Advanced Linux Shell Scripting for DevOps Engineers with User management
 priyanka varshney
priyanka varshneyTable of contents
- Task 1: You have to do the same using Shell Script i.e using either Loops or command with start day and end day variables using arguments -
- Task 2:Write a Script to back up all your work done till now.
- Task 3: Read About Cron and Crontab, to automate the backup Script
- Task 4: What is user management in Linux?
- Task 5: Create 2 users and just display their Usernames.

#Day5 #DevOps #90daysofDevops #trainwithshubham #AWS #linuxcommands #linuxshellscripting #shellscript
Task 1: You have to do the same using Shell Script i.e using either Loops or command with start day and end day variables using arguments -
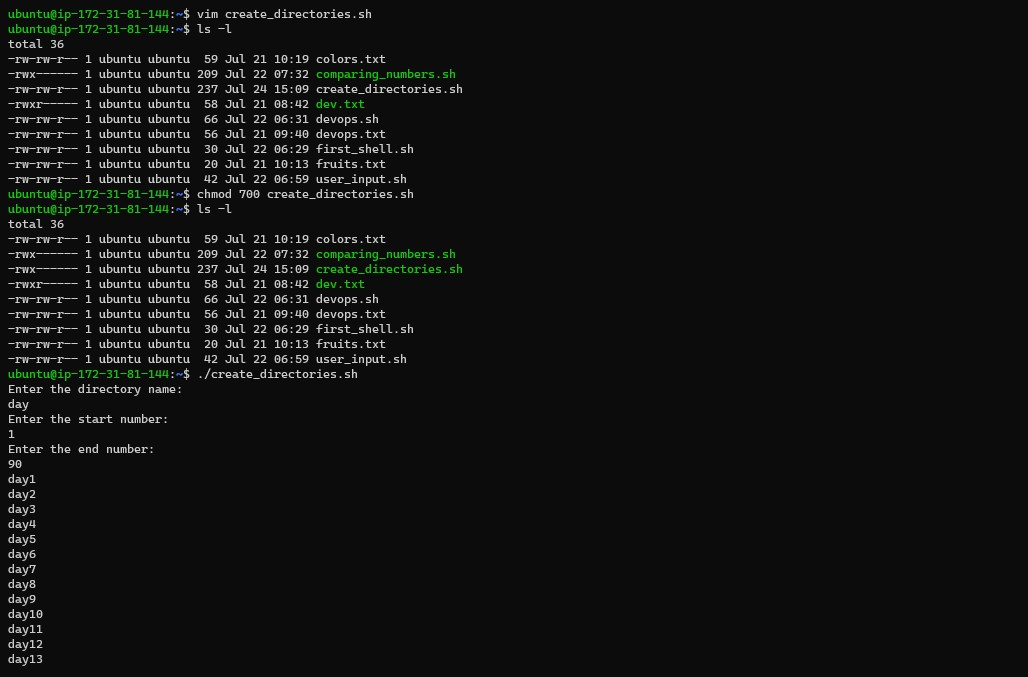
So Write a bash script to create_directories.sh that when the script is executed with three given arguments (one is the directory name and second is the start number of directories and third is the end number of directories ) it creates a specified number of directories with a dynamic directory name.

vim create_directories.sh #to create bash script
#Don't forget to change file permission otherwise, you will face a Permission denied error.
#To check file permission type ls -l and to change permission type chmod 700 and create directories.sh
./create_directories.sh #to run the bash script
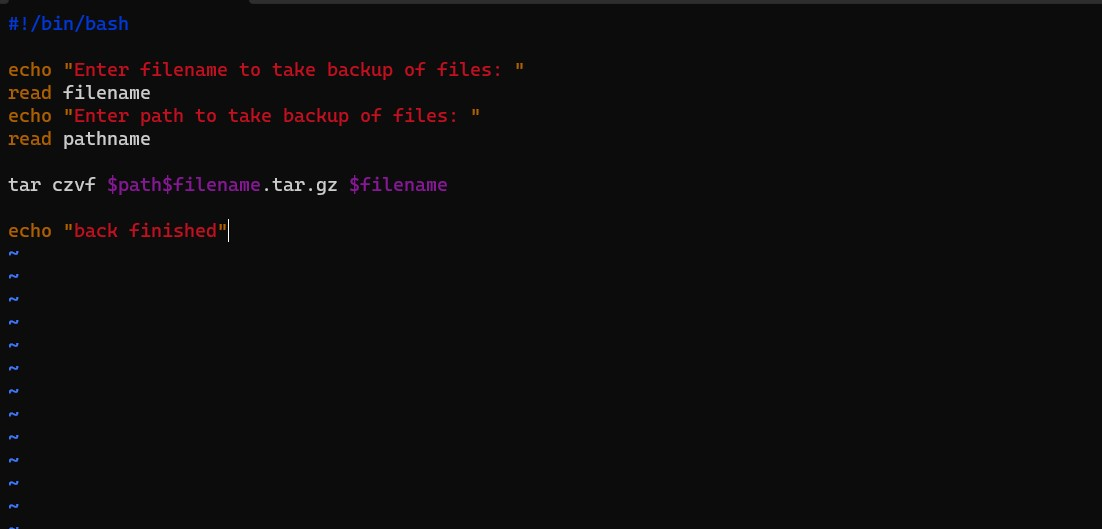
Task 2:Write a Script to back up all your work done till now.
Task 3: Read About Cron and Crontab, to automate the backup Script
Cron is the system's main scheduler for running jobs or tasks unattended. A command called crontab allows the user to submit, edit or delete entries to cron. A crontab file is a user file that holds the scheduling information.

crontab -l will list the active crontab list.
crontab -e is used to edit the crontab file.
crontab - r is used to remove all cron jobs.
Task 4: What is user management in Linux?
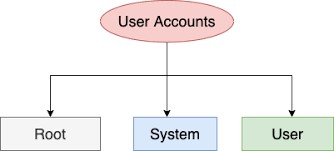
A user is an entity, in a Linux operating system, that can manipulate files and perform several other operations. Each user is assigned an ID that is unique for each user in the operating system. In this post, we will learn about users and commands which are used to get information about the users. After installation of the operating system, the ID 0 is assigned to the root user and the IDs 1 to 999 (both inclusive) are assigned to the system users hence the ids for local user begins from 1000 onwards.
Task 5: Create 2 users and just display their Usernames.

Thank you for reading :)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from priyanka varshney directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

priyanka varshney
priyanka varshney
👋 Hello, and welcome to my DevOps journey! 🚀 I am Priyanka Varshney,🛠️ As an aspiring DevOps engineer, I'm all about bridging the gap between development and operations, making software delivery seamless and efficient. 💻🔧 On this Hashnode blog, I'll be sharing my learnings, experiences and adventures as I dive deep into the world of continuous integration, automation, and cloud technologies. ☁️⚙️ Let's connect, learn, and grow as a vibrant DevOps community. Follow my Hashnode blog, and let's embrace the DevOps adventure together! 🤝🔗