Embracing Ethereum
 Priyanshi Rai
Priyanshi Rai
When I first encountered Ethereum as a student, I wonder if it is the same as Bitcoin and why it was needed.
The emergence of blockchain technology has ignited a transformative wave across industries, that promise transparency, security, and decentralization. While blockchain is a foundational technology, the shift towards Ethereum, a decentralized platform, has gained significant momentum. We all must have heard these kind of sentences from various articles. But the question is what Ethereum is, how's it different from Bitcoin, and why developers are hustling for it.
What is Ethereum?
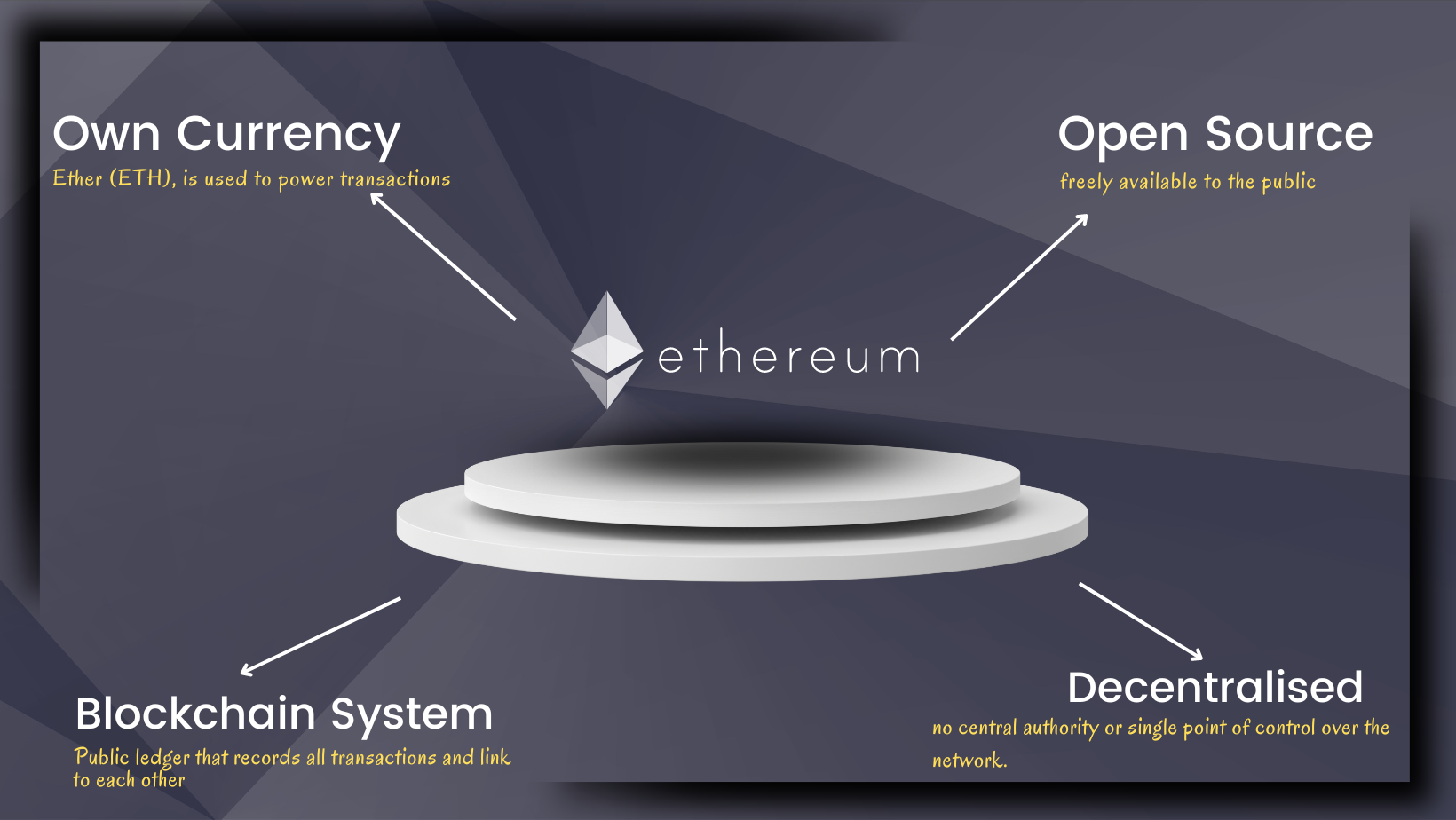
Ethereum was proposed by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 and launched in July 2015. Unlike traditional blockchains that primarily serve as digital currencies (like Bitcoin), Ethereum is designed to be more flexible and can be used beyond the boundaries of a simple transaction. We all know that transactions are very transparent and secure using Bitcoin, so why not use the same technology for other purposes? That's where Ethereum comes into the picture.
