Mastering Hypothesis Testing in Machine Learning: A Beginner's Guide
 ANKIT ANAND
ANKIT ANAND
Hmm, I wonder, what intriguing mysteries might we uncover as we embark on our journey to explore Hypothesis Testing? Let's begin by posing a thought-provoking question, shall we?
What is Hypothesis Testing and Why do we need it?
Hypothesis Testing can be defined as a statistical method used to determine whether the results of an experiment are significant or not. By utilizing sample data from a population, we can draw meaningful conclusions about that population. The outcome of hypothesis testing indicates whether we should accept or reject the null hypothesis, which will be discussed later.
The question arises, why do we need this?
If we propose any hypothetical statement, how can we determine its validity? It is our responsibility to provide evidence for its plausibility. Hypothesis testing offers various techniques to evaluate the hypothesis statement based on the variables and data inputs. It is applicable in nearly every field of research, addressing questions such as whether a new medicine will be effective, if a novel testing method is suitable, or whether the results of random experiments are likely or not.
Important parameters of hypothesis testing
Null Hypothesis -> Null Hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. Hypothesis testing is used to accept or reject a null hypothesis. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted by H₀. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis -> It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It is denoted by H₁ or Ha. For the above example mentioned, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
The p-value is utilized to determine whether the results obtained from a test are statistically significant. It also indicates the likelihood of making an error in either rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. The p-value always falls between 0 and 1 and is compared to an alpha level (α) or significance level, which typically ranges from 1% to 5%.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Z-Test ->
The Z-test is a method of hypothesis testing used for large sample sizes (n ≥ 30). It is employed to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. Additionally, it can be used to compare the means of two samples.
Below are the formulas:
One Sample Z Test Formula

The one-sample Z-test formula is a ratio.
The numerator is the difference between the sample mean and a hypothesized value for the population mean (µ0). This value is often a conjectural argument that you aim to disprove.
The denominator is the standard error of the mean. It represents the uncertainty in how accurately the sample mean estimates the population mean.
"This is the quoted text from the website." (Source: [Statistics By Jim](Z Test: Uses, Formula & Examples - Statistics By Jim))
Two Sample Z Test Formula

The two-sample Z-test formula is also a ratio.
The numerator represents the difference between the two sample means.
The denominator calculates the pooled standard error of the mean by combining both samples. In this Z-test formula, input the population variances (σ2) for each sample.
"This is the quoted text from the website." (Source: [Statistics By Jim](Z Test: Uses, Formula & Examples - Statistics By Jim))
- T-test ->
The T-test is utilized for small sample sizes (n<30). It is also employed to compare the sample mean with the population mean. Additionally, the T-test can be used to compare the means of two samples.



- Chi-Square -> Chi-square is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not.

One-Tailed Hypothesis Testing -> One-tailed hypothesis testing is employed when the rejection region is limited to a single direction. It is also referred to as directional hypothesis testing since it allows for testing the effects in only one specific direction.
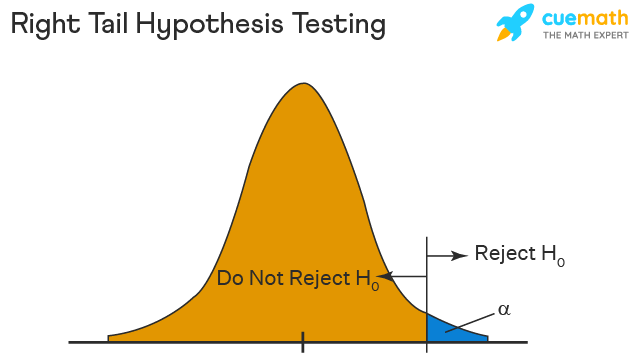
- Right-Tailed Hypothesis Testing-> The right-tail test, alternatively known as the upper-tail test, is utilized to examine whether the population parameter exceeds a certain value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are stated as follows:
1.1) H₀- The population parameter is ≤ some value
1.2) H1- The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
"This is the quoted text from the website." (Source: [Cuemath](Expert Maths Tutoring in the UK - Boost Your Scores with Cuemath))
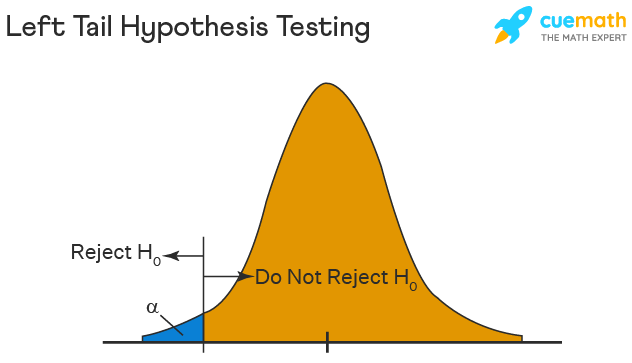
- Left-Tailed Hypothesis Testing-> The left-tail test, also referred to as the lower tail test, is employed to assess whether the population parameter is lesser than a specific value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be formulated as follows:
2.1) H₀- The population parameter is ≥ some value
2.2) H1-The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
"This is the quoted text from the website." (Source: [Cuemath](Expert Maths Tutoring in the UK - Boost Your Scores with Cuemath))
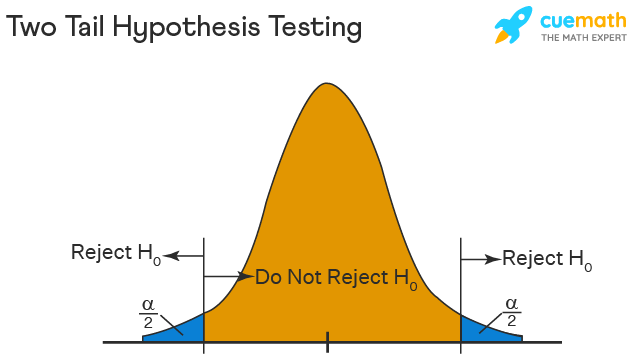
Two-Tailed Hypothesis Testing -> In this method of hypothesis testing, the critical region encompasses both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also referred to as a non-directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is employed when the objective is to determine whether the population parameter differs from a specific value. The hypotheses can be formulated as follows:
H₀- the population parameter = some value
H1- the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
"This is the quoted text from the website." (Source: [Cuemath](Expert Maths Tutoring in the UK - Boost Your Scores with Cuemath))
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be conducted through a straightforward five-step process. One crucial step is correctly formulating the hypotheses and selecting the appropriate method for testing. The fundamental steps for performing hypothesis testing are as follows:
Step 1: Establish the null hypothesis, identifying whether it involves left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed testing.
Step 2: Define the alternative hypothesis.
Step 3: Choose the significance level, α, and determine the critical value.
Step 4: Compute the relevant test statistic (z, t, or χ) and p-value.
Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with α to make a decision. In other words, determine whether to reject the null hypothesis or not.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hypothesis testing is a vital statistical method that helps validate or refute conjectures based on sample data. By understanding the various types of tests, parameters, and steps involved, researchers can derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions in a wide range of fields. Beginners in machine learning must master hypothesis testing to ensure their models are built on solid statistical foundations.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ANKIT ANAND directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

ANKIT ANAND
ANKIT ANAND
👋 Hi, I'm Ankit Anand—a tech enthusiast passionate about web development, Java Full Stack, MERN Stack, and AI/ML. 🚀 Here to share my learning journey, insights, and projects as I explore and grow in the world of tech. Let's learn together! 🌱