Mastering Linux Basics: User Management and Automated Backups
 Shakshi Jain
Shakshi Jain
Welcome to Day 5 of the #90DaysOfDevOpsChallenge! Today, we'll delve into advanced Linux shell scripting, focusing on User Management and creating powerful automated backup scripts. Let's harness the full potential of shell scripting for DevOps efficiency! 💻🚀
What are Dynamic Directories?
Dynamic Directories refer to directories or folders that are created programmatically or automatically with a changing or dynamic nature. In the context of shell scripting, creating dynamic directories means generating folders on the fly, usually based on certain conditions, user inputs, or time-based factors.
Dynamic directories are commonly used in scenarios where the number or naming of directories needs to adapt to different situations, making the script more flexible and adaptable. Some common use cases for dynamic directories include:
Automated Backup, User Management, Log Files
Task 1:
Create a bash script named create directories. sh that, when executed with three arguments, generates a specified number of directories with dynamic names. The script should take the following three arguments: Directory Name, Start Number and End Number
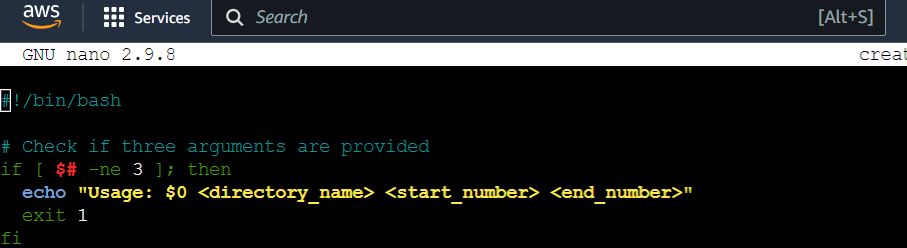
The if statement checks whether the number of arguments provided when executing the script is not equal to 3. If there are not exactly three arguments, the script will print a usage message with instructions on how to use the script and exit with a status of 1, indicating an error.
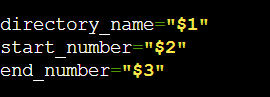
These lines store the three arguments provided when executing the script into three variables: directory_name, start_number, and end_number.
The $1, $2, and $3 represents the first, second, and third arguments, respectively.

This block of code defines a function called create_directories. Functions in bash allow us to group and reuse code. Inside the function, a for loop is used to iterate from start_number to end_number.
In each iteration, a variable dir_name is created by combining directory_name with the current value of i. For example, if directory_name is "day" and i = 3, dir_name will be "day3".

Task 2:
Create a Script to back up all your work done till now.
Automated backup is the process of automatically creating copies of important data and configurations at regular intervals.
For DevOps engineers, it ensures data safety, allows system recovery, reduces downtimes, simplifies testing, and prepares for disaster scenarios.
It ensures that data remains available and intact, allowing engineers to focus on continuous improvement and innovation rather than worrying about potential data loss.
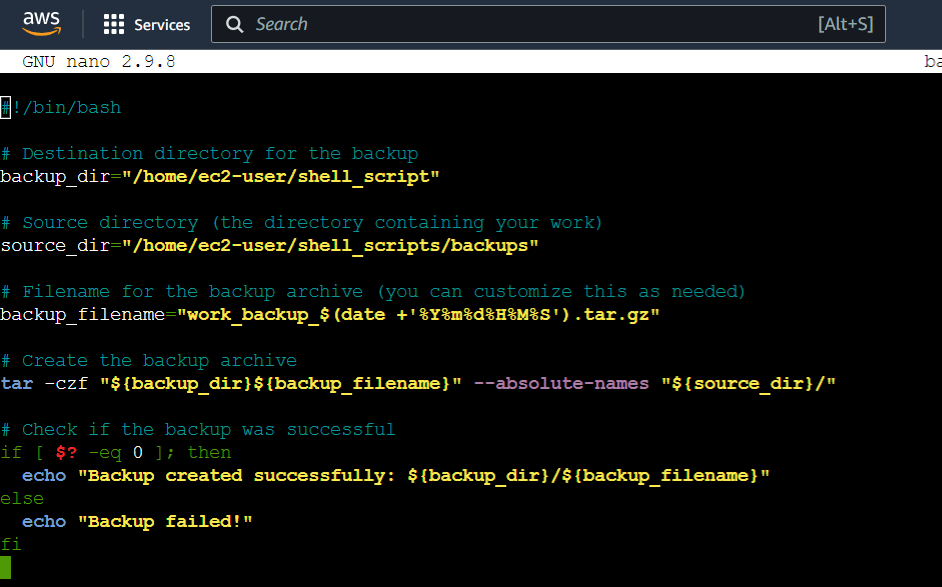

