Run GPT4ALL Locally and Build a Simple QnA Program
 Tanmay Sarkar
Tanmay Sarkar
Introduction 🙋🏻♂️
Hey Guys, It's Tanmay here, and today I'll be talking about How you can run a smaller version of LLM on your machine directly, totally free of cost.
As we all know, Using and building on top of LLMs is costlier. Some students and researchers can't pay much amount of money to further study these models. That's why GPT4ALL is here.
Today, we'll use this quantized model to build a very simple QnA program instead of OpenAI's GPT. So stay along and enjoy the journey.
Also, if you are not the reader type, watch this video Here. I covered all everything in that video but this blog is necessary because I can write in detail here.
How Quantized GPT4ALL works?
GPT4ALL is trained on top of Facebook's LLaMA. We can't run Facebook's model on our machine because it is very big and has more than 7 billion parameters. That's why engineers used tricks like fine-tuning and inference to make smaller versions.
The underlying algorithm that takes place is Quantization, where it maps every continuous infinite value to a smaller set of discrete values. It basically converts the pre-trained model weights to 4-bit precision using the GGML format. So, the model uses fewer bits to represent the numbers. Therefore, reducing memory usage and faster inference.
Running GPT4ALL Locally 👷🏻
Requirements :
Steps :
Download the model: You have to download the quantized model weight from this link (https://the-eye.eu/public/AI/models/nomic-ai/gpt4all/). The model name is
