Advance Git & GitHub for DevOps Engineers | Part 1
 Ashmi Sinha
Ashmi Sinha
🎋 Git Branching
Use a branch to isolate development work without affecting other branches in the repository. Each repository has one default branch "main"/"master" and can have multiple other branches. You can merge a branch into another branch using a pull request.
Branches allow you to develop features, fix bugs, or safely experiment with new ideas in a contained area of your repository.
🔂 Git Revert and Reset
Two commonly used tools that git users will encounter are git reset and git revert. The benefit of both of these commands is that you can use them to remove or edit changes you’ve made in the code in previous commits.
🔃 Git Rebase and Merge
What Is Git Rebase?
Git rebase is a command that lets users integrate changes from one branch to another, and the logs are modified once the action is complete. Git rebase was developed to overcome merging’s shortcomings, specifically regarding logs.
What Is Git Merge?
Git merge is a command that allows developers to merge Git branches while the logs of commits on branches remain intact.
The merge wording can be confusing because we have two methods of merging branches, and one of those ways is actually called “merge,” even though both procedures do essentially the same thing.
Task 1:
Add a text file called version01.txt inside the Devops/Git/ with “This is first feature of our application” written inside. This should be in a branch coming from master, [hint try git checkout -b dev], swithch to dev branch ( Make sure your commit message will reflect as "Added new feature"). [Hint use your knowledge of creating branches and Git commit command]
- version01.txt should reflect at local repo first followed by Remote repo for review. [Hint use your knowledge of Git push and git pull commands here]
Let's do it! 😈
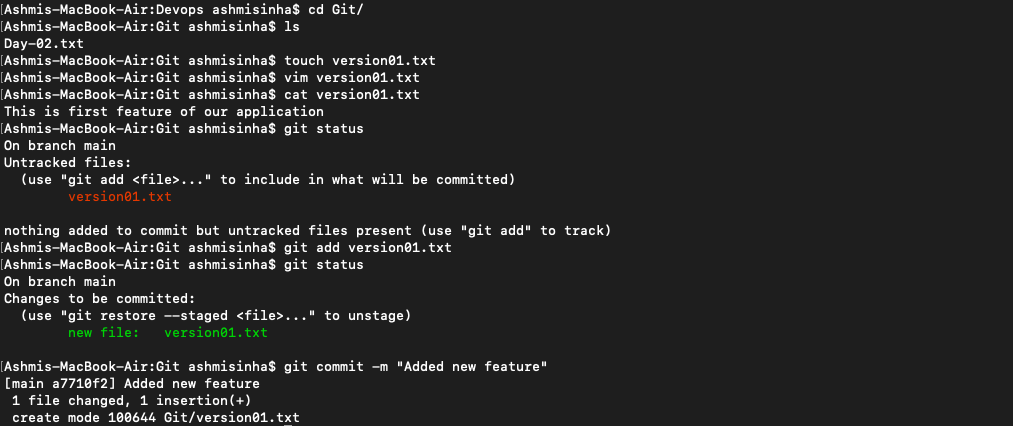
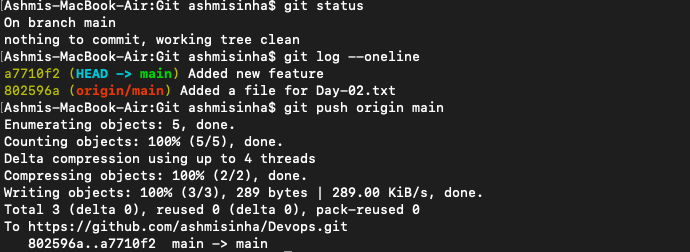
𝌣 Added new file touch version01.txt inside DevOps/Git/ folder, then wrote “This is first feature of our application” inside the file vim version01.txt Run cat version01.txt to see what's written inside the code. git add version01.txt to add the working directory to staging and then git commit -m "Added new feature" to commit changes to the local repository. Run git push origin main to push it to the remote repo (Github).
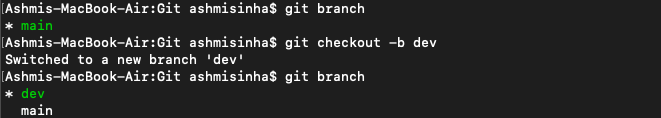
Now do git checkout -b dev to create a new branch "dev" and switch to dev branch. Run git branch to see how many branches you have and which branch you are in currently.
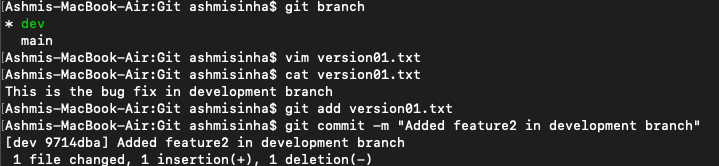
Subtask: Add new commit in dev branch after adding below mentioned content in Devops/Git/version01.txt: While writing the file make sure you write these lines
1st line>> This is the bug fix in development branch
Commit this with message “ Added feature2 in development branch”
2nd line>> This is gadbad code
Commit this with message “ Added feature3 in development branch
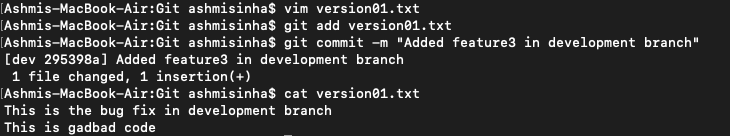
3rd line>> This feature will gadbad everything from now.