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Ethereum has its own cryptocurrency called "Ether" often denoted by the symbol "ETH." Ether serves as the fuel for the Ethereum network and plays a vital role in various functions within the platform.
Now the two terms we need to understand:- Smart Contracts and Decentralised Apps to figure out the role of Ethereum
Smart Contracts
Imagine you have a magic contract that automatically does something for you when certain conditions are met. This magic contract is like a computer program, but instead of being stored on a single computer, it is saved on many computers around the world.
Let's say you and your friend want to make a bet. You both put some money into the magic contract, and you decide that the winner of a game will get all the money in the contract. The magic contract knows the rules of the bet and watches the game closely. As soon as one of you wins the game, the magic contract automatically gives all the money to the winner. No one can cheat or change the rules because the contract is like a very honest and fair referee.
Smart contracts on Ethereum work in a similar way. They are a fundamental feature of Ethereum, distinguishing it from traditional blockchains. They are self-executing contracts with pre-defined rules and conditions that automatically execute when these conditions are met.
Now you must be wondering what's its practical implementation :
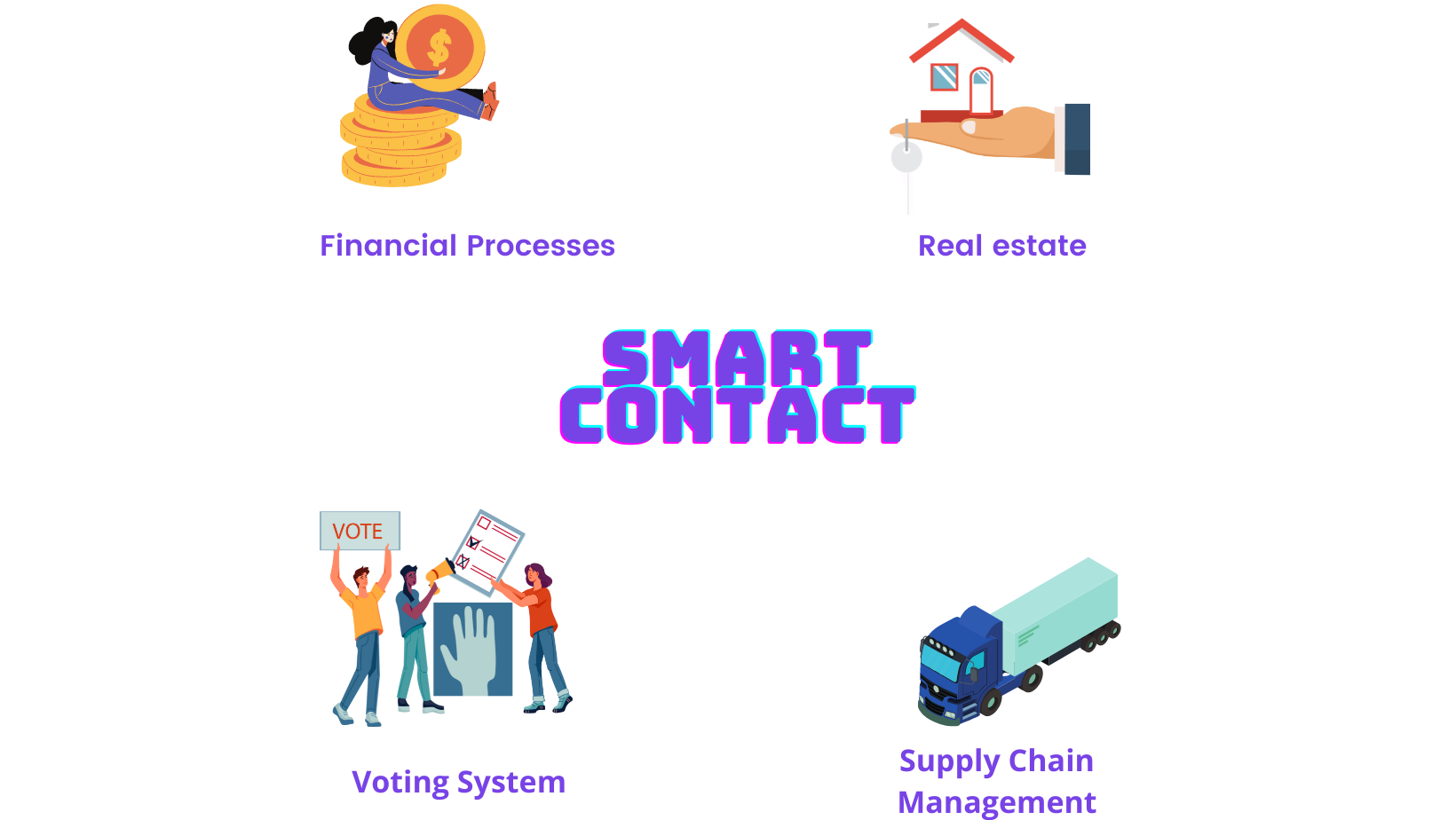
Smart contracts can streamline financial processes, such as facilitating peer-to-peer lending, automatic payment processing, insurance claims settlement, etc.
