Day 23 Task: Jenkins Freestyle Project for DevOps Engineers
 Gopal Gautam
Gopal Gautam🔹What is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (or Deployment). Continuous Integration is the practice of frequently merging code changes into a shared repository. It involves automating the build, unit testing, and code quality checks to detect issues early. Continuous Delivery focuses on automating the deployment process to make software releases ready for production at any time.

🔹What Is a Build Job?
A Jenkins build job contains the configuration for automating a specific task or step in the application building process. These tasks include gathering dependencies, compiling, archiving, or transforming code, and testing and deploying code in different environments.
Jenkins supports several types of build jobs, such as freestyle projects, pipelines, multi-configuration projects, folders, multibranch pipelines, and organization folders.
🔹What is Freestyle Projects ?? 🤔
A Freestyle Project in Jenkins allows you to create a job without adhering to a strict pipeline structure. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) where you can configure various build steps, triggers, post-build actions, and more. This approach is especially useful for projects that don't follow a standard build and deployment process or for teams that prefer a more manual and ad-hoc approach to setting up their automation tasks.
🔹Task-01
create a agent for your app. ( which you deployed from docker in earlier task
In your Jenkins instance, go to "Manage Jenkins" > "Nodes".
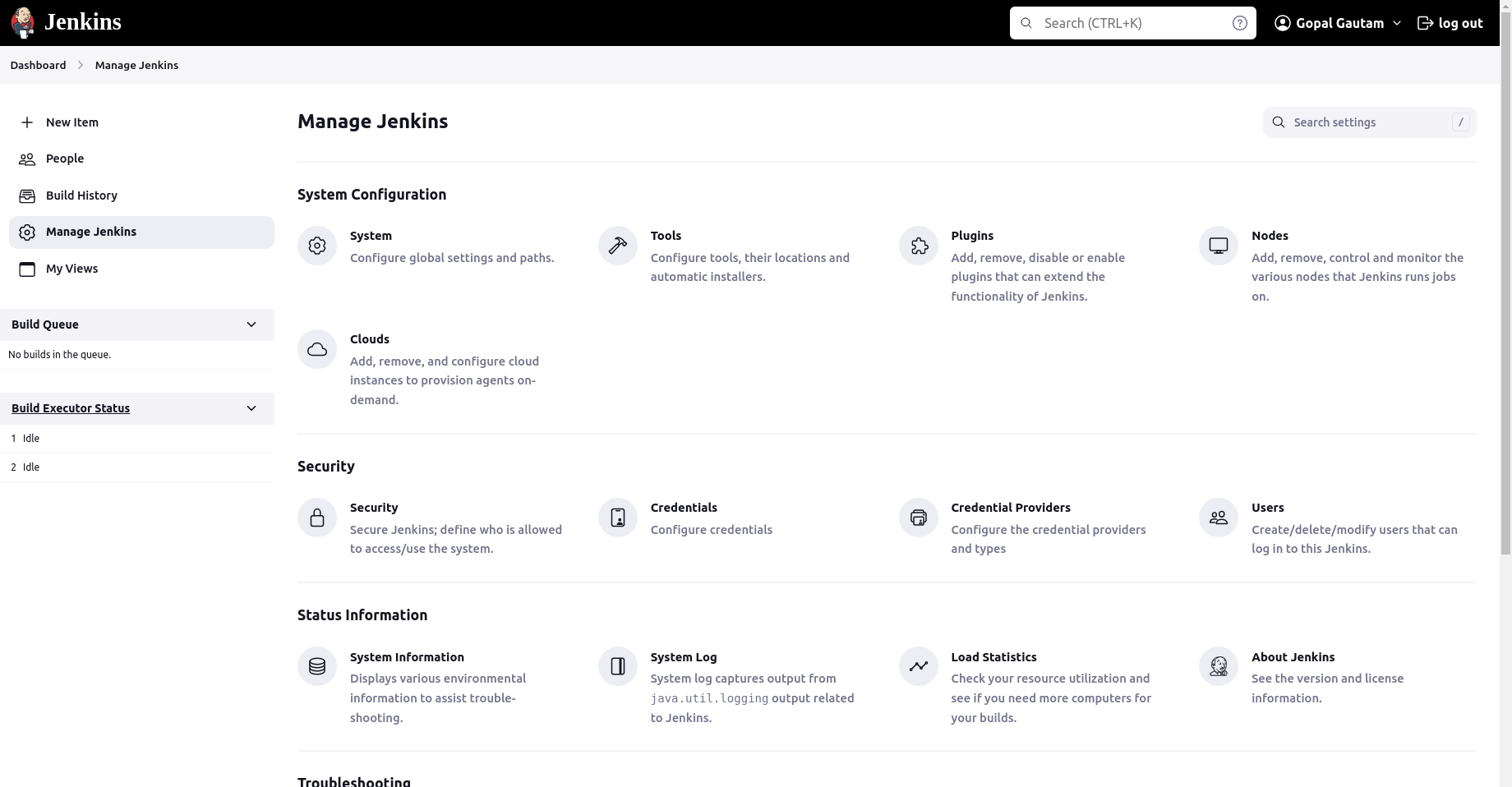
Click on "New Node" or "New Agent" to create a new agent.
