Kali Linux File System
 Ruturajsingh Rahevar
Ruturajsingh Rahevar
Kali Linux is a Debian-based Linux distribution that is designed for digital forensics and penetration testing. Originally known as BackTrack, Kali Linux was developed and maintained by Offensive Security, a cybersecurity training company.
Kali Linux file system hierarchy :-
The Kali Linux file system hierarchy is structured similarly to other Linux operating systems. At the top level, we have the root directory, denoted by /, which contains all other files and directories. Underneath the root directory, there are several other directories, including bin, boot, dev, etc, home, lib, media, mnt, opt, proc, root, run, sbin, srv, sys, tmp, usr, and var.
/ (Root): Primary hierarchy root and root directory of the entire file system hierarchy. Every single file and directory starts from the root directory The only root user has the right to write under this directory.
/bin: Essential command binaries that need to be available in single-user mode; for all users, e.g., cat, ls, cp. Contains binary executables Commands used by all the users of the system are located here e.g. ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
/boot: Boot loader files, e.g., kernels.
/etc: Host-specific system-wide configuration files.
/home: Users’ home directories, containing saved files, personal settings, etc.Home directories for all users to store their files.
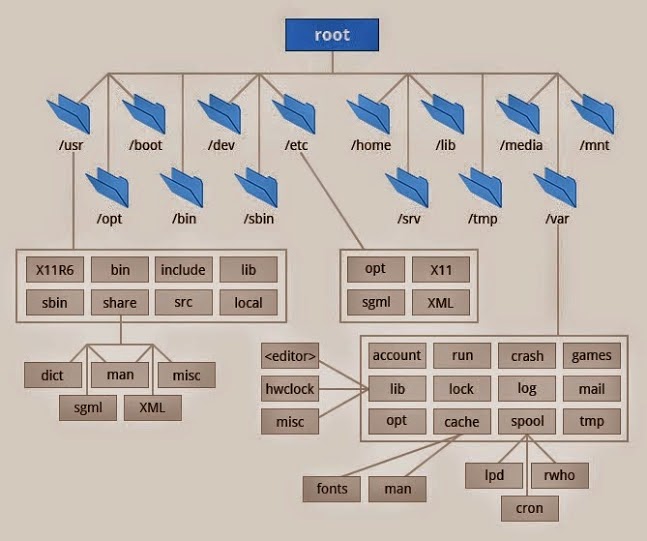
/lib: Libraries essential for the binaries in /bin/ and /sbin/ .
/media: When removable media (USB drives, CDs, etc.) are mounted.Temporary mount directory for removable devices.
/mnt: Temporarily mounted filesystems.
/opt: Optional application software packages.
/sbin : Similar to /bin, but contains binaries for system administrators (superuser) rather than regular users. Example: iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon.
/tmp: A directory for temporary files. The contents of this directory are usually cleared upon system reboot.
/usr: Secondary hierarchy for read-only user data; Contains user-specific applications and files, including executables, libraries, documentation, and more. If you can’t find a user binary under /bin, look under /usr/bin. For example: at, awk, cc, less, scp.
/proc: A virtual file system that provides information about running processes and system configuration.
/run: A temporary file system used to store runtime data of processes.
/srv: Used for data that the system serves, such as websites or FTP directories.
/sys: Another virtual file system, which exposes information and configuration options for the kernel.
/var: Holds variable data that frequently changes during system operation, like log files, spool files, etc.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ruturajsingh Rahevar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ruturajsingh Rahevar
Ruturajsingh Rahevar
Hello, I'm a Computer Science student at SVBIT Gandhinagar and I'm passionate about cybersecurity, Ethical Hacker, python, data structures, and algorithms. I enjoy learning new things and applying them to real-world problems.