Time-Series Database (TSDB) for IoT: The Missing Piece
 EMQX
EMQX
What Is a Time-Series Database (TSDB)?
A Time-Series Database (TSDB) is a software system specifically designed to handle time-series data, sequences of data points indexed by time. These data points typically consist of successive measurements made over a time interval and are used to track and analyze patterns of change over time.
The main difference between time-series data and other data types is that time information is an integral part of the data. For instance, think about monitoring the stock market. The value of a particular stock is only meaningful at a specific point in time. As such, time-series data often consists of timestamps and corresponding values, making it different from traditional relational data.
TSDBs are optimized for handling this type of data, providing functionalities that are not available in other database systems. They are designed to efficiently ingest, store, and query large amounts of time-stamped data. This makes them ideal for many applications—first and foremost, data streaming from IoT devices.
How Does a Time-Series Database Work?
A TSDB stores data in a time-series format, organizing it based on timestamps. This structure allows for efficient querying and analysis of data over time. When new data arrives in a TSDB, it gets appended to the existing time-stamped data, creating a continuous time-series. The database then uses various indexing and compression techniques to store this data efficiently. This allows for fast retrieval of data when queried for specific time periods or patterns.
One of the key features of a TSDB is its ability to handle high write and read loads. Given that time-series data is continuously generated, the database needs to be capable of ingesting large amounts of data in real-time. Similarly, the database also needs to provide fast query responses, as users often need to analyze recent data in a time-sensitive manner.
Why Are Time-Series Databases Critical for the Internet of Things (IoT)?
IoT devices have become increasingly prevalent in various industrial sectors, generating massive volumes of data. These devices, such as sensors, actuators, and connected machines, collect real-time data about the environment, equipment, and processes.
Time-series data, representing data points indexed by time, is particularly relevant in industrial settings. It provides a historical perspective on how variables change over time, enabling trend analysis, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics. Industries can leverage this data to monitor performance, detect patterns, identify inefficiencies, and anticipate future events.
Time-series databases are an excellent choice for IoT data storage and analysis. They offer several advantages uniquely suited for handling time-series data from IoT devices:
Efficient storage and scalability: A typical TSDB is designed to efficiently store and manage time-series data at scale. It leverages advanced storage techniques like data compression and time-partitioning, which optimize storage utilization and improve query performance. As IoT devices generate a massive volume of data, TSDB’s ability to handle large datasets and scale horizontally makes it well-suited for IoT deployments.
High ingestion rate: IoT devices often produce data at high velocities, requiring fast data ingestion capabilities. TSDB excels in this area, providing high-speed data ingestion to handle millions of data points per second. This ensures that incoming data from IoT devices can be efficiently and promptly stored in the database without overwhelming the system.
Fast and flexible querying: TSDB offers query capabilities tailored for time-series data analysis. It includes optimized functions, operators, and indexing techniques that enable efficient querying and analysis of time-stamped data. With its ability to handle complex queries involving time intervals, sliding windows, and aggregations, TSDB empowers users to extract valuable insights from IoT time-series data quickly and accurately.
Continuous aggregations: TSDBs introduce the concept of continuous aggregations, which allows users to precompute and store aggregate data at different time intervals. This feature significantly accelerates performance for common aggregation queries, such as computing averages, sums, or counts over specific time ranges. For IoT applications requiring real-time analytics and dashboards, continuous aggregations provide a significant performance boost.
The Missing Piece: Why TSDB Needs an Efficient Communication Protocol for IoT
While TSDBs are highly suitable for the unique characteristics and demands of time-series IoT data, they do not operate in isolation. In fact, they are just one piece of a much larger IoT ecosystem. To fit seamlessly into this ecosystem, TSDBs require a highly efficient communication protocol. This protocol needs to be capable of reliably and effectively transmitting the high-volume, high-velocity time-series data generated by IoT devices.
The need for an efficient communication protocol arises from the unique challenges associated with IoT data:
Time-sensitive data
The data generated by IoT devices is typically time-sensitive, requiring rapid and reliable transmission. Any delays or data loss could significantly impact real-time analytics and decision-making processes.
Unreliable connectivity
IoT devices often operate in environments with intermittent or low-bandwidth connectivity. Traditional data transfer protocols that work well in stable, high-bandwidth environments are unsuitable in such cases. Thus, the communication protocol must be lightweight, ensuring that data can be transmitted efficiently even under challenging network conditions.