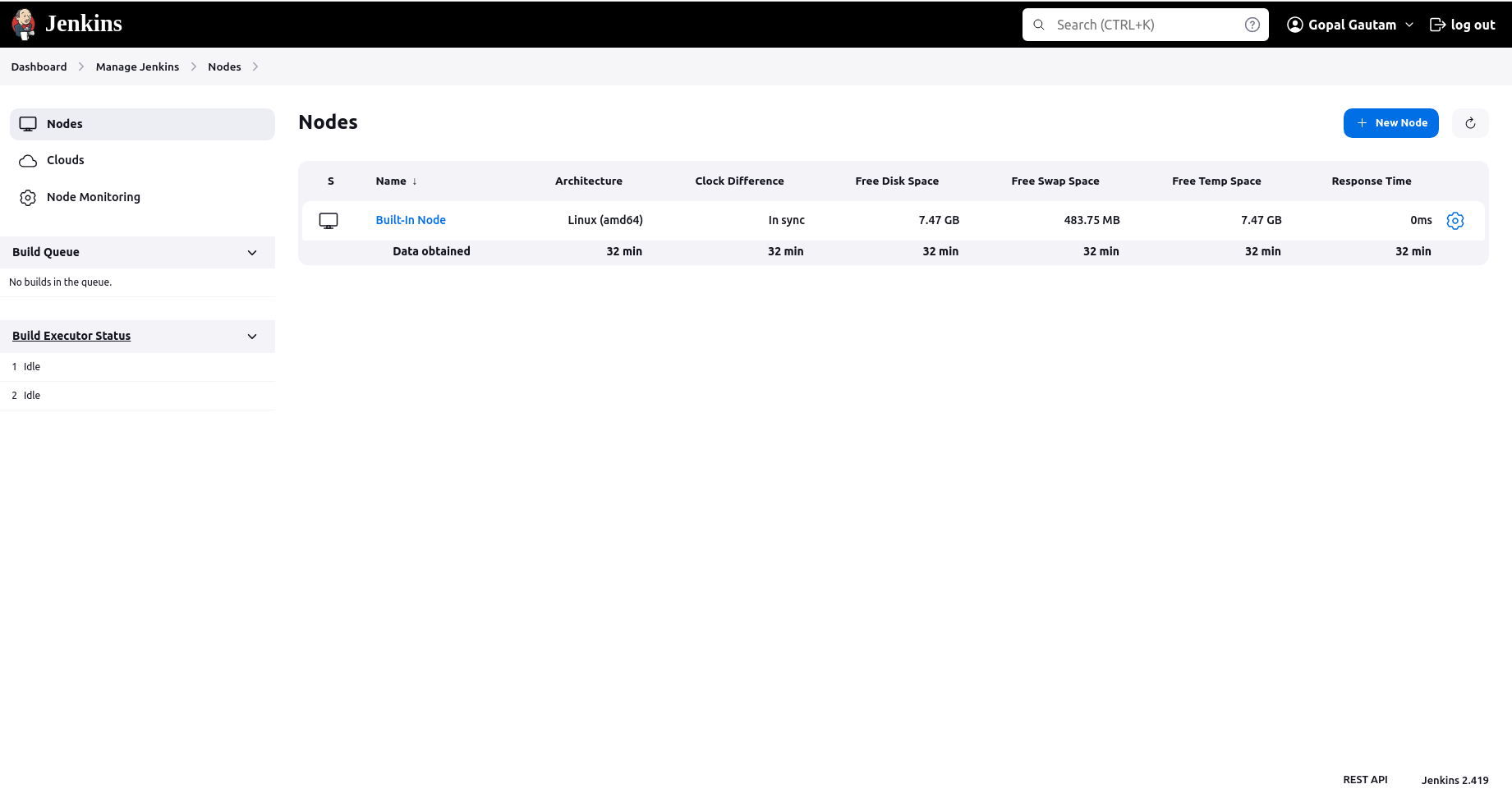
Provide a name for the agent and select "Permanent Agent".
