1.VMWare:VSphere
 Goutam Kumar
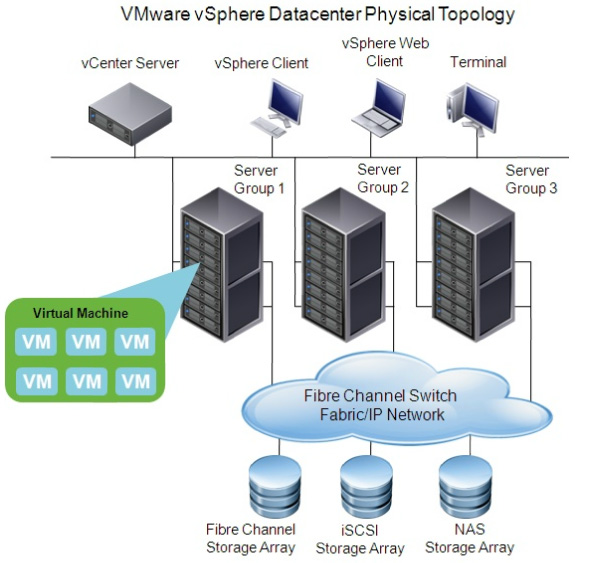
Goutam KumarVMware ESXi | A virtualization layer runs on physical servers that abstract processor, memory, storage, and resources into multiple virtual machines. |
VMware vCenter Server | The central point for configuring, provisioning, and managing virtualized IT environments. It provides essential datacenter services such as access control, performance monitoring, and alarm management. |
VMware vSphere Client | An interface that enables users to connect remotely to vCenter Server or ESXi from any Windows PC. |
VMware vSphere Web Client | A Web interface that enables users to connect remotely to vCenter Server from a variety of Web browsers and operating systems. |
VMware vSphere SDKs | Feature that provides standard interfaces for VMware and third-party solutions to access VMware vSphere. |
vSphere Virtual Machine | A high performance cluster file system for ESXi virtual machines. |
vSphere Virtual SMP | Enables a single virtual machine to use multiple physical processors simultaneously. |
vSphere vMotion | Enables the migration of powered-on virtual machines from one physical server to another with zero down time, continuous service availability, and complete transaction integrity. |
vSphere Storage | Enables the migration of virtual machine files from one datastore to another without service interruption. You can place the virtual machine and all its disks in a single location, or select separate locations for the virtual machine configuration file and each virtual disk. The virtual machine remains on the same host during Storage vMotion. |
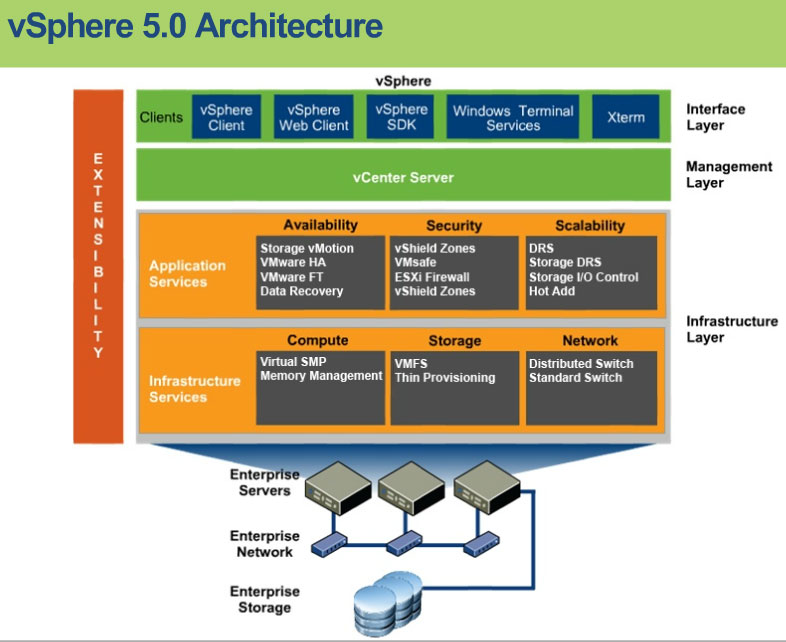
vSphere High | A feature that provides high availability for virtual machines. If a server fails, affected virtual machines are restarted on other available servers that have spare capacity. |
vSphere Distributed | Allocates and balances computing capacity dynamically across collections of hardware resources for virtual machines. This feature includes distributed power management (DPM) capabilities that enable a datacenter to significantly reduce its power consumption. |
vSphere Storage DRS | Allocates and balances storage capacity and I/O dynamically across collections of datastores. This feature includes management capabilities that minimize the risk of running out of space and the risk of I/O bottlenecks slowing the performance of virtual machines. |
vSphere Fault Tolerance | Provides continuous availability by protecting a virtual machine with a copy. When this feature is enabled for a virtual machine, a secondary copy of the primary virtual machine is created. All actions completed on the primary virtual machine are also applied to the secondary virtual machine. If the primary virtual machine becomes unavailable, the secondary machine becomes immediately active. |
vSphere Distributed | A virtual switch that can span multiple ESXi hosts, enabling significant reduction of on-going network maintenance activities and increasing network capacity. This increased efficiency enables virtual machines to maintain consistent network configuration as they migrate across multiple hosts. |
Host Profiles | A feature that simplifies host configuration management through user-defined configuration policies. |
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Goutam Kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