Very large scale
The sheer scale of IoT deployments presents a challenge. With potentially millions of devices each generating data continuously, the communication protocol must be capable of handling this massive data volume without becoming a bottleneck. This requires a protocol that can maintain high throughput and low latency under heavy loads.
The need for publish-subscribe
The communication protocol needs to support a publish-subscribe model to efficiently distribute data. IoT devices often generate data that is of interest to multiple applications or services. Instead of each service independently pulling the data from each device—a highly inefficient approach—a publish-subscribe model allows the devices to publish data once, with the protocol then taking responsibility for distributing the data to all interested subscribers.
In summary, while TSDBs provide the capabilities necessary for storing and analyzing time-series IoT data, they need to be complemented by an efficient communication protocol to be effective. This protocol needs to be fast, reliable, lightweight, scalable, and support a publish-subscribe model. Without such a protocol, the full potential of TSDBs in IoT applications cannot be realized.
What Is MQTT?
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight messaging protocol that is used to send data between devices, often in the context of IoT. It's designed for situations where network bandwidth is limited, and it's particularly useful for remote locations where other protocols might not be practical.
MQTT is based on the publish-subscribe model. Devices, or "clients", subscribe to topics. When a message is published to a topic, the MQTT broker ensures all subscribers receive the message. This model is efficient and flexible, allowing for communication between a wide range of devices and systems without the need for a direct connection.
MQTT plays a crucial role in time-series data, and is especially designed for IoT scenarios. Since it's designed to handle intermittent connections and ensure message delivery, it's ideal for sending time-series data from IoT devices to a TSDB. The lightweight nature of MQTT means it can handle the high volumes of data generated by IoT devices, making it an integral part of the data pipeline.
Use Cases of MQTT in Industrial IoT Data Collection and Storage
Many use cases demonstrate the versatility and power of integrating MQTT with TSDB for Industrial IoT applications:
Industrial production monitoring: Collecting and storing real-time sensor data from manufacturing equipment, machinery, and processes to monitor performance, detect anomalies, and optimize operations
Energy management: Integrating MQTT with TSDB to track and analyze energy consumption patterns in industrial facilities, enabling better energy management strategies and identifying opportunities for energy savings.
Predictive maintenance: Utilizing MQTT and TSDB to gather sensor data from industrial machinery and equipment for predictive maintenance analysis, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Quality control and defect detection: Collecting and Storing time-series data from IoT sensors and devices integrated with manufacturing processes to monitor product quality in real-time, detect defects, and trigger corrective actions.
Supply chain and logistics: Leveraging MQTT for real-time tracking and monitoring of goods, vehicles, and assets in the supply chain. Meanwhile, using TSDB for storing and analyzing the data to optimize logistics operations, improve inventory management, and enhance delivery efficiency.
How EMQX Enables Easy Integration of Time-Series Databases with MQTT
EMQX, provider of a popular MQTT broker, can seamlessly integrate with various TSDBs, such as Timescale, InfluxDB, and Apache IoTDB, making them compatible with various IoT frameworks and tools. This integration facilitates smooth data flow from Industry IoT devices to TSDB, streamlines data processing pipelines, and simplifies Industry IoT data management architecture.