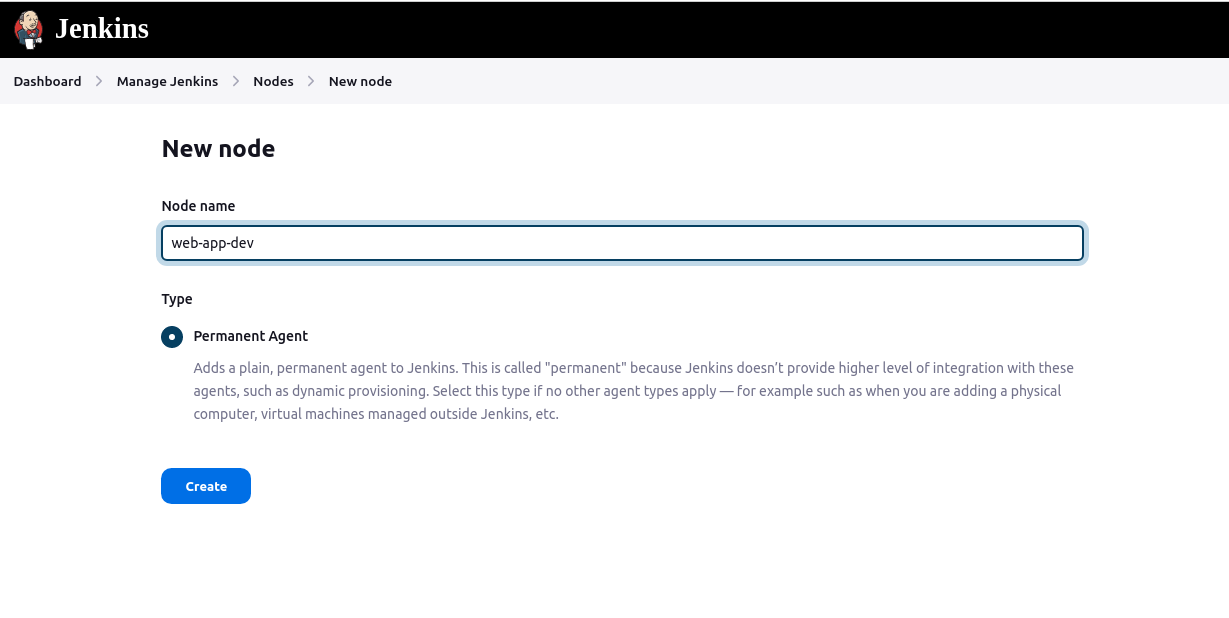
Configure the agent settings, such as the number of executors and remote root directory.
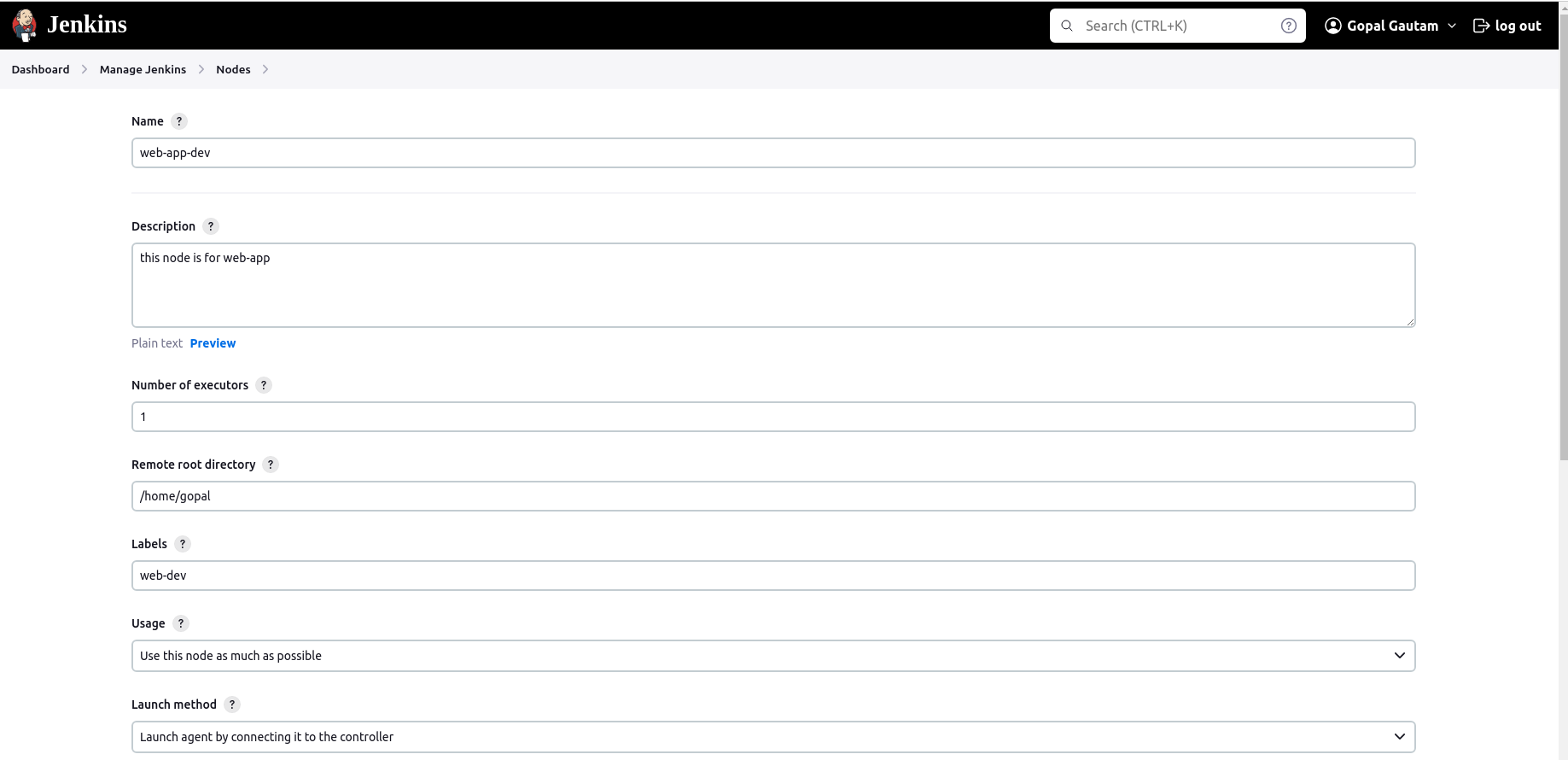
