Hosting a Static Website on Amazon S3 using Terraform
 Sharad Tiwari
Sharad Tiwari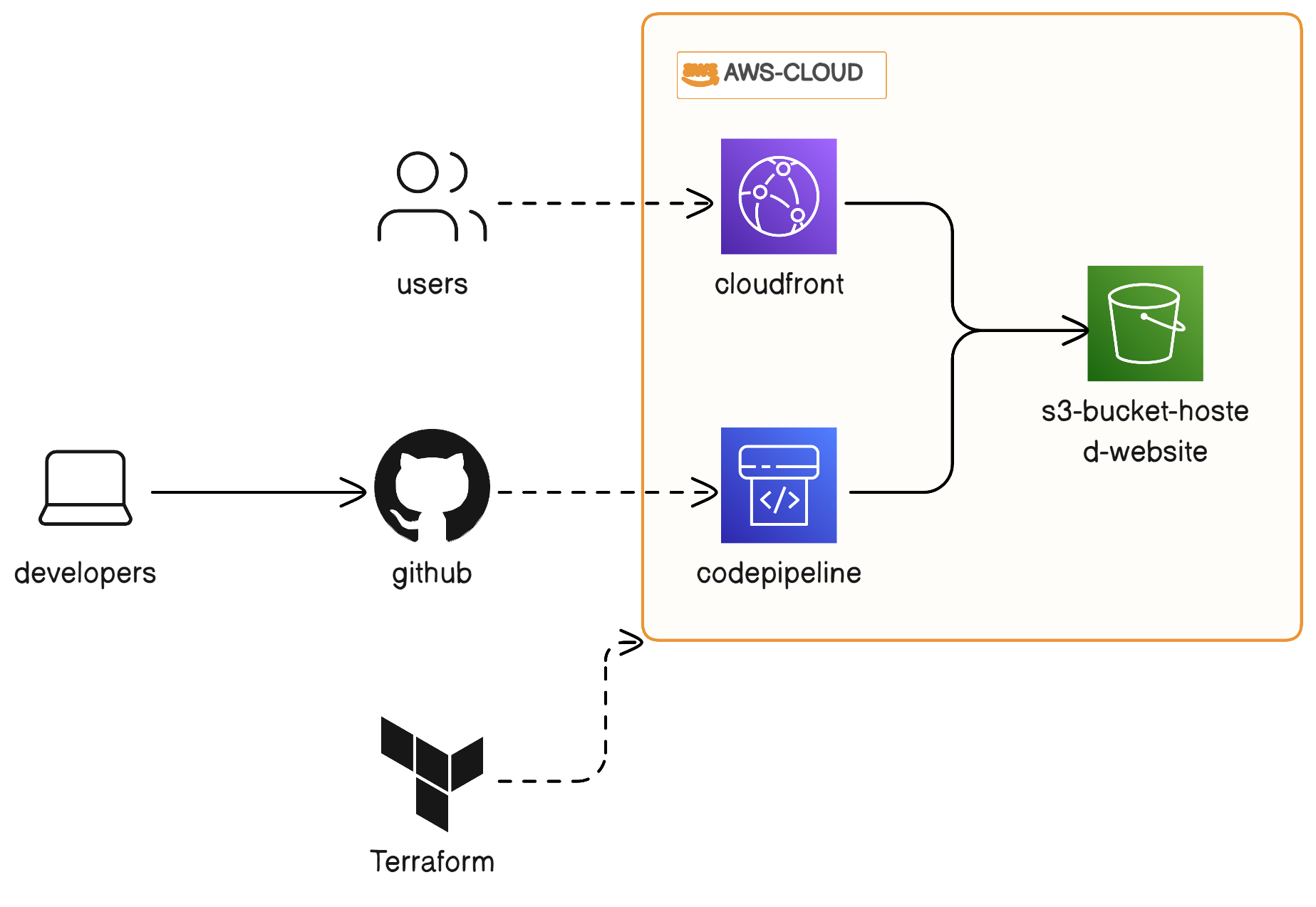
Introduction
In this blog post, we will explore how to set up a static website hosting environment on Amazon S3 with Amazon CloudFront and deploy code to the S3 bucket using AWS CodePipeline, all managed as code with Terraform. This combination allows you to create a highly available and scalable static website with automated deployment.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have the following prerequisites in place:
An AWS account with appropriate permissions.
Terraform is installed on your local machine. You can download it here.
A basic understanding of Terraform, AWS, and static website hosting concepts.
Step 1: Configure AWS Credentials
Ensure that you have configured your AWS credentials either through the AWS CLI or by setting environment variables (AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY).