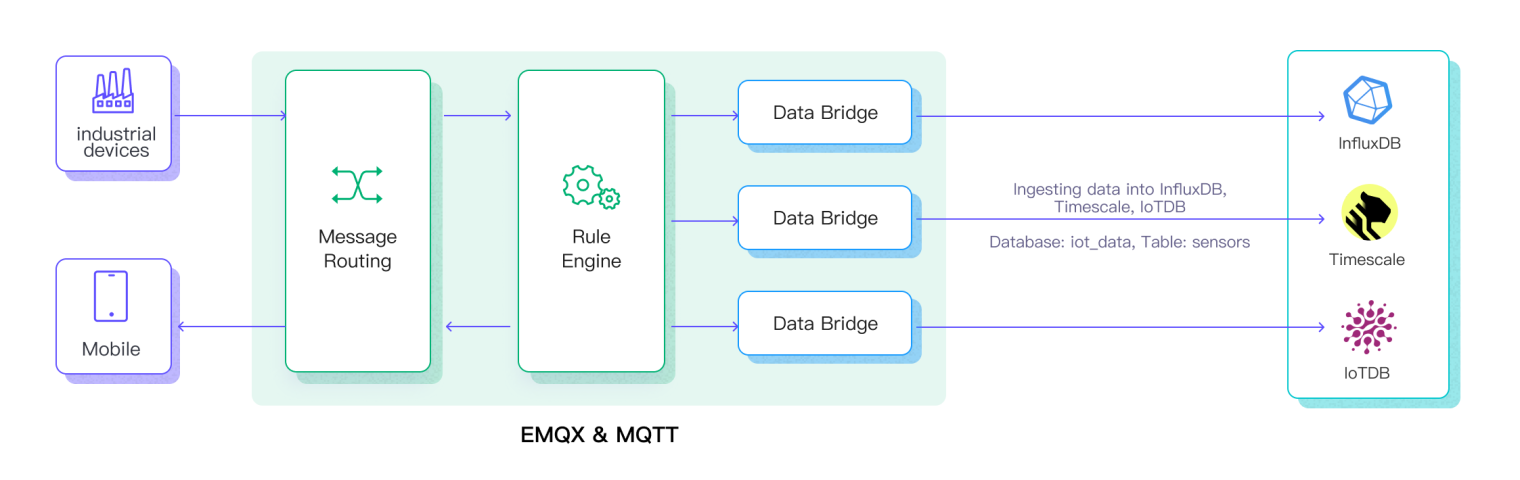
The EMQX Data Integration component provides the following features when integrating with a TSDB:
Full support for MQTT 5.0: EMQX enables devices to connect to a TSDB using either MQTT protocol version 5.0 or 3.1.1.
Reliable data ingestion to TSDB: EMQX has an on-disk message buffer to prevent data loss when the TSDB is unavailable.
Real-time data transformation: Extract, filter, enrich, and transform in-flight data using an SQL-based rule engine.
Real-time metrics and monitoring: EMQX enables real-time monitoring for messages transferred between the MQTT broker and TSDB.
Integrating EMQX with your TSDB solution has several significant benefits for IoT time-series workloads:
Efficient Data Collection: MQTT is a lightweight and efficient messaging protocol for IoT devices with limited resources. It enables efficient and reliable data transmission between IoT devices and brokers. By integrating EMQX with TSDB, IoT time-series data can be seamlessly collected and ingested into the database, ensuring reliable and efficient data collection from a large number of devices.
Scalability and High Throughput: Harnessing the power of EMQX and TSDB integration, organizations can achieve remarkable scalability and high throughput for their IoT time-series workloads. EMQX is designed to scale horizontally, effortlessly managing the surging message traffic generated by an ever-expanding fleet of IoT devices. This solution effortlessly accommodates the increasing data volume and supports high-concurrency access. As a result, IoT time-series workloads can effortlessly handle the mounting demands of data ingestion, storage, and processing as IoT deployments scale to new heights.
Optimized Time-Series Storage: TSDB, a purpose-built time-series database, provides optimized storage for time-stamped data. It leverages time-partitioning, compression, and data retention policies to store and manage large volumes of time-series data efficiently. This ensures a minimal storage footprint while maintaining high performance, essential for IoT workloads that generate massive amounts of time-series data.
Fast and Complex Querying: TSDB offers powerful time-series-specific functions, operators, and indexing techniques. This enables fast and efficient querying of time-series data, allowing complex analyses, aggregations, and filtering based on time intervals or specific conditions. Integrating EMQX data with TSDB facilitates seamless querying of IoT time-series data, empowering organizations to extract valuable insights and perform advanced analytics for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and decision-making.
Conclusion
Integrating MQTT and EMQX with TSDB offers a powerful solution for managing Industry IoT time-series workloads. EMQX's reliability, scalability, and support for high message throughput make it an excellent choice for handling the vast amounts of data generated by Industry IoT devices. Combining EMQX and TSDB empowers organizations to efficiently collect, store, process, and analyze IoT time-series data, leading to real-time insights, proactive decision-making, and improved operational efficiency.
Originally published at www.emqx.com
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from EMQX directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

EMQX
EMQX
EMQX is the world's most scalable open-source MQTT broker with a high performance that connects 100M+ IoT devices in 1 cluster, while maintaining 1M message per second throughput and sub-millisecond latency.