Optionally, configure labels to associate with this agent and select "Use WebSocket" Save the configuration.
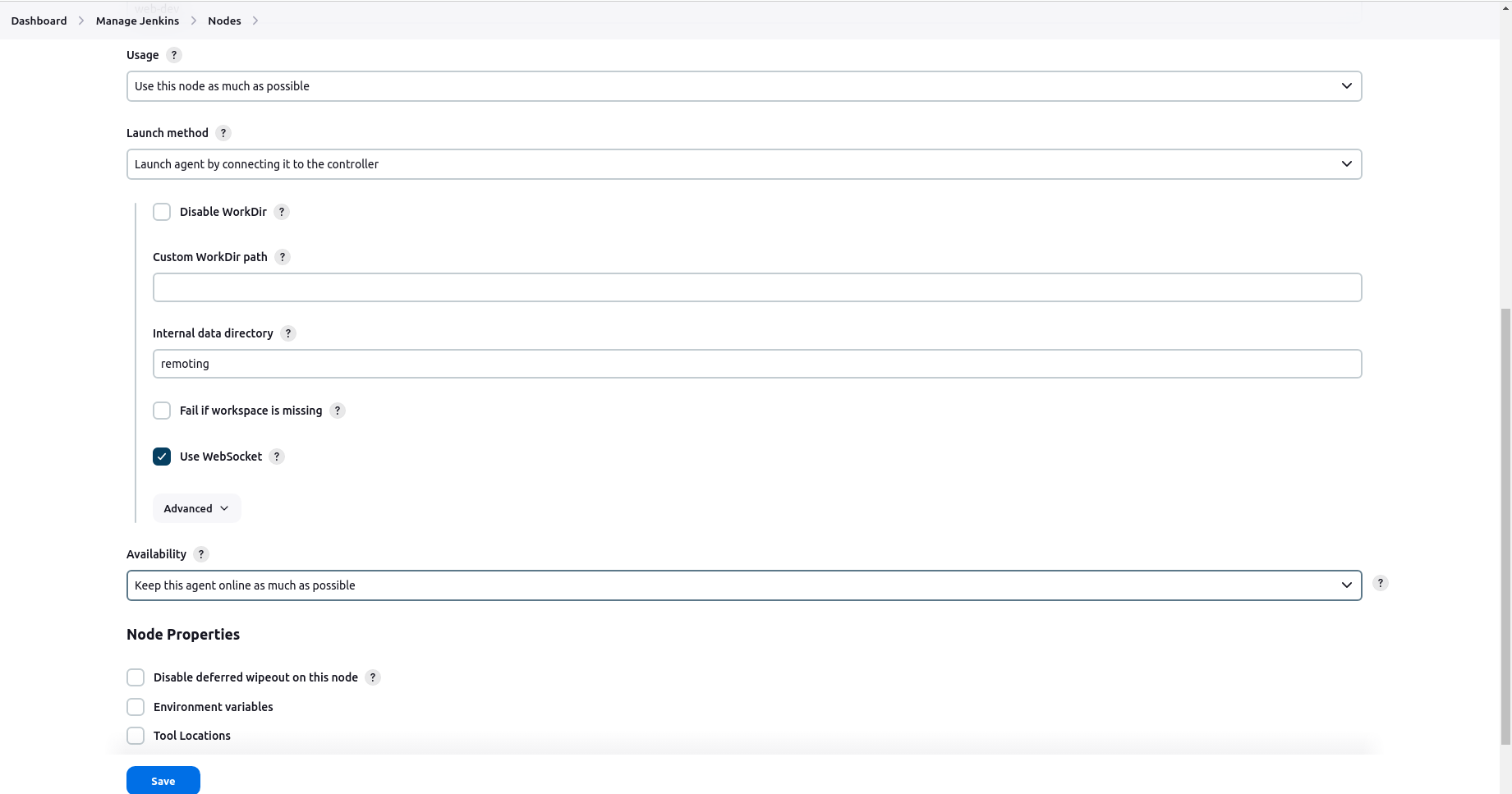
the agent is created.