Smart contracts can create transparent and tamper-resistant voting systems, enhancing the integrity and security of elections and decision-making processes.
Smart contracts can track the movement of goods along the supply chain, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
Smart contracts can automate property transfers, rental agreements, and real estate transactions, reducing paperwork and increasing efficiency.
Decentralized Apps (dApps)
dApps is an application that doesn't have any central authority and operates on a decentralized network.
In simple words when we upload our files on google drive we are dependent on Google for our data storage and security. Now assume suddenly the drive stopped working due to some problem in the Google system. We won't be able to access our own files. This is one of the problems of the centralized system (power in one hand).
Here comes in picture the "dApps" which operates on a distributed network of computers (nodes) that work together to validate and execute transactions and operations. In dApps, users typically have ownership and control over their data and digital assets. They can interact directly with the app and manage their assets using their private keys, enhancing user autonomy. Since most of the dApps are open source, meaning their source code is publicly available for inspection, modification, and contribution by the community. This transparency fosters trust and encourages collaboration.
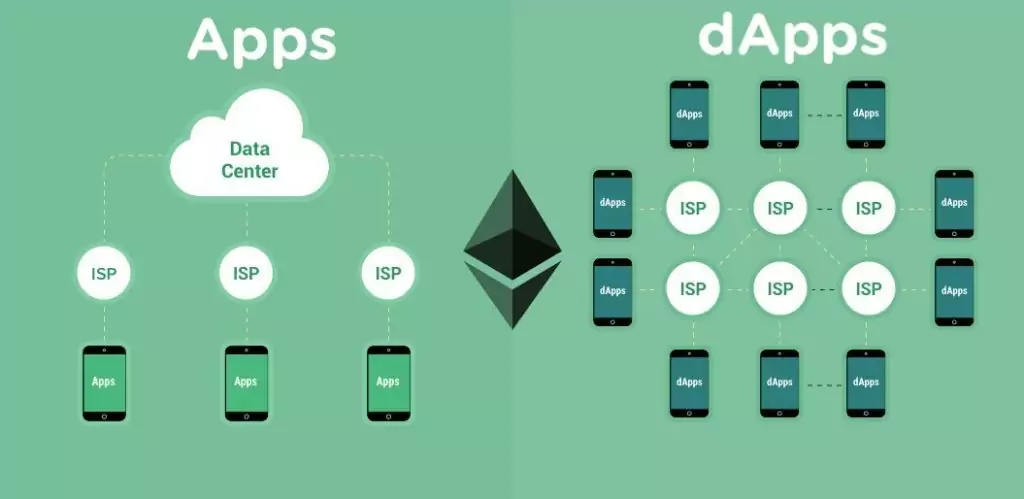
Now the question is if the power is distributed among the nodes then anyone can make the changes and if not then how the changes are done?
Here we introduce the most used term "Consensus"
The process of reaching an agreement among multiple participants is called "consensus." It ensures that everyone in the network agrees on the validity of transactions and the state of the shared ledger (the list of transactions).
In a blockchain network, consensus is achieved through a consensus mechanism, which is a set of rules and protocols that dictate how nodes in the network agree on the state of the blockchain and which transactions are considered valid. The two primary types of consensus mechanisms used in blockchain networks are:
Proof of work
Proof of stake
Ethereum initially operated on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, similar to Bitcoin. However, Ethereum is undergoing a transition to Ethereum 2.0, which will introduce a new consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Stake (PoS).

