Data Types and Data Structures
 Ajay Gite
Ajay GiteTable of contents
- Data Types
- Data Structure in Python
- Primitive Data Structures
- Non-primitive Data Structures
- Tasks:
- Difference between List, Tuple and Set.
- Create the below Dictionary and use Dictionary methods to print your favorite tool just by using the keys of the Dictionary.
- Create a List of cloud service providers and sort the list in alphabetical order.

Data Types
Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value that tells what operations can be performed on a particular data.
Since everything is an object in Python programming, data types are actually classes and variables are instance (object) of these classes.
Python has the following data types built-in by default: Numeric(Integer, complex, float), Sequential(string,lists, tuples), Boolean, Set, Dictionaries, etc
To check what is the data type of the variable used, we can simply write: your_variable=100 type(your_variable)
Data Structure in Python
Data structures are a way of organizing and storing data so that they can be accessed and worked with efficiently. There are two types of Data Structures in Python - Primitive Data Structures and Non-primitive Data Structures.
Primitive Data Structures
Primitive Data Structures are the basic building block of data manipulation and contain simple and pure data values. Python has four primitive variable types:
INTEGER - It represents numeric data i.e. whole numbers from negative infinity to infinity, like 4, 5, or -1. Ex-
num=20print(num)Output
20FLOAT - It represents rational numbers i.e. numbers containing decimal figures, like 2.32, 4.90 or -109.20. Ex-
num=20.12print(num)Output
20.12STRING - It is a collection of alphabets, words, or other characters. It is created by enclosing a sequence of characters within a pair of single or double quotes. For example: "Python", "programming", etc. Ex-
name="Python"print(name)Output
PythonBOOLEAN - It is a built-in datatype and contains only two values - True and False and is used for conditional and comparison operations. Ex-
x=2y=4print(x==y)Output
False
Non-primitive Data Structures
Non-primitive data structures are one of the most complex form of the data structure family. It not only stores the value of a single datatype but also stores a collection of values with different datatypes. There are 5 five non-primitive data structures available:
LIST - Lists are used to store collections of heterogeneous data and is an in-built datatype in Python. It is mutable means the values can change even after its initialization. The values are written inside square braces. Ex-
x=[] #empty listy=[1,3,"python",5,10.21]print(y) #This prints the listprint(type(y)) #This returns the kind of datatypeOutput
[1, 3, 'python', 5, 10.21]<class 'list'>DICTIONARY - It is made of key-value pairs. Key is used to identify the item and the value holds the value of the item. Key has to be unique value as it is used as an identifier and value can store repeated values. It is written inside curly braces. Ex-
dict = {"student1" : 20, "student2" : 30}print(dict)print(type(dict))Output
{'student1': 20, 'student2': 30}<class 'dict'>SET - It is an unordered data structure that stores unique values. It is written inside curly braces. It is mutable means the values can change even after its initialization. Ex-
set= { 21, 32, 34, 43}print(set)print(type(set))Output
{32, 34, 43, 21}<class 'set'>TUPLES - Tuple is also used to store collections of heterogeneous data but it is immutable means once initialized it's values cannot be further changed or modified. It is very fast as compared to list. It is written inside round brackets. Ex-
tuple = ("Ajay Gite", 32, "30", True)print(tuple)print(type(tuple))Output
('Ajay Gite', 32, '30', True)<class 'tuple'>ARRAY - Arrays are used to store collections of homogeneous data. Array in Python can be created by importing array module. array(data_type, value_list) is used to create an array with data type and value list specified in its arguments. Ex-
# importing "array" for array creationsimportarray as arr# creating an array with integer typea =arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3])print(a)print(type(a))Output
array('i', [1, 2, 3])<class 'array.array'>
Tasks:
Difference between List, Tuple and Set.
List:
An ordered collection of items, denoted by square brackets
[ ].Mutable: You can change, add, or remove elements.
Elements can be of different data types.
Preserves element order, allowing access by index.