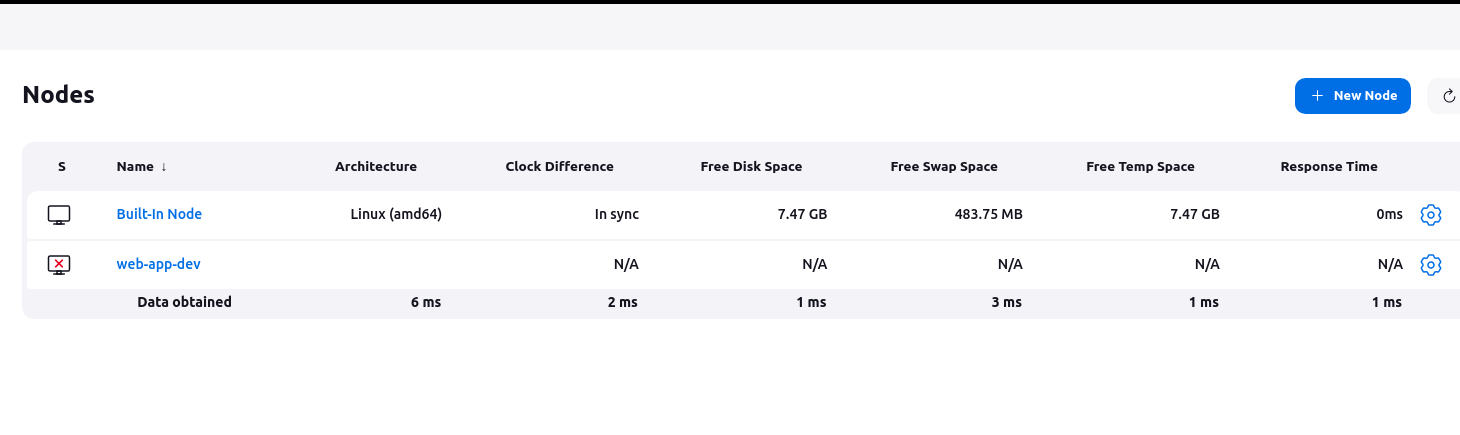
Create a new Jenkins freestyle project for your app.
From the Jenkins dashboard, click on "New Item" to create a new project.
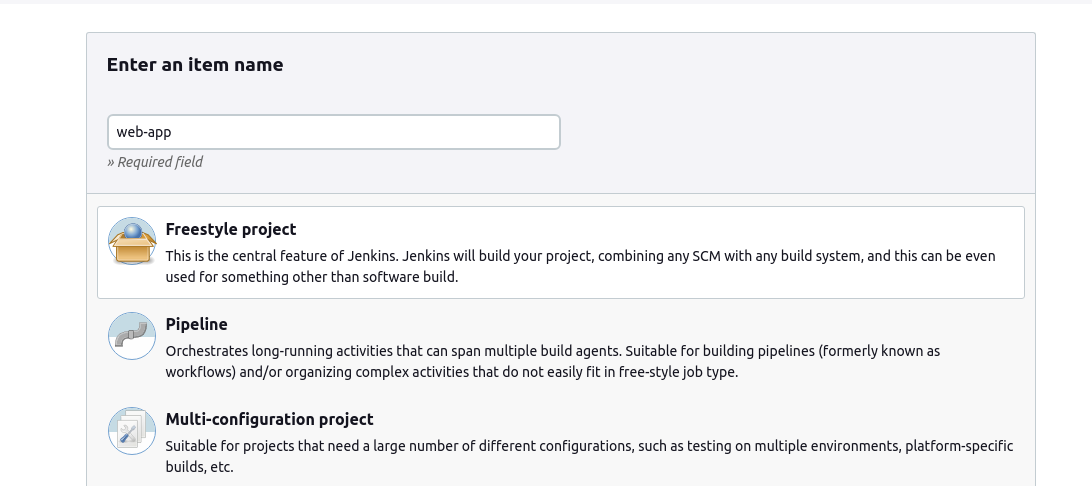
Enter a project name and select "Freestyle project" Click "OK" to create the project.