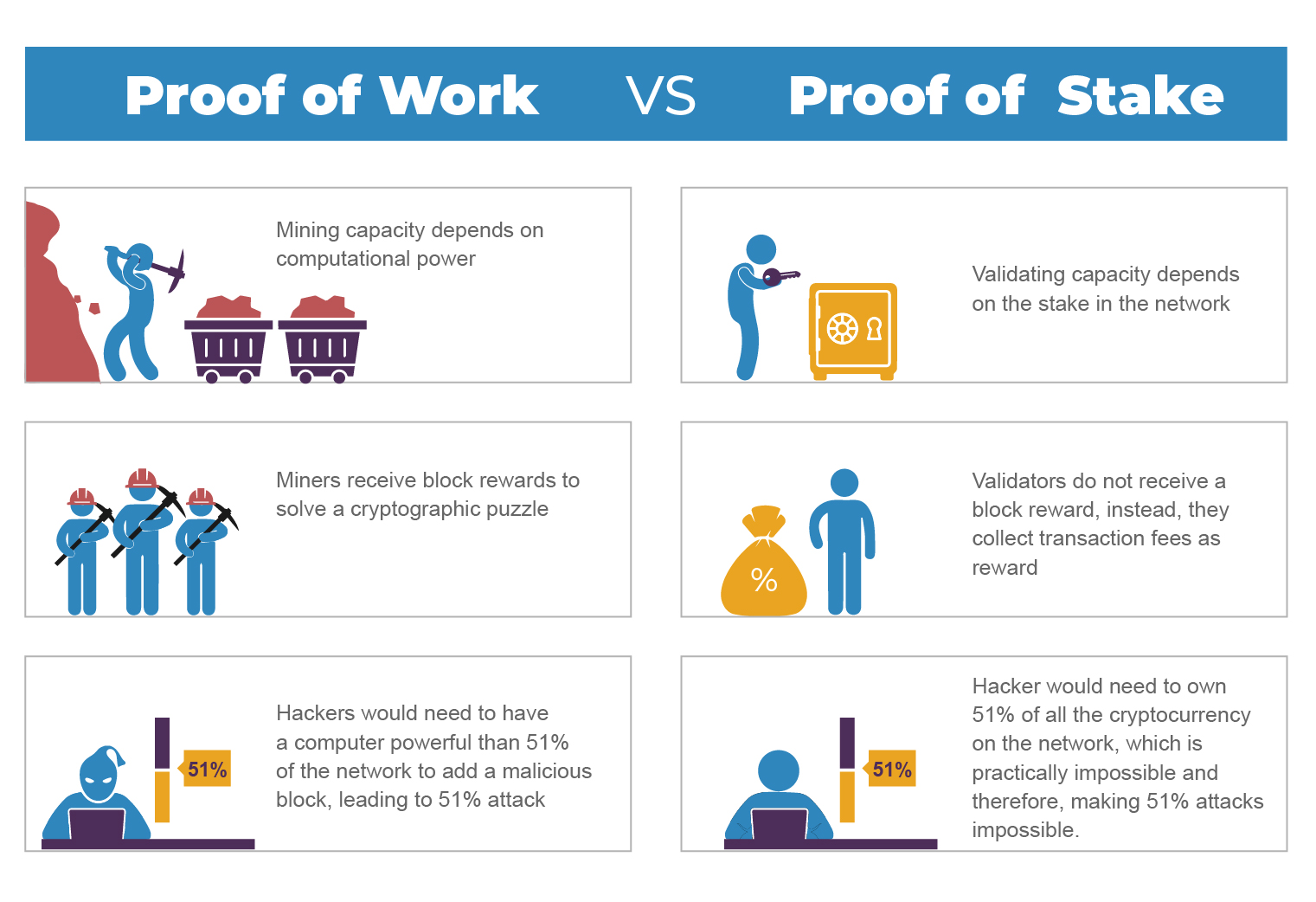
Proof of work PoW
Proof of work is a consensus mechanism where different nodes (known as miners) compete with each other to solve a mathematically complex problem. The difficulty increases as more miners join the network, maintaining a stable block creation rate. Once a miner successfully solves the puzzle, they broadcast the solution to the rest of the network. The other nodes can easily verify that the solution is correct, without having to perform the same amount of computational work. The first miner to solve the puzzle and add a new block of transactions to the blockchain is rewarded with newly created cryptocurrency tokens, such as Bitcoin. This process is often referred to as "mining".
Drawbacks:
PoW requires significant computational power, making it energy-intensive. Miners compete by performing numerous calculations until one of them finds the correct solution. Only the first one who finds the correct solution gets rewarded and others' hard work has no appreciation. Therefore it has scalability issues and intensive energy utilization.
Proof of Stake PoS
Instead of miners who use computational power to solve puzzles, PoS relies on validators. Validators are participants in the network who are chosen to validate transactions and create new blocks. The selection process is often based on the number of cryptocurrency tokens they hold and "stake" as collateral. Validators take turns proposing new blocks of transactions. Other validators then verify and agree on the proposed blocks. This process is more energy-efficient than PoW since there is no need for complex mathematical calculations.
Ethereum's decentralized and programmable nature has revolutionized the world of blockchain technology, opening up new possibilities for applications and services that operate transparently and securely without relying on intermediaries. Many startups are now using these technologies for various purposes like Social3 for hiring platforms, Brave Browser, Dtube, etc.
Will be uploading more content related to web3 and Ethereum especially <3.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Priyanshi Rai directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