Example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 'apple', 'banana']
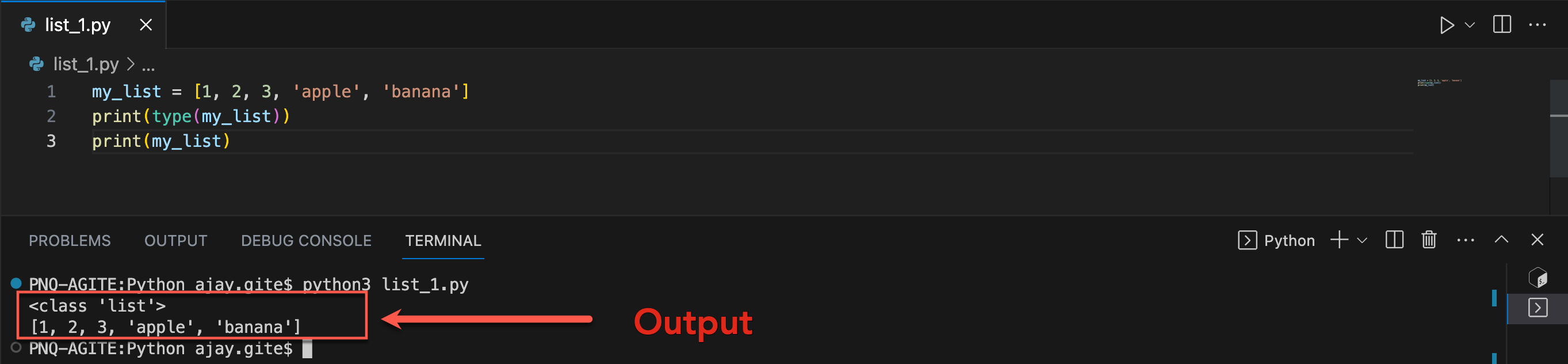
Tuple:
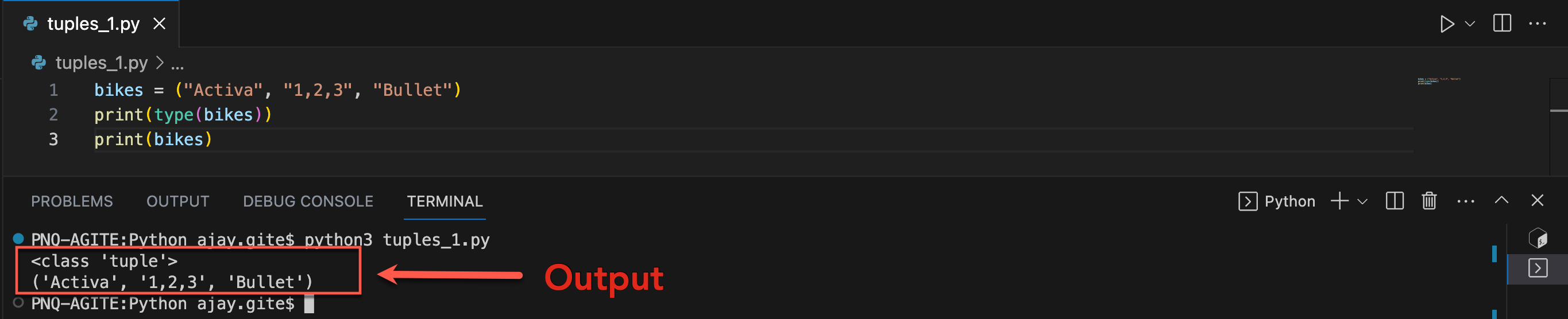
Tuples are used to store multiple items in a single variable. Tuple is one of 4 built-in data types in Python used to store collections of data. A tuple is a collection that is ordered and unchangeable. Tuples are written with round brackets.