The backup script (backup. sh) automatically creates a compressed backup of specified directories. It takes the base directory name, start and end numbers as inputs. The script uses tar to create a backup archive with the current date and time in the specified backup directory.
Task 3:
Automating Backup. sh Script with Cron:
With this Cron job, you ensure that your data is regularly backed up, reducing the risk of data loss and allowing you to restore your work to a previous state if needed. The automation provided by Cron simplifies the backup process and ensures consistency in performing the task.
Open a terminal or command prompt.
Type the command: crontab -e to edit the cron schedule.
Add a new line to schedule the backup.sh script. For example, to run it every day at 2:00 AM, write:

Replace "/path/to/your/backup_script.sh" with the actual path to your backup script.
Save the cron schedule and exit the text editor.
Now, the backup. sh script will be automatically executed every day at 2:00 AM, creating backups of the specified directories as per the arguments provided.
Task 4:
User Management in Linux
User management scripts are scripts designed to automate the process of managing user accounts on a computer system.
These scripts allow DevOps engineers to create, modify, delete, and configure user accounts, groups, and permissions in an automated and efficient manner.
By leveraging user management scripts, organizations can efficiently manage user accounts, enforce security measures, reduce administrative overhead, and maintain a consistent and secure user environment.
Overall, user management scripts are a vital tool for ensuring a well-organized and secure user management process in various IT and DevOps environments.
Task 5:
Create a script for creating users and displaying their Usernames
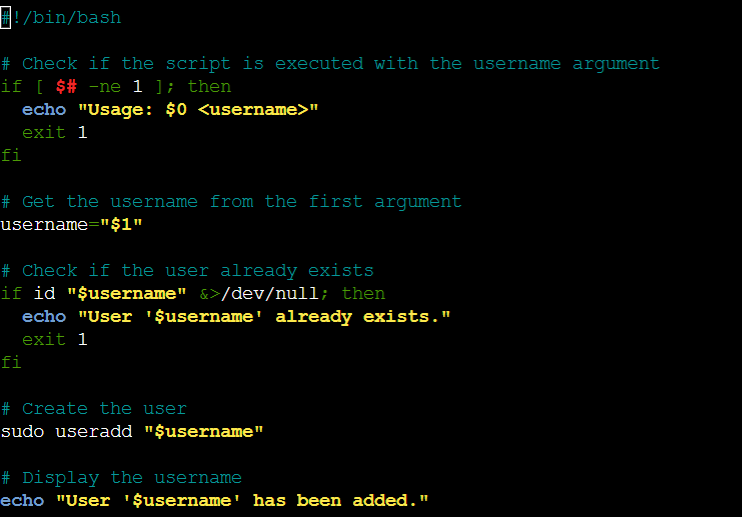
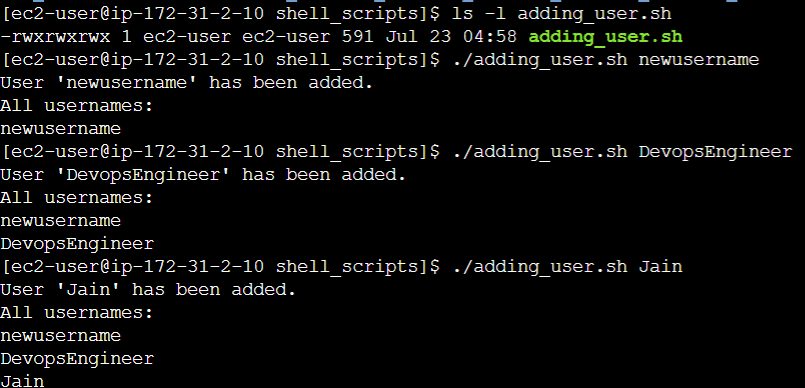
Saved the above script as a file named adding_user.sh. Give execute permission to the script using the command: chmod +x adding_user.sh
The script will create the user (if it doesn't already exist), display the username, and append it to the usernames.txt file.
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing Day 5 of the #90DaysOfDevOps challenge! 🌟 I hope you found the content insightful and useful in your journey to becoming a skilled DevOps engineer. Thanks for taking the time to read my blog!
If you enjoyed the blog, please like and share it with your friends and colleagues. Sharing knowledge and insights within the DevOps community is a fantastic way to inspire and support one another.
Stay tuned for more exciting content in the upcoming days of this challenge. Keep up the great work, and let's continue our DevOps adventure together! 🚀💻 Don't hesitate to reach out if you have any questions or need further assistance. Happy learning! 👍😊
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shakshi Jain directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Shakshi Jain
Shakshi Jain
Welcome to my tech blog! 🚀 Exploring the world of AWS and DevOps tools with passion and curiosity. Join me on this exciting journey as we uncover the wonders of cloud computing and collaborative development Let's level up our tech skills together! 👩💻🌟 #AWS #DevOps #CloudComputing #TechJourney"