[CSS] Display Property - Block, Inline, Inline-block, None
 Lim Woojae
Lim Woojae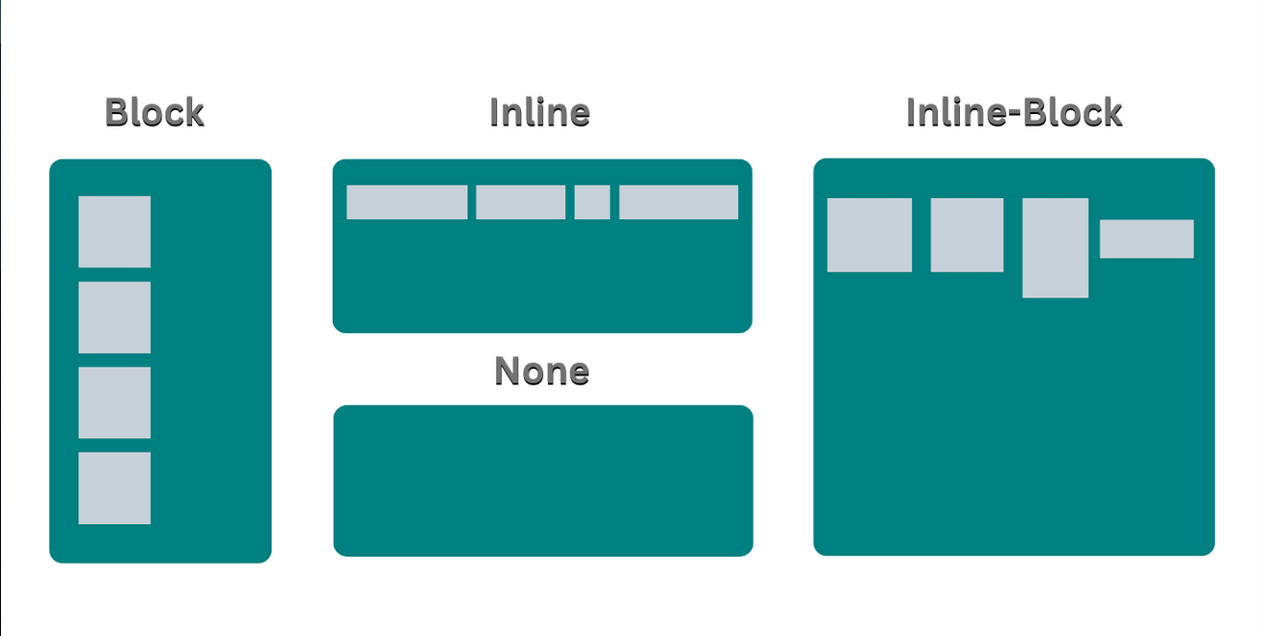
Introduction
In CSS, a display property decides how the HTML elements will be displayed and rendered on the browser. In this article, I will be talking about the four display values and the differences between those values.
FOUR(4) display values:
display: block
display: inline
display: inline-block
display: none
display: block
Characteristics of display: block:
By default, your HTML element is set to
display: block.By default, your HTML element is set to
{ width: 100%; height: auto; }Elements are placed from top to bottom.
You can use width and height to customize the size of an element.
You can use padding & margin to customize the box model.
Generates line breaks
Example of
display: block--><div>, <p>, <h1>
Of course, it is not essential to know all those characteristics, but it is good to know that elements are placed from top to bottom, you can set the width & height, and you can use padding & margin.
Now, let's look at the example.
HTML:
<div id="ex1">display: block -> from top to bottom</div>
<div id="ex2">display: block -> can set the width and height</div>
CSS:
#ex1 {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
#ex2 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
/* don't need to set display: block */
}

As you can see, the width covers the entire body (browser) because the width: 100% by default. Moreover, you don't need to set display: block because your HTML element is already display: block by default. Also, notice that the elements are placed along the y-axis.
display: inline
Characteristics of display: inline:
You CAN'T set the width and height.
By default, your HTML element is set to
{ width: auto; height: auto; }You can only set the left & right margin and padding.
The next HTML element will be on the same line if there is space.
Therefore, we can use
display: inlinewhen we want to insert the text.DOES NOT generate line breaks
Example of
display: inline-><span>, <img>
Again, no need to know all these characteristics, but it is good to know that the HTML elements will go from left to right, you cannot set the width & height, and you can only use left & right margin and padding
Now, let's look at the example.
HTML:
<div id="ex1">display: inline -> from left to right</div>
<div id="ex2">display: inline -> CANT set the width and height</div>
CSS:
#ex1 {
background-color: blueviolet;
display: inline;
width: 9999px;
height: 250px;
margin-top: 20px;
}
#ex2 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
display: inline;
width: 2929px;
height: 999px;
padding-left: 25px;
padding-right: 50px;
border: solid black 2px;
}
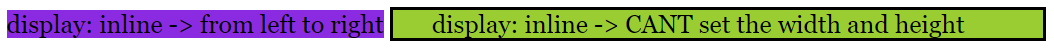
Notice that the elements now go from left to right. In the display: block, the width was 100%, which covers the entire window. Now, the width: auto, but also you cannot set the width and height.
As you can see, I gave the { width: 9999px; height: 250px; }, but it is not applied, as well as margin-top: 20px.
display: inline-block
display: inline-block is somewhat a mixture of block and inline.
Characteristics of display: inline-block:
By default, your HTML element is set to
{ width: auto; height: auto; }(same as the inline)Your HTML elements are placed from left to right (same as the inline).
DOES NOT generate line breaks (same as the line).
You can set the width & height (same as the block).
You can set the margin and padding (same as the block).
Now let's have a look at an example.
HTML:
<span id="ex1">display: inline-block1</span>
<span id="ex2">display: inline-block2</span>
CSS:
#ex1 {
background-color: #8a2be2;
display: inline- block;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
padding-top: 25px;
margin: 10px;
}
#ex2 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
display: inline-block;
width: 50px;
height: 100px;
padding: 20px;
}

Notice that you can set width, height, margin and padding, just like display: block. The elements go from left to right just like display: inline.
display: none & Web Accessibility
display: none is commonly used with JavaScript to hide and show elements without deleting and recreating them. So, elements with display: none property will not be rendered on your webpage. But, there is a disadvantage of display: none.
display: none is not a good choice if you are considering a web accessibility. For people with disabilities, the screen reader will read your entire web page. If you use display: none, the browser cannot find and read the hidden elements/scripts.
Reference
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/display
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Lim Woojae directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Lim Woojae
Lim Woojae
Computer Science Enthusiast with a Drive for Excellence | Data Science | Web Development | Passionate About Tech & Innovation