Commit with message “Added feature4 in development branch"
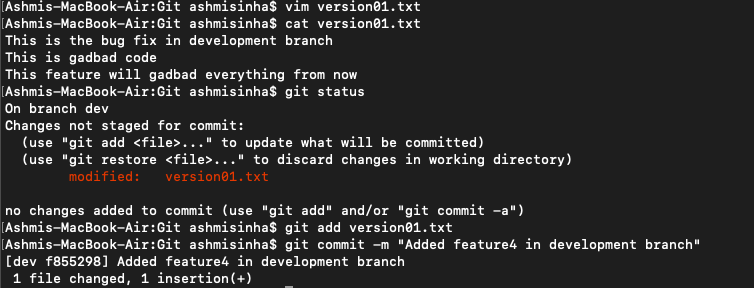
Restore the file to a previous version where the content should be “This is the bug fix in development branch”.
👾 For this, we will use
git revert <commit_it_for_gadbad_feature>The reason being, we want it to be transparent and have the commit history. If we useresetinstead ofreverthere, the commit history will be gone which we do not want.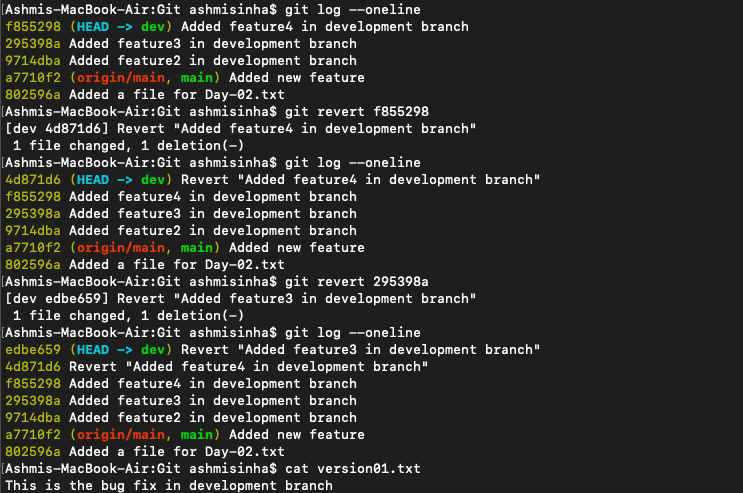
Here you go, we have reverted the code back to "This is the bug fix in development branch"
Task 2
Demonstrate the concept of branches with 2 or more branches with a screenshot.
Right now we have 2 branches, "main" and "dev".
git branchshows all the branches and also, points "*" to the branch you are currently working on (checked in).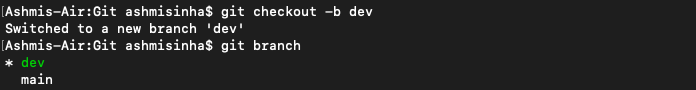
Add some changes to
devbranch and merge that branch inmasterMade a few changes to the file in the dev branch in version01.txt and the changes using
git add version01.txtand then commit the changes usinggit commit -m ""then switched to the "main" branch. Then, rangit merge devcommand to merge thedevbranch intomainbranch.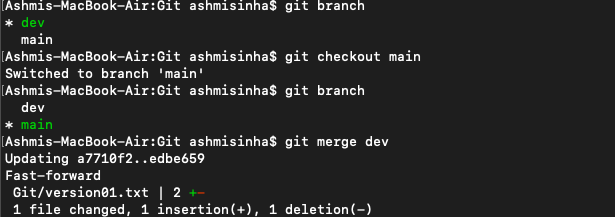
📢 Let's talk about Git Rebase a little bit more (although, Git merge is mostly and widely used)
Rebasing moves the commits from one branch to another, creating a linear history.
It replays the commits of the current branch on top of another branch.
The commit history appears as if the work was done sequentially on the main branch. It merges the branch maintaining the linear history.
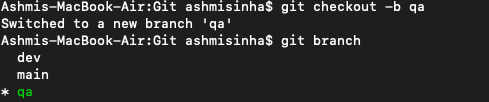
To understand this, created a new branch "qa" and checked out to main again.
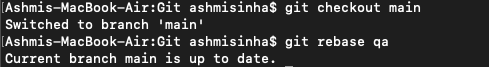
Then, used git rebase qa .
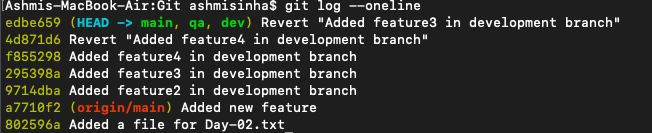
Always check the workflow before choosing git merge or git rebase as git merge preserves separate commit paths, while git rebase creates a linear history.
That's all for today! Happy learning! :)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ashmi Sinha directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