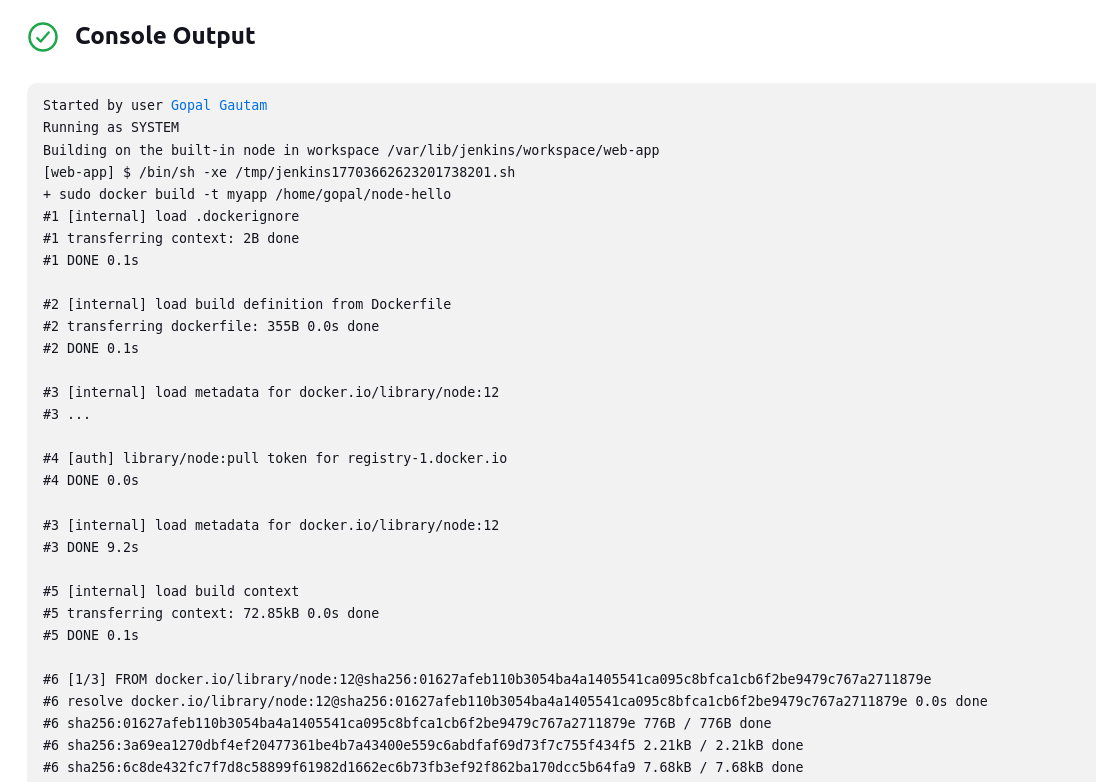
In the "Build" section of the project, add a build step to run the "docker build" command to build the image for the container.
In the project configuration, navigate to the "Build" section.
Click on "Add build step" and select "Execute shell" (or the relevant option for your environment).
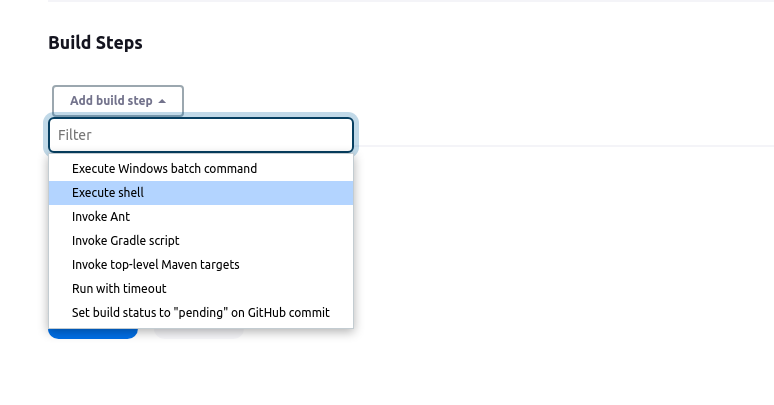
In the "Execute shell" build step, add the command to build the Docker image for your app. Replace
<app_directory>with the actual directory of your app.docker build -t myapp <app_directory> docker run -d -p 8000:8000 myapp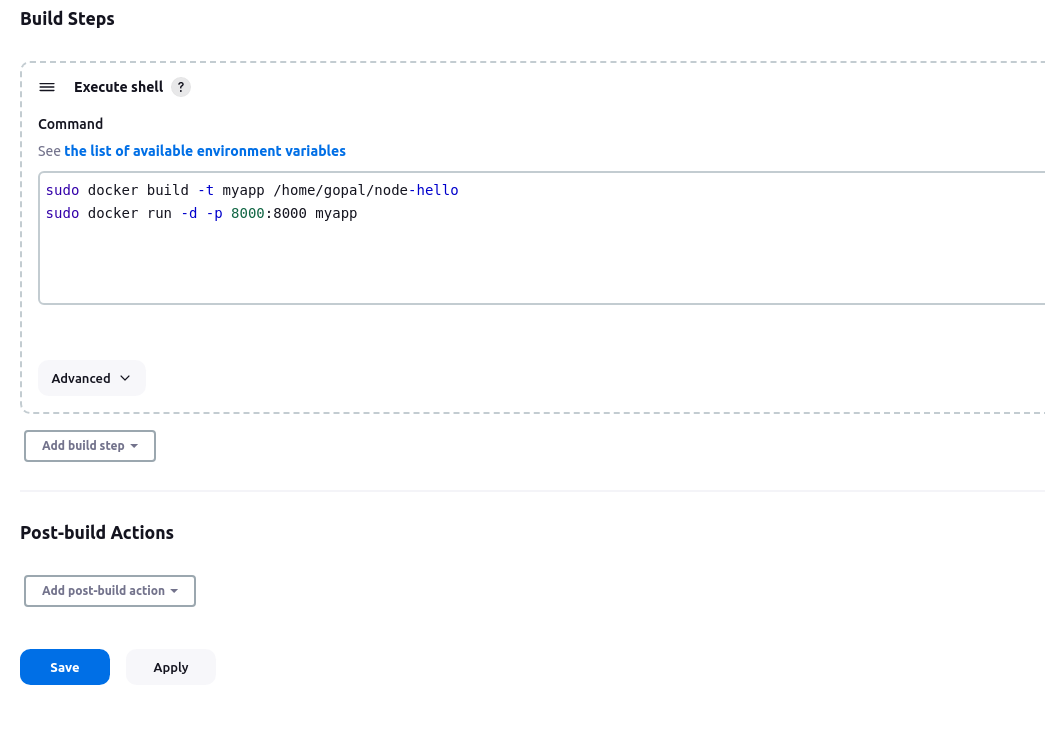
Save the project configuration.
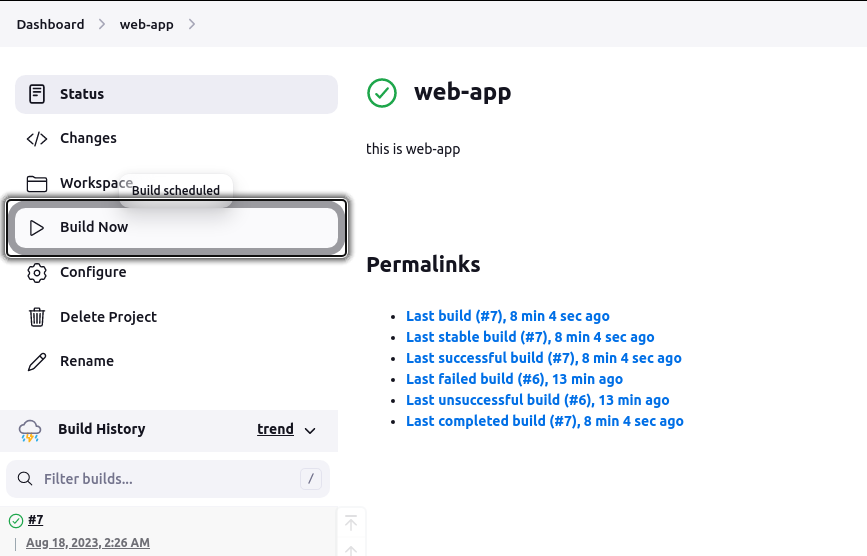
Build and Deploy
🔹Task-02
