AIOT - Artificial intelligence of things
 Microsoft Innovations Club
Microsoft Innovations Club
Artificial intelligence of things (AIoT) is the combination of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies and the internet of things (IoT) infrastructure. AIoT's goal is to create more efficient IoT operations, improve human-machine interactions and enhance data management and analytics.
Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household objects to sophisticated industrial tools. With more than 7 billion connected IoT devices today, experts are expecting this number to grow to 10 billion by 2020 and 22 billion by 2025.
AIoT is transformational and mutually beneficial for both types of technology, as AI adds value to IoT through machine learning capabilities and improved decision-making processes, while IoT adds value to AI through connectivity, signalling and data exchange. AIoT can improve businesses and their services by creating more value out of IoT-generated data. AI enables the IoT device to use gathered big data to better analyse, learn and make decisions without the need for a human.
How does AIoT work?
In AIoT devices, AI is embedded into infrastructure components, such as programs and chipsets, which are all connected using IoT networks. APIs are then used to ensure all hardware, software and platform components are able to operate and communicate together without effort from the end user.
When operational, IoT devices create and gather data, and then AI analyses it to provide insights and improve efficiencies and productivity. Insights are gained by AI using processes like data learning.
AIoT data can also be processed at the edge, meaning the data from IoT devices is processed as close to these devices as possible to minimise the bandwidth needed to move data while avoiding possible delays to data analysis.
APPLICATIONS OF AIOT:
Although many AIoT applications focus on the implementation of cognitive computing in consumer appliances, the following highlights several examples of the wider use of AIoT:
1. Cobots
Collaborative robots, known as cobots, are designed to work alongside humans in manufacturing and assembling units. With the help of data generated by IoT devices and AI programs such as computer vision, cobots assist humans in the following areas:
a. Production – loading and unloading materials from conveyor belts
b. Assembly – lifting and positioning heavy parts in automobile assembly
c. Quality Control – measuring, testing, and inspecting products
d. Packaging – counting, packaging, labelling, and placing finished products in cartons
Cobots depend on IoT data to work efficiently and the reduced latency of AIoT devices enable cobots to manage human-machine interactions.
2. Here are some examples of how some applications are using AIoT for new benefits.
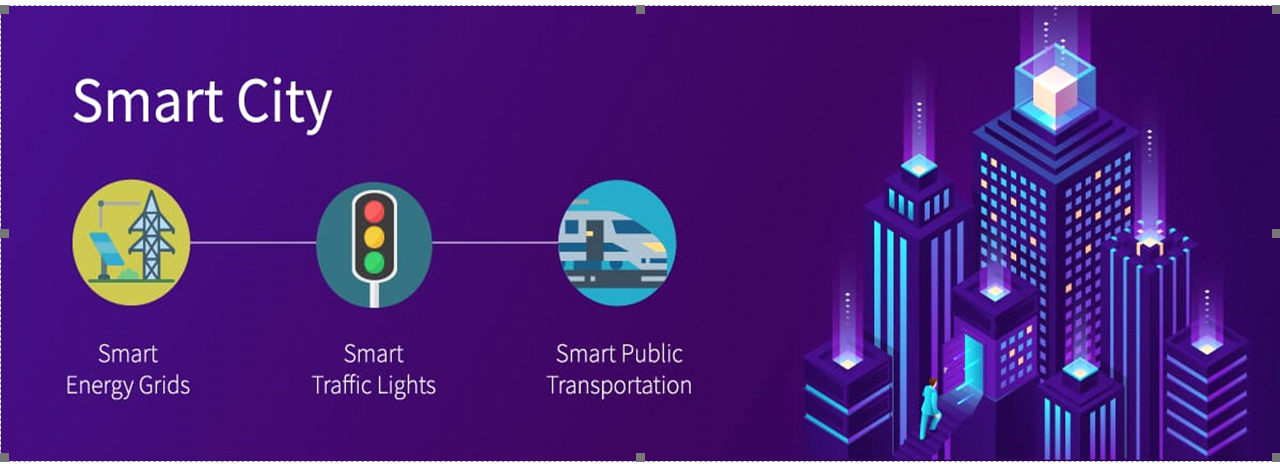
Smart cities.
Smart technology such as economic growth and improved quality of life for residents.[if gte vml 1]>
Smart retail.
Retailers use smart cameras to recognize shoppers' faces and detect if they have scanned their items at the self-checkout before leaving the store.