gpt4all-lora-quantized-ggml.bin.Clone converter repo: Run the command to clone
llama.cppthat is used to convert our model weight to a newer format. Becauselangchainonly supports the newer formatted models.git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp.gitCheckout to a specific stage: You've to set the repo to a previous stage
2b26469. Because the latest versionllama.cppdoesn't quite work well and throws a lot of errors.cd llama.cpp && git checkout 2b26469Convert the model: To convert it, you have to run the
convert.pyargument valuepath-to-our-downloaded-modelSo you can just move the model tollama.cpp/modelsthe directory.# Inside llama.cpp directory python3 convert.py models/gpt4all-lora-quantized-ggml.bin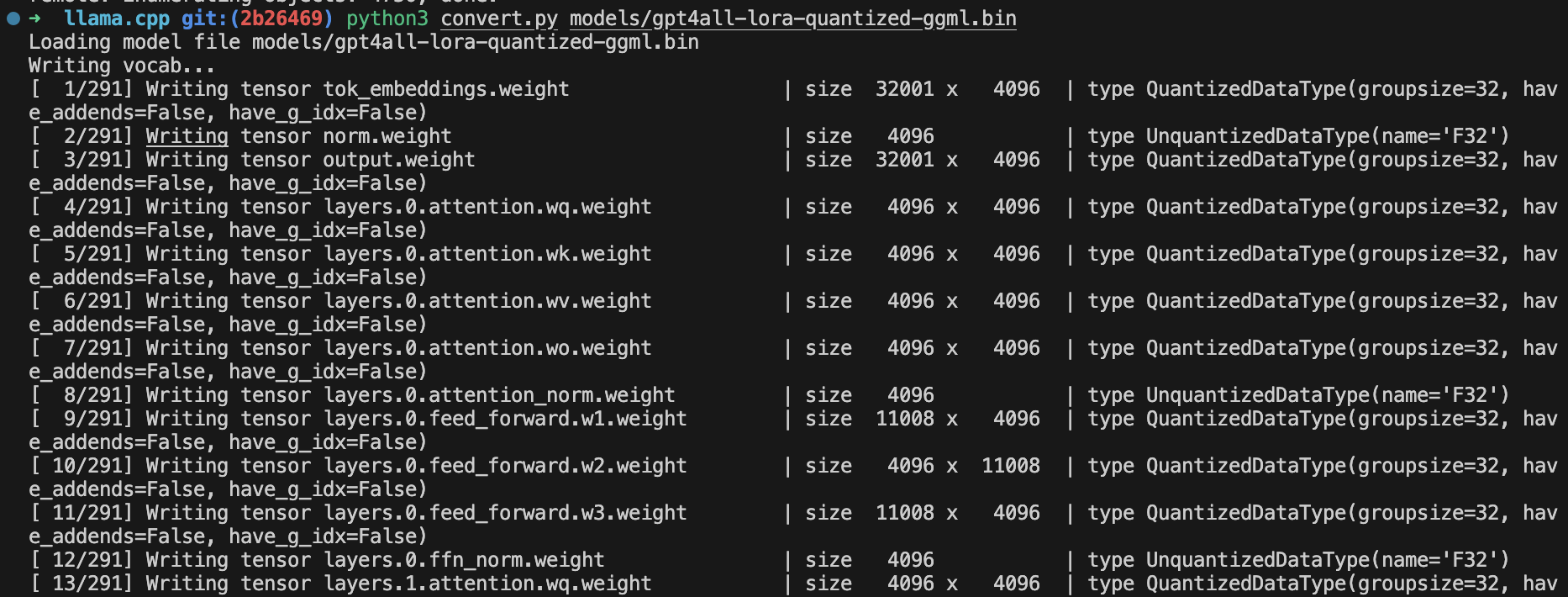
Our conversion to a newer format is now successfully done, you can check that out in the
/models/directory. There must be a new file named similar toggml-model-q4_0.bin. Now, we can build a simple program using GPT4ALL.Now, Coding the program: Our program will take any question and try to answer in a step-by-step manner in 100 words.
Before starting, you have to install
langchainthe library bypip install -q langchain==0.0.152from langchain import PromptTemplate, LLMChain from langchain.llms import GPT4All from langchain.callbacks.base import CallbackManager from langchain.callbacks.streaming_stdout import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler # Create a callback manager and add a callback handler for streaming stdout callback_manager = CallbackManager([StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()]) # Create an LLM using the GPT4All model llm = GPT4All(model="llama.cpp/models/ggml-model-q4_0.bin", callback_manager=callback_manager, verbose=True) # Create a template for prompting the LLM template = """Question: {question} Answer: Let's think step by step in 100 words. """ prompt = PromptTemplate( template=template, input_variables=["question"] ) # Create an LLM chain chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt) # Prompt the chain with a question q = "How rain falls?" chain.run(q)Running our program: You can change the
qvariable to ask any question you want. Try out different questions, and see our this model performs on your machine. I have an MBA 8GB with 256GB SDD, and I still think a 16GB version would do a lot better in terms of faster output generation time.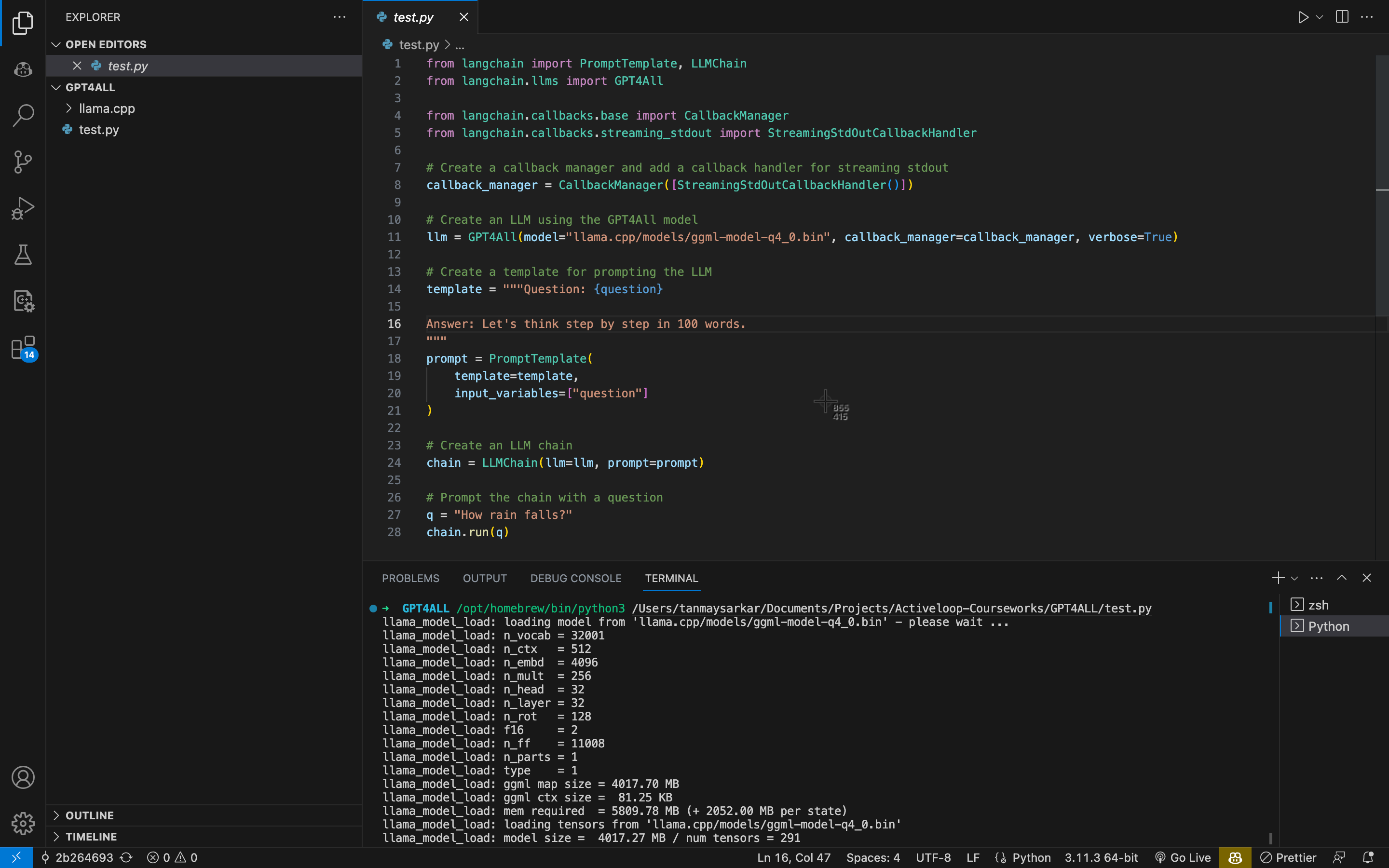
pip3 test.py # will run the programRunning the code may take a lot of time, so you've to be patient at first.
Understanding the Output: Let us see the output first.

This 100 words output took a lot of time on my machine, if there is any trick to make it faster, please do tell us in the comments.
In the code, we used the
StreamingStdOutCallbackHandlerandverbose=Truebut why? It is because we want to see the output in real-time and with a lot of extra system details.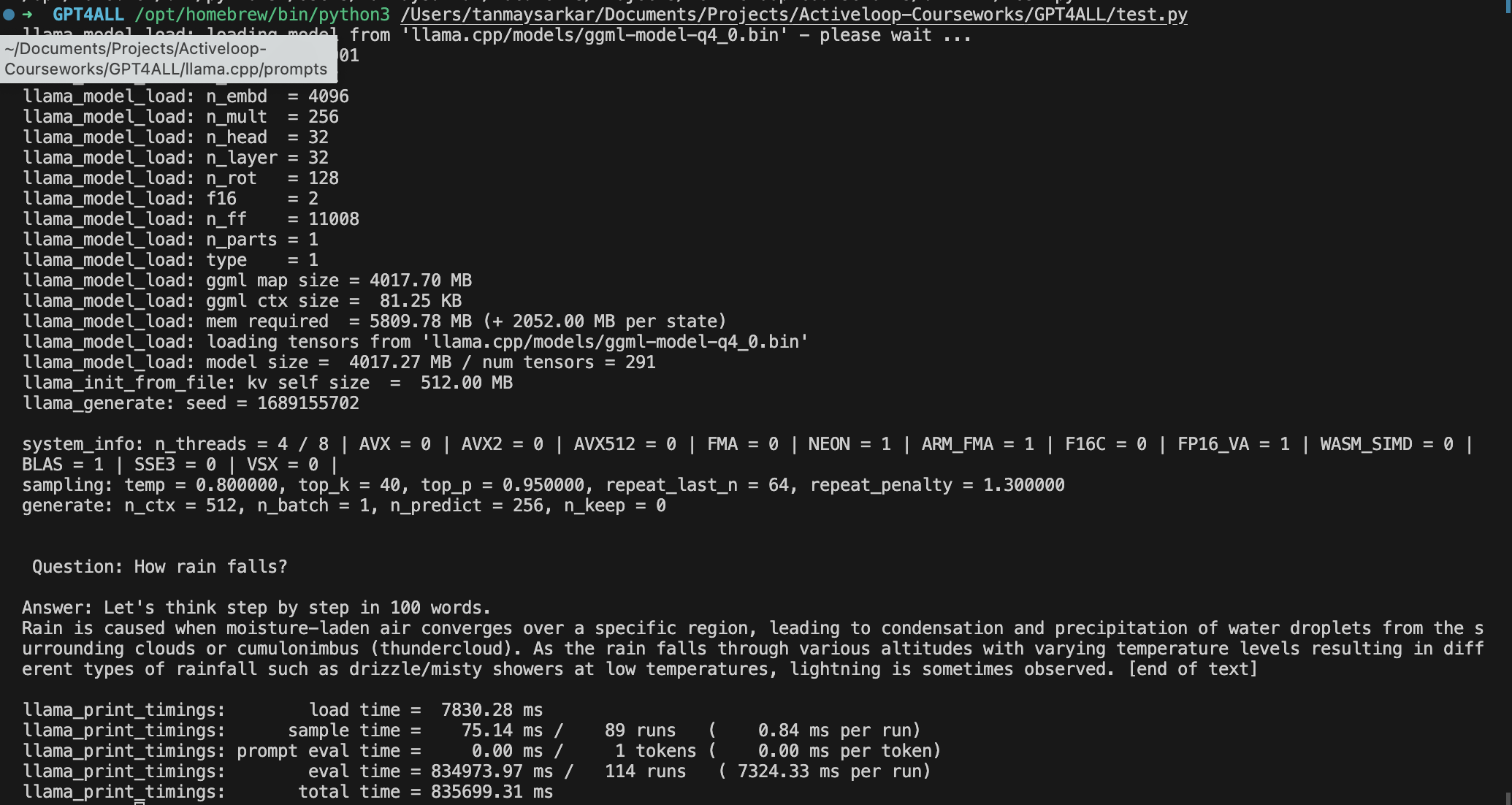
Conclusion ⏰
In this blog post, I showed you how to run a smaller version of LLM on your machine directly, totally free of cost. I used GPT4ALL, which is an open-source software ecosystem that allows anyone to train and deploy powerful and customized large language models (LLMs) on everyday hardware.
I also showed you how to build a simple QnA program using GPT4ALL. Our program takes any question and tries to answer in a step-by-step manner in 100 words.
Here are some additional thoughts:
The GPT4ALL model is still under development, so the output may not always be perfect. However, it is a great way to get started with LLMs and see how they can be used to build real-world applications.
The code in this blog post is just a starting point. You can experiment with different questions and prompts to see how the model performs. You can also try to improve the performance of the model by using a faster machine or by fine-tuning the model.
I hope you learned something new today. If you have any questions, feel free to ask me in the comments below. I will be happy to help you. It would be great if you share this article with your developer friends who are new to tech.
For reference, I wrote this article after learning these topics from a course called LangChain & Vector Databases in Production. I highly suggest you join it and learn in-depth about these topics. I've used some code snippets and an image from their coursework.
Follow me on @sarkartanmay393
Direct mail me at sarkartanmay393@gmail.com
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tanmay Sarkar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tanmay Sarkar
Tanmay Sarkar
DevOps and Open Source Enthusiast and CSE Student