AWS regions and Availability Zones
 Christober
Christober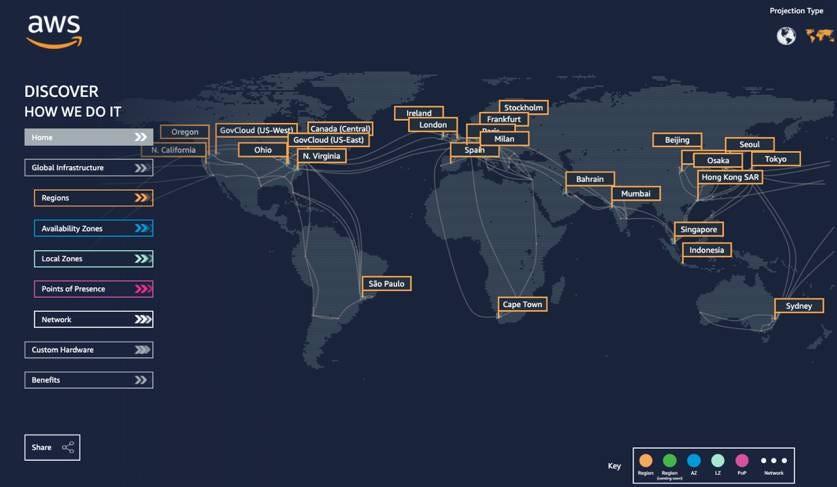
AWS Global Infrastructure
Why choose AWS?
For the tenth year in a row, AWS is evaluated as a Leader in the 2021 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services
AWS has Global Infrastructure with over 26 geographic regions worldwide and 84 Availability Zones with announced plans for more Regions and Availability Zones(AZ) in future. It has resources and data in multiple locations to improve performance, provide fault tolerance, high availability, and cost optimization.
AWS Regions
AWS Region is cluster of data centers which are located on separate geographic area. Every AWS Region is physically isolated from every other region. Moreover every region is independent of location, power, cooling , physical security etc. from every other region.
Interestingly, not all AWS services are available in every region. Each region offers different services, so we must take into consideration while architecting infrastructure that some services are classed as global services, such as Route 53, Identity and Access Management (IAM) , CloudFront etc. which means they are not tied to a specific region while most services are region-specific i.e. they are tied to specific region. So, when you view your resources, you see only those resources that are tied to the AWS Region that you specified.
Here’s a look at the different regions…..

AWS regions
AWS regions are present worldwide to handle workloads that are latency-sensitive. We can see in above picture, we have a whole lot of regions .In AWS, regions have names such as us-east-1, eu-west-1, eu-west-2 etc.. Inside each region, we have Availability Zones. Usually we have 3 AZ, minimum we can have 2 AZ and maximum 6 AZ in a region. Pricing varies from region to region. It’s also recommended to launch services to the nearest region possible to reduce latency.

Source: Amazon docs
In this example, we have two regions, which contains 3 availability zones each. AZ’s are interconnected to each other with ultra low-latency network. Both regions 1&2 are physically isolated and independent of each other. While each region is isolated from one another, they can communicate with each other over the Amazon Global Network.
Availability Zones
AWS region consists of multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones. Availability Zone is a grouping of one or more discrete data centers that provide applications and services in AWS region. Each AZ has independent cooling, power, and physical security.
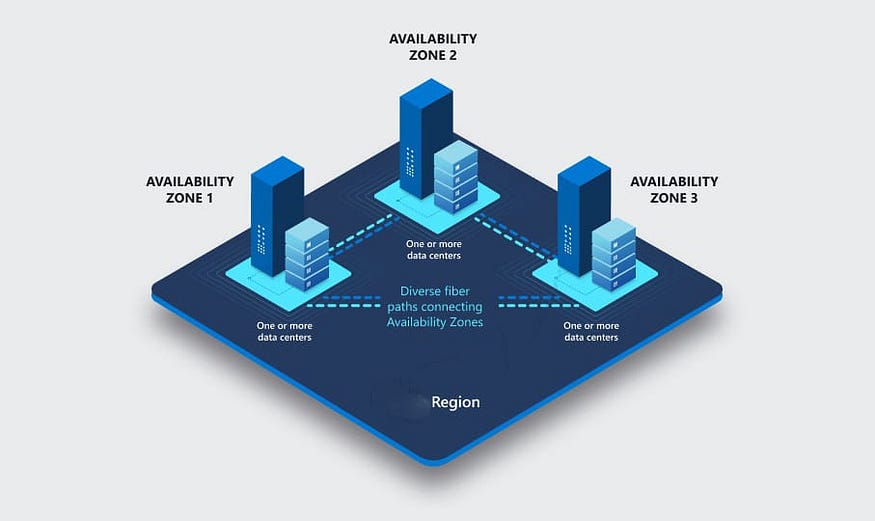
All AZs are physically isolated from each other by significant distance, although all are within 60 miles of each other. Every AZ in AWS Region are interconnected through low latency , high throughput. fully redundant networking channels.
AZs give customers the ability to operate production applications and databases. This is where the actual compute, storage, network, and database resources are hosted that we as consumers provision within our Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs). All traffic between AZs is encrypted.
N**OTE: 1 AZ doesn’t mean only 1 data center, 1 AZ can have one or more data centers.

In above example, we have 1 region consisting of 3 availability zones (physically isolated but interconnected through low latency network). If you distribute the resources across all availability zones, even if one zone fails, the resource will still be available redundantly across other AZ’s.

These are the list of Availability zones currently available to us. Suppose we are in Ireland region( eu-west-1), it consists of 3 AZ’s, its names are eu-west-1a, eu-west-1b, eu-west-1c(these represents Ireland’s Availability zones)
NOTE: While using AWS services, its recommended to use the AZ that is nearest to you to reduce latency.
NOTE: Data transfer fee is generated if you wish to transfer data across regions(one region to another region), but its free of cost if your transfer data across AZ’s within same region.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Christober directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Christober
Christober
A sophomore undergrad Engineering Student Learning DevOps and like to deepen my Knowledge in this field.