Smart home Smart appliances learn through human interaction and response. AIoT appliances can also store and learn from user data to understand user habits to provide customised support.
Enterprise and industrial.
Manufacturers use smart chips to detect when equipment is not functioning properly, or a part needs to be replaced.
Social media and human resources (HR).
AIoT tools can be integrated with social media and HR-related platforms to create an AI decision as a service function for HR professionals.
Autonomous vehicles.
Autonomous vehicles rely on multiple video cameras and sensor systems to gather data about nearby vehicles, monitor driving conditions and look for pedestrians.
Autonomous delivery robots.
Sensors gather data about the robot's environment, for example a warehouse, and then use AI to make traversal-based decisions.
Healthcare.
Medical devices and wearables collect and monitor real-time health data, such as heart rate, and can delete irregular heartbeats
What are the benefits and challenges of AIoT?
Benefits of AIoT include the following:
• Increased operational efficiency. AI-integrated IoT devices can analyse data to reveal patterns and insights and adjust system operations to become more efficient.
• Ability to adjust on the fly. Data can be generated and analysed to identify points of failure, which enable the system to make adjustments as needed.
• Data analytics done by AI. Employees do not have to spend as much time monitoring IoT devices, thus saving money.
• Scalability. The number of devices connected to an IoT system can be increased to optimise existing processes or introduce new features.
But there are also instances where AIoT may fail, causing a backup in production or other negative consequences. For example, autonomous delivery robots that fail might cause a delay in the delivery of a product; smart retail stores could fail to read a customer's face, leading to the customer accidentally stealing a product; or an autonomous vehicle may fail to read its surroundings, like an oncoming stop sign, and cause an accident.
What is the future of AIoT?
AIoT applications are being developed with the latest technological innovations. Companies are constantly testing newer levels of machine intelligence and how future advancements will provide new opportunities for AIoT devices. Here are some examples of how some applications are using AIoT for new benefits.
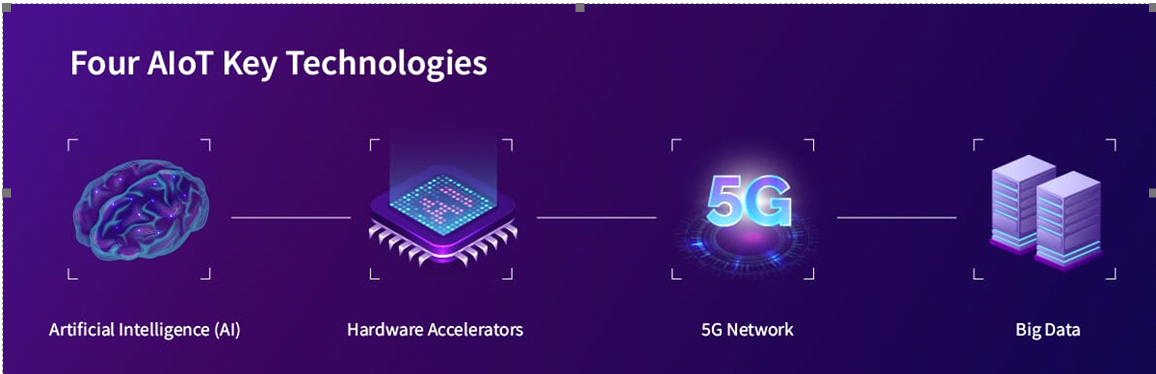
1. 5G
5G is designed to enable faster transfer of large data files in IoT devices, through higher bandwidth and lower latency. AIoT can help solve existing operational problems, such as the costs associated with effective human resource management or the complexity of supply chains and distribution models.
