
My DSA with Java Repository: DSA-Java BinaryTrees (Github). Give it a proper look and you may find useful codes and explanations.
Traversing Binary Trees 🎋
Time to explore the exciting world of traversing binary trees. Think of it as navigating through the tree and visiting each node. There are three popular techniques: pre-order, in-order, and post-order traversal.
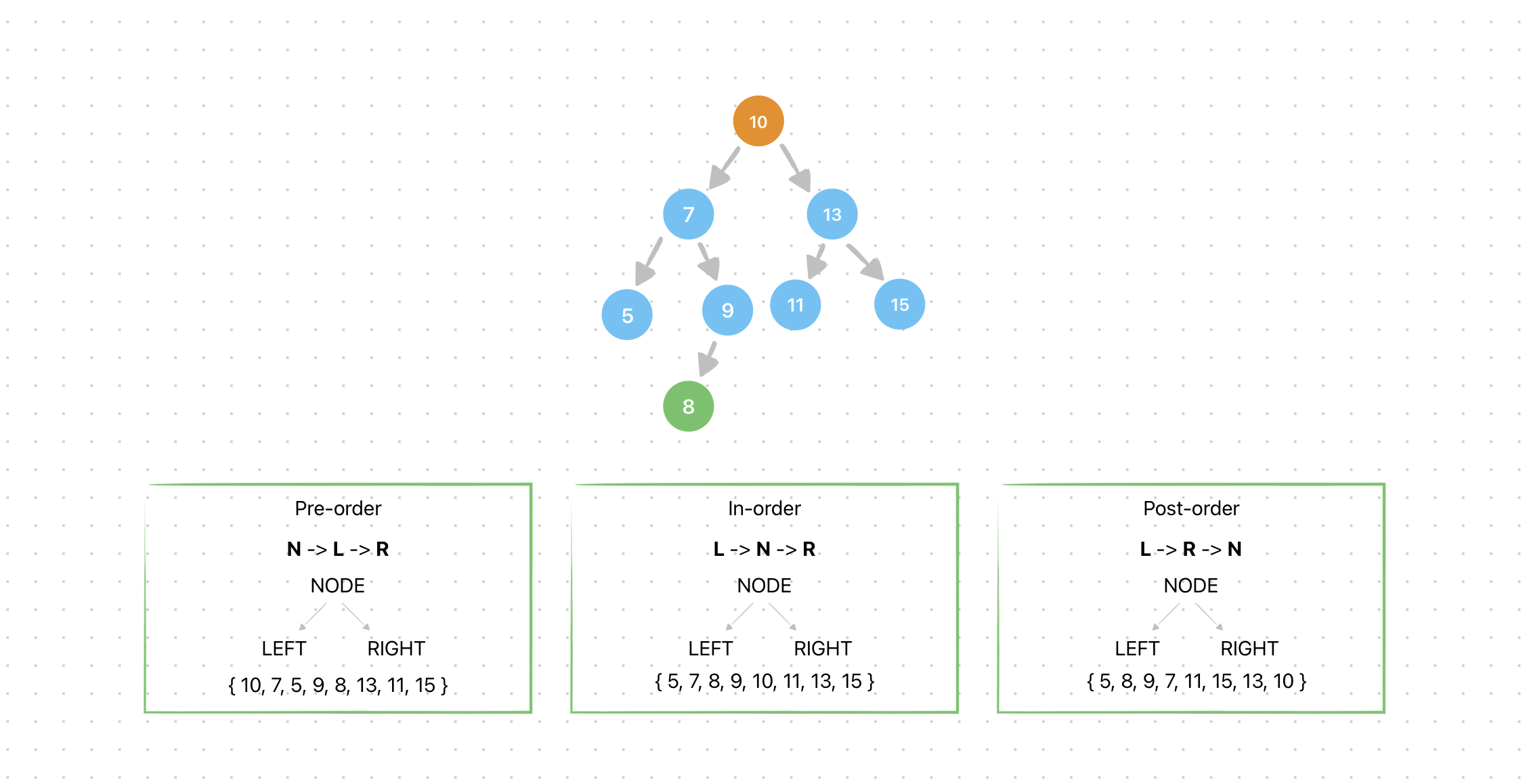
Pre-order traversal is primarily used for obtaining prefix expressions, creating copies of trees, and generating prefix notations. It provides a systematic way of visiting nodes in a binary tree, allowing for various applications in expression evaluation, tree manipulation, and programming.
In-order traversal is a valuable technique used for retrieving data in sorted order, evaluating expressions, creating copies of binary trees, and validating the structure of binary search trees. Its properties and applications make it an essential tool in various algorithms and data-processing tasks involving binary trees.
Post-order traversal is primarily used for evaluating expressions in expression trees, deleting nodes while maintaining proper dependencies, and generating postfix representations of expressions. Understanding the different traversal orders, including post-order, provides valuable tools for efficiently manipulating and analyzing binary trees.
We'll take a greater look and code each traversal technique in our upcoming post where I'll explain Binary Search Tree aka BST.
Short Note of Binary Search Tree 📝
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree with an ordering property where the left child contains smaller values and the right child contains greater values. BSTs enable efficient searching, insertion, and deletion operations with a logarithmic time complexity of O(log n). They are widely used in applications requiring fast searching and sorting, such as dictionaries, symbol tables, and databases. An in-order traversal of BSTs provides a sorted sequence of values. While the efficiency of BST operations depends on maintaining balance, they serve as the foundation for more advanced balanced tree structures. Overall, BSTs offer an ordered and efficient way to store and retrieve data.
I'll be coming up with a new blog very soon, explaining Binary Search Tree and more about Binary Trees.
Conclusion 🙌🏼
Congratulations! You've successfully started the journey through the world of binary trees, and you've done it with confidence and ease. Remember, mastering binary trees takes time and practice, but you're well on your way. Keep exploring advanced topics and challenging yourself with new projects. With each step, you'll enhance your problem-solving skills and become a proficient programmer.
So, go ahead and embrace the power of binary trees. You're now equipped with the knowledge and understanding to tackle complex data structures. Happy coding and enjoy your newfound binary tree prowess!
Follow me on 🐦 @sarkartanmay393
Direct mail me 📧 sarkartanmay393@gmail.com
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tanmay Sarkar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tanmay Sarkar
Tanmay Sarkar
DevOps and Open Source Enthusiast and CSE Student