File Permissions and Access Control Lists
 Ahmed Nisar
Ahmed Nisar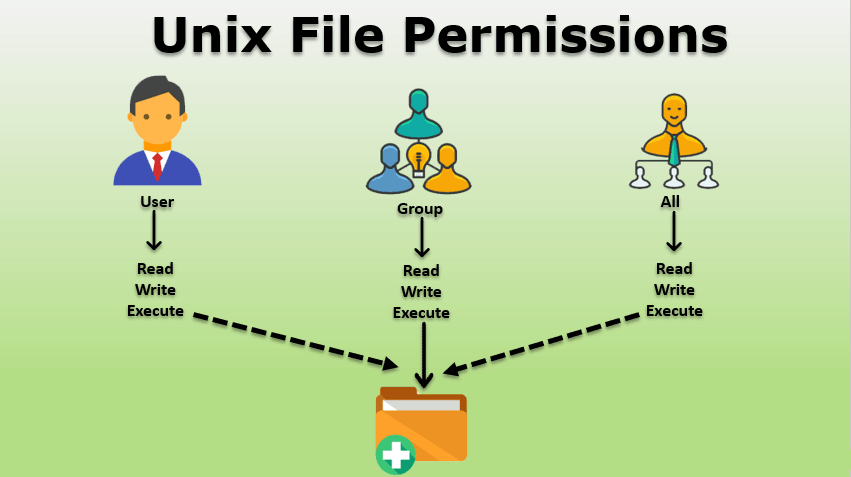
The concept of Linux 📂 File permission 🔐 and ownership is important in Linux. Here, we will be working on Linux permissions and ownership and will do tasks on both of them. Let us start with the Permissions.
Create a simple file and do
ls -ltrto see the details of the filesEach of the three permissions are assigned to three defined categories of users. The categories are:
👤owner — The owner of the file or application.
👥👥group — The group that owns the file or application.
🌍👥others — All users with access to the system. (outside the users are in a group)
Change file permission of a file:
👑👤"chown" is used to change the ownership permission of a file or directory.
👑👥"chgrp" is used to change the group permission of a file or directory.
👑👥🌍 "chmod" is used to change the other users permissions of a file or directory.
As a task, change the user permissions of the file and note the changes after ls -ltr
create a .txt file and see the permission (read and write permissions to owner and group and read only for other users)
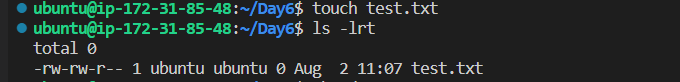
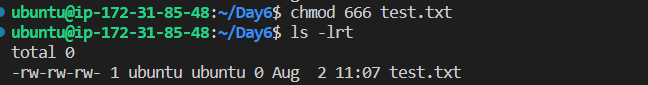
add the permission for others to write the test.txt file
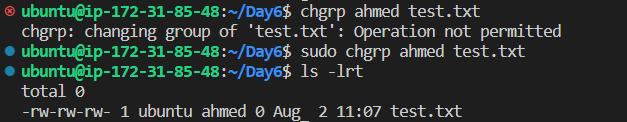
and change the group from ubuntu to ahmed
Write an article about File Permissions based on your understanding from the notes.
🔒 File permissions in Linux are like a lock on a door. They control who can do what with a file or directory.
🔑 three main types of users can access a file:
the owner, the group, and others (everyone else).
🔐 Each type of user can have three types of permissions:
Read 📖: Allows you to see the contents of the file.
Write ✍️: Allows you to make changes to the file.
Execute 🏃♂️: Allows you to run the file if it's a program or enter a directory.