2. AI Edge Computing
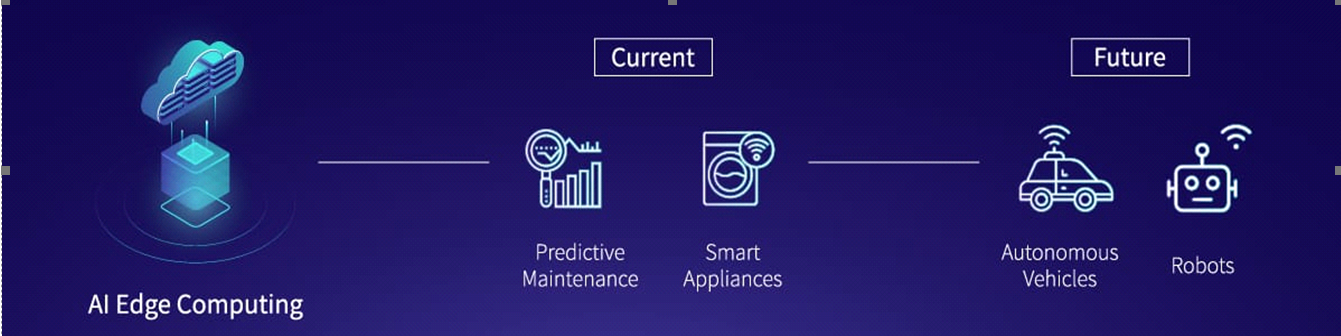
AI edge computing is processing the data with an AI algorithm using only the computer itself. This AI edge computer is performing AI-enabled applications right at the edge without relying on remote data centres.
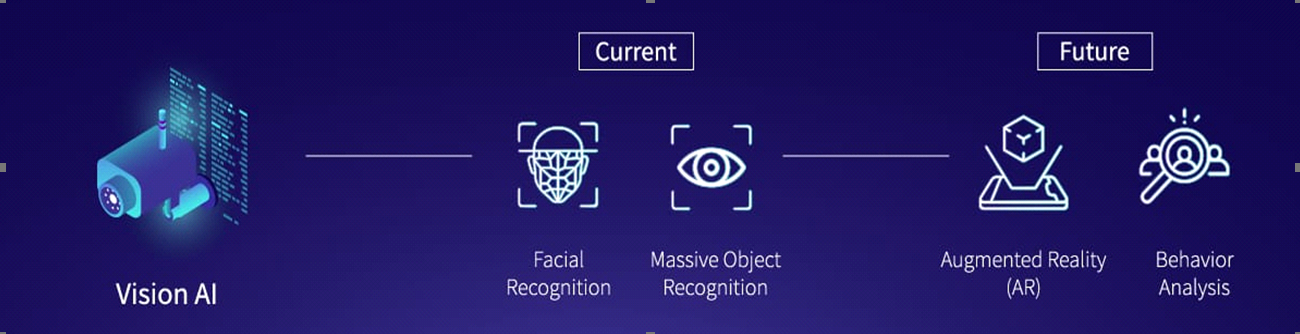
3. Vision AI[if gte vml 1]><v:rect
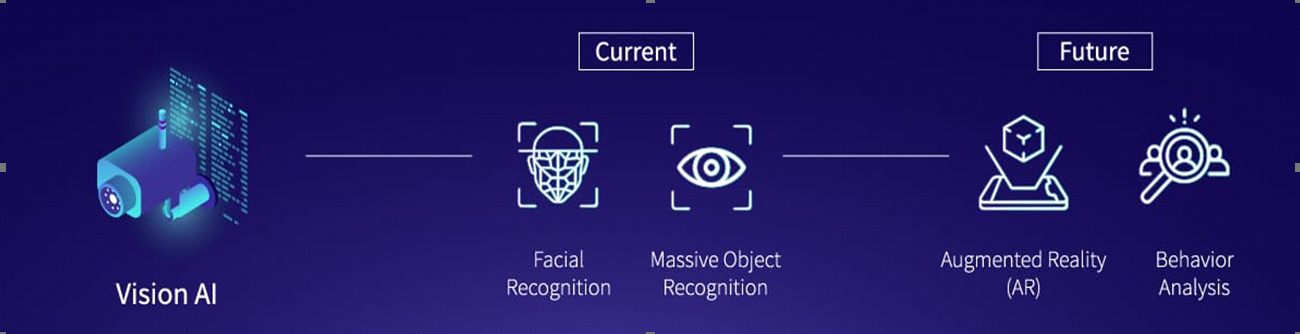
Machine inferencing is capable of detecting a massive number of objects in real-time. With powerful dedicated AI processors, machine vision will not only be able to detect different objects but also quickly predict the behaviour of the objects for a thorough comprehension of the situation.
4. Voice AI
Speech recognition and the voice assistant is just the early stage for voice AI. The future will enable much more complex Voice AI applications such as natural language processing and real-time language translation.
~ Preethi D ,Microsoft Innovations Club , VITC
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Microsoft Innovations Club directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