Create Jenkins project to run "docker-compose up -d" command to start the multiple containers defined in the compose file (Hint- use day-19 Application & Database docker-compose file)
Create docker-compose.yml file inside your project
version: '3.9' services: web: build: context: . dockerfile: Dockerfile image: gopalgtm001/django-auth:latest command: bash -c "python3 manage.py makemigrations && python3 manage.py migrate && python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000" ports: - "8000:8000" environment: - DB_USER=django_user - DB_PASSWORD=django_pass - DB_NAME=django_db depends_on: - db db: image: postgres:15 volumes: - db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data/ environment: - POSTGRES_USER=django_user - POSTGRES_PASSWORD=django_pass - POSTGRES_DB=django_db volumes: db_data:
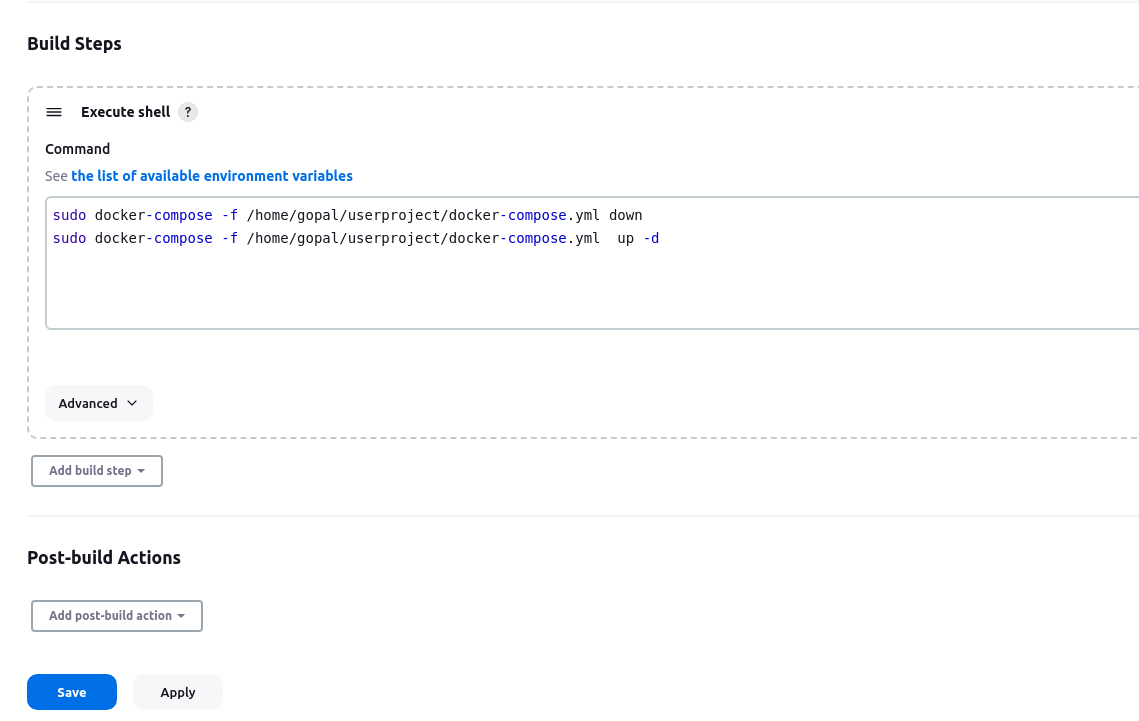
In the "Build" section of the project, add a build step "docker-compose down" command to stop and remove the containers defined in the compose file. then add "docker-compose up -d" command.
After a build is completed, you can view the console output.
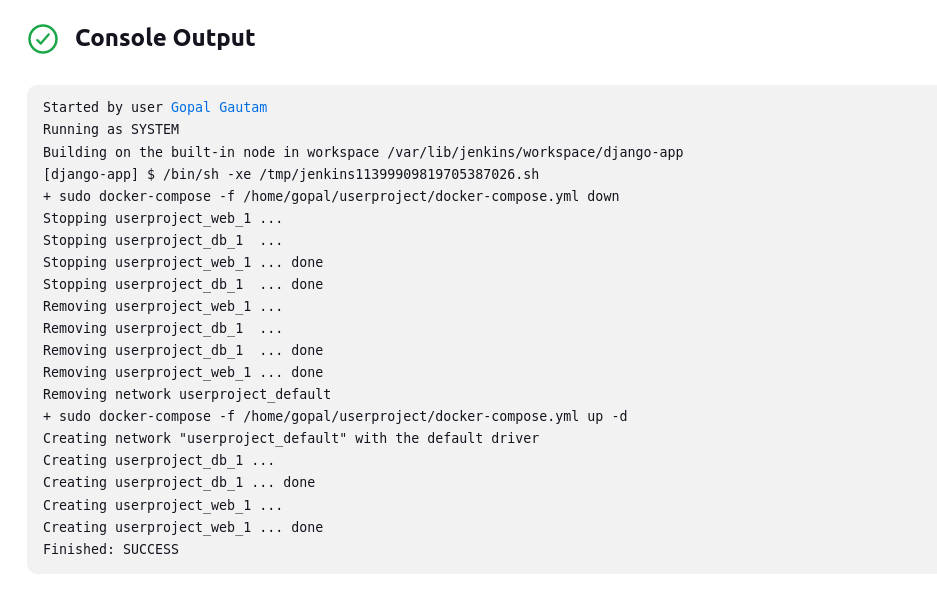
You can see container is created.

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Gopal Gautam directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Gopal Gautam
Gopal Gautam
Hii I am a backend/DevOps engineer.I have a experience with development and automation.I mostly work with Python, django, Cloud based technologies.