Let's create program for tuple
Set
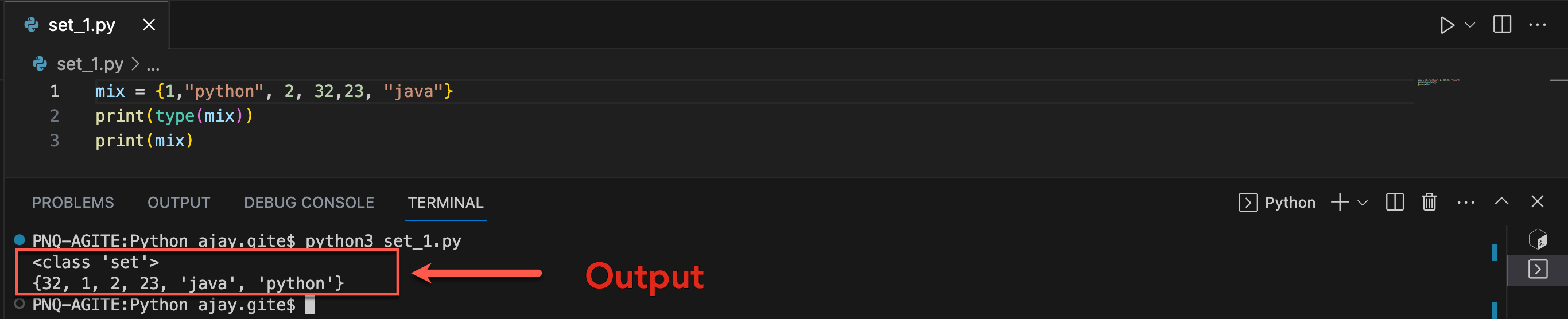
Python Set is the unordered collection of the data type. It may change after creation and has unique elements. In a set, the order of the elements is undefined; it may return the changed sequence of the element. The set is created by using a built-in function set(), or a sequence of elements is passed in the curly braces and separated by the comma.
Let's create a program for Set
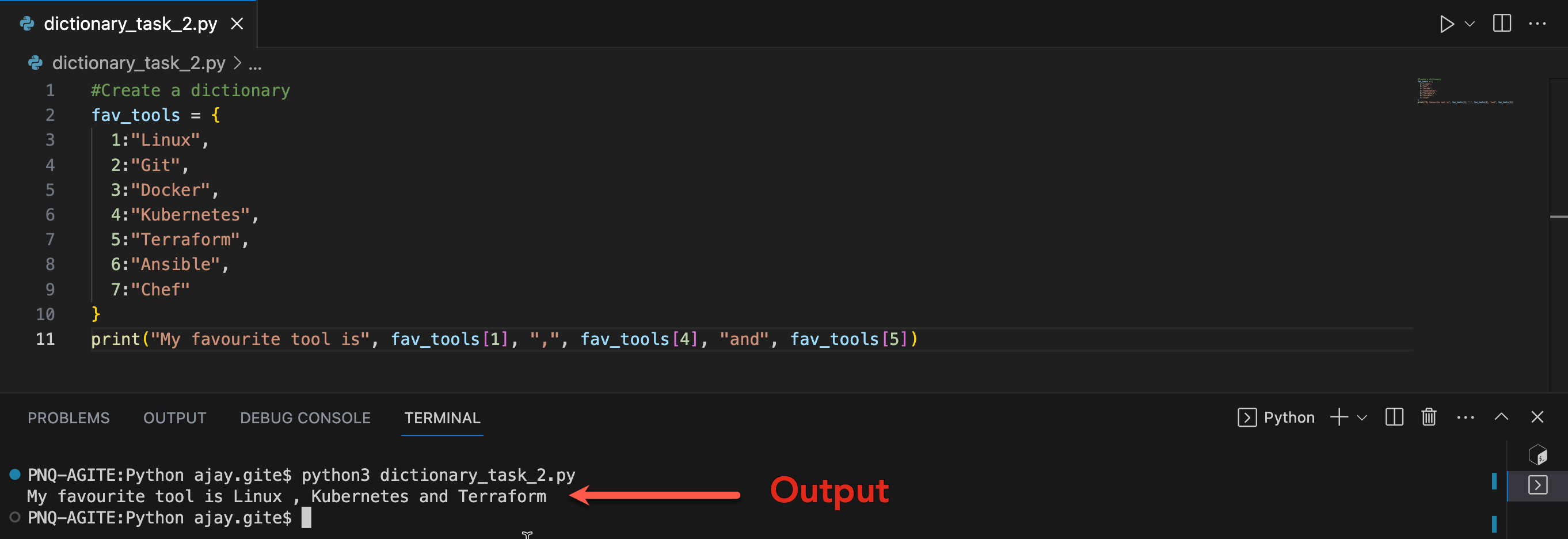
Create the below Dictionary and use Dictionary methods to print your favorite tool just by using the keys of the Dictionary.