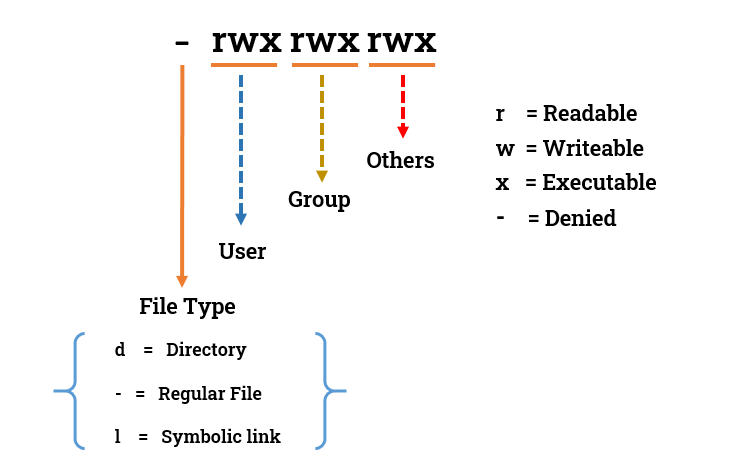
👤🔓 The file owner has special powers and can change the permissions, read, write, and execute the file.
👥🔒 The group members have permissions that the owner has set for them.
🌍🔒 Others are all the rest of the users who don't own the file or belong to the group.
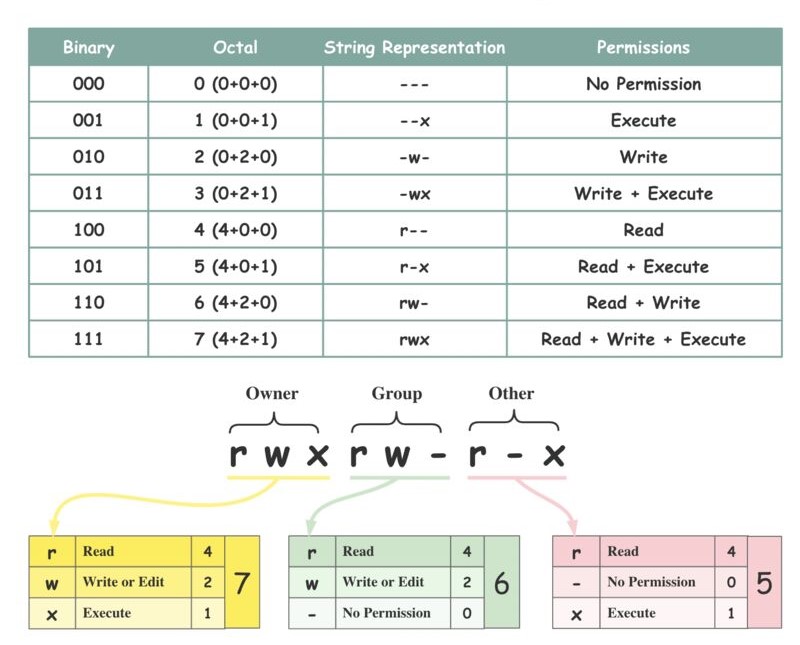
🗝️ You can set these permissions using numbers (0-7) or letters (r, w, x) to make sure your files are safe and only accessible to the right people.
Read about ACL and try out the commands getfacl and setfacl
🔒📂 Access Control Lists (ACLs) are an extension of the standard Linux file permissions that provide more granular control over access rights for files and directories. 🗝️ While traditional Linux file permissions (user, group, others) offer three levels of access (read, write, execute) for the owner, group, and other users, ACLs allow you to define permissions for specific users or groups beyond those categories. 👥🔐
With ACLs, you can finely tune access privileges, granting or revoking permissions for individual users or groups, empowering you to manage file access in a more flexible and nuanced manner. 🛠️🔍
try to install acl on ubuntu: sudo apt install acl
use setfacl to add read and write permissions for ubuntu and read permission for ubuntu to the test.txt file.

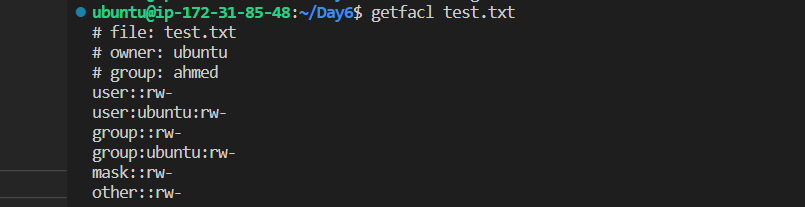
To view the ACL entries for the file, use the getfacl command:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ahmed Nisar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ahmed Nisar
Ahmed Nisar
AWS Devops | Linux | Docker | Jenkins | Terraform | Kubernetes | Ansible |