Quadratic Voting
 recursive eth
recursive eth 
Table Content:
what is quadratic voting
Traditional voting
How quadratic voting happens
How does it affect the normal Voting system
Conclusion
what is quadratic voting
It's a voting mechanism to allow the participants to express, their preferences more accurately and effectively. Especially when there are several options available.
Traditional voting
In the Traditional voting system each participant can vote for an individual completely, a one can donate only to a single entity. For example:- one person in a country can elect only one president.
How quadratic voting happens
Voice Credit
Allocations
Cost quadratic
Result
Voice Credit:
Voters are given a certain number of voting credits (e.g., coins), which they can use to "purchase" votes. Each vote they cast costs them a certain number of credits, typically following a quadratic cost curve.
Allocations
Voters can distribute their votes across different options or candidates in any way they see fit. They can concentrate all their votes on a single option or spread them out among multiple choices.
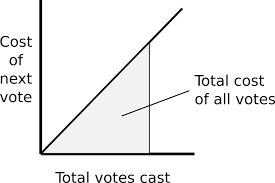
Cost quadratic
The cost of casting votes increases quadratically with the number of votes cast for a single option. For example, if a voter wants to cast 1 vote, it may cost them 1 credit; if they want to cast 2 votes, it may cost them 4 credits; if they want to cast 3 votes, it may cost them 9 credits, and so on.

Result
Finally, results will be counted based on the input and preference chosen by the voters.
How does it affect the normal Voting system:
The idea behind the quadratic cost is that it helps capture the intensity of preferences. Voters must weigh their options carefully, as casting multiple votes for a single choice becomes increasingly expensive. This discourages strategic voting and encourages voters to vote based on their true preferences.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, quadratic voting is an innovative voting mechanism that aims to address the limitations of traditional one-person-one-vote systems. By allowing voters to allocate votes based on their preferences and the intensity of those preferences.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from recursive eth directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