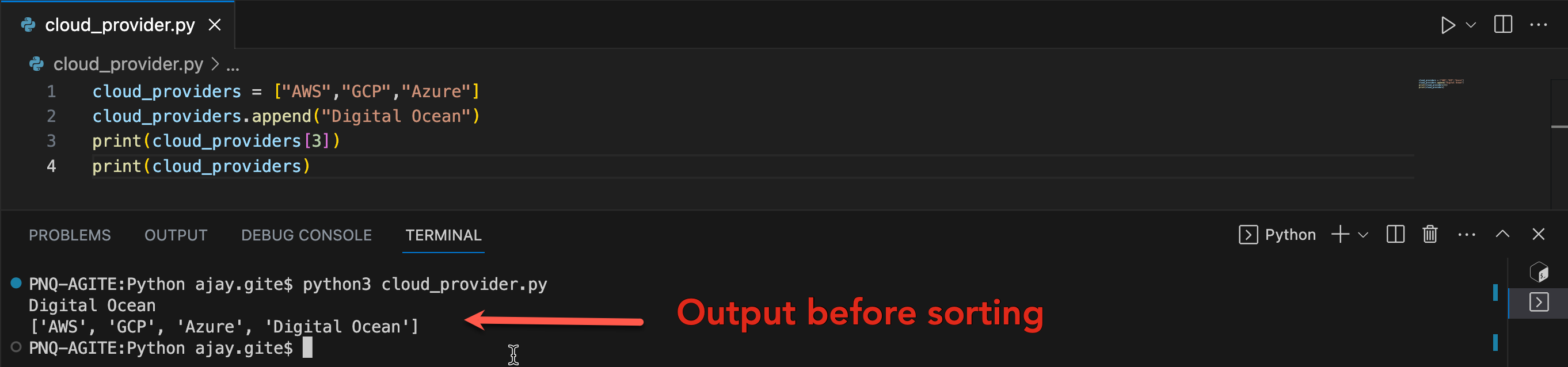
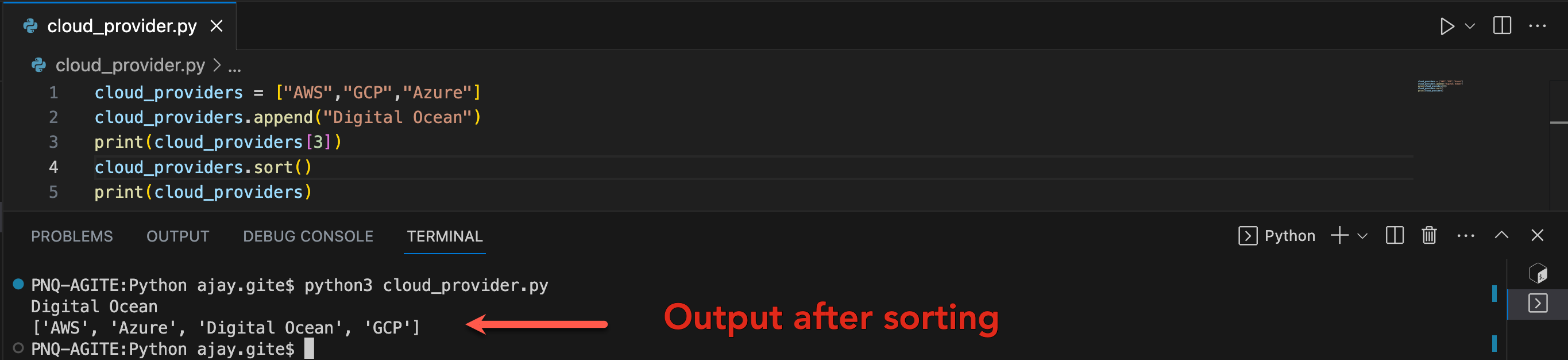
Create a List of cloud service providers and sort the list in alphabetical order.
Before sorting:
After sorting:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ajay Gite directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