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="your_access_key"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="your_secret_key"
Step 2: Create a Terraform Configuration
Create a new directory for your Terraform configuration, and within that directory, create the following files:
s3-bucket.tf: This file contains the S3 Bucket configuration.codepipeline.tf: This file contains the code pipeline configuration.cloudfront.tf: This file contains the Cloudfront configuration.variables.tf: Define variables here.outputs.tf: Define outputs here.
s3-bucket.tf
data "aws_caller_identity" "current" {}
#Create s3 Bucket for website hosting
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "bucket" {
bucket = "${var.bucketname}-${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}"
force_destroy = var.force_destroy
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "bucket_acl" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.id
block_public_acls = true
block_public_policy = true
ignore_public_acls = true
restrict_public_buckets = true
}
#Create s3 bucket website configuration
resource "aws_s3_bucket_website_configuration" "static_website" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.id
index_document {
suffix = "index.html"
}
}
#create s3 bucket policy
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "allow_access_cloudfront" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.id
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.s3_policy.json
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "s3_policy" {
statement {
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["cloudfront.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = [
"s3:GetObject",
]
resources = [
aws_s3_bucket.bucket.arn,
"${aws_s3_bucket.bucket.arn}/*",
]
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "pipeline_bucket" {
bucket = "${var.codepipeline_bucket_name}-${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}"
force_destroy = var.force_destroy
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "pipeline_bucket_acl" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.pipeline_bucket.id
block_public_acls = true
block_public_policy = true
ignore_public_acls = true
restrict_public_buckets = true
}
codepipeline.tf
#Create codepipeline for s3 website deployment
resource "aws_codepipeline" "codepipeline" {
name = var.codepipeline_name
role_arn = aws_iam_role.codepipeline_role.arn
artifact_store {
location = aws_s3_bucket.pipeline_bucket.bucket
type = var.artifact_store_type
}
stage {
name = "Source"
action {
name = var.source_stage
category = var.source_stage
owner = var.owner
provider = var.source_provider
version = "1"
output_artifacts = ["source_output"]
configuration = {
ConnectionArn = aws_codestarconnections_connection.codestarconnections.arn
FullRepositoryId = var.repository_id
BranchName = var.branch_name
}
}
}
stage {
name = "Deploy"
action {
name = var.deploy_stage
category = var.deploy_stage
owner = var.owner
provider = var.deploy_provider
input_artifacts = ["source_output"]
version = "1"
configuration = {
BucketName = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.id
Extract = true
}
}
}
}
resource "aws_codestarconnections_connection" "codestarconnections" {
name = var.codestar_connection_name
provider_type = var.codestart_connection_provider_type
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "assume_role" {
statement {
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["codepipeline.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole"]
}
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "codepipeline_role" {
name = var.codepipeline_role_name
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role.json
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "codepipeline_policy" {
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectVersion",
"s3:GetBucketVersioning",
"s3:PutObjectAcl",
"s3:PutObject",
]
resources = [
aws_s3_bucket.pipeline_bucket.arn,
"${aws_s3_bucket.pipeline_bucket.arn}/*",
aws_s3_bucket.bucket.arn,
"${aws_s3_bucket.bucket.arn}/*"
]
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = ["codestar-connections:UseConnection"]
resources = [aws_codestarconnections_connection.codestarconnections.arn]
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"codebuild:BatchGetBuilds",
"codebuild:StartBuild",
]
resources = ["*"]
}
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "codepipeline_policy" {
name = var.codepipeline_role_policy
role = aws_iam_role.codepipeline_role.id
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.codepipeline_policy.json
}
cloudfornt.tf
locals {
s3_origin_id = var.s3_origin_id
}
#crate cloudfront origin access control
resource "aws_cloudfront_origin_access_control" "origin_access_control" {
name = var.origin_access_control_name
origin_access_control_origin_type = var.origin_access_control_type
signing_behavior = var.origin_access_control_signing_behavior
signing_protocol = var.origin_access_control_signing_protocol
}
#create cloudfront distribution
resource "aws_cloudfront_distribution" "s3_distribution" {
origin {
domain_name = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.bucket_regional_domain_name
origin_access_control_id = aws_cloudfront_origin_access_control.origin_access_control.id
origin_id = local.s3_origin_id
}
enabled = true
default_root_object = "index.html"
default_cache_behavior {
allowed_methods = var.cache_behavior
cached_methods = var.cache_method
target_origin_id = local.s3_origin_id
forwarded_values {
query_string = false
cookies {
forward = "none"
}
}
viewer_protocol_policy = "allow-all"
min_ttl = 0
default_ttl = 3600
max_ttl = 86400
}
viewer_certificate {
cloudfront_default_certificate = true
}
restrictions {
geo_restriction {
restriction_type = var.geo_restriction_type
locations = var.location
}
}
}
variable.tf
variable "bucketname" {
type = any
default = "static-website-bucket"
}
variable "codepipeline_name" {
type = string
default = "my-s3-website-pipeline"
}
variable "artifact_store_type" {
type = any
default = "S3"
}
variable "source_stage" {
type = string
default = "Source"
}
variable "owner" {
type = string
default = "AWS"
}
variable "source_provider" {
type = string
default = "CodeStarSourceConnection"
}
variable "repository_id" {
type = string
default = "sharadtiwari78/my-s3-website" #put your repository id
}
variable "branch_name" {
type = string
default = "main"
}
variable "deploy_stage" {
type = string
default = "Deploy"
}
variable "deploy_provider" {
type = string
default = "S3"
}
variable "codestar_connection_name" {
type = string
default = "mygithub-connection"
}
variable "codestart_connection_provider_type" {
type = string
default = "GitHub"
}
variable "codepipeline_bucket_name" {
type = string
default = "s3-website-pipeline"
}
variable "force_destroy" {
type = bool
default = true
}
variable "codepipeline_role_name" {
type = string
default = "pipeline-role"
}
variable "codepipeline_role_policy" {
type = string
default = "codepipeline_policy"
}
variable "s3_origin_id" {
type = string
default = "myS3Origin"
}
variable "origin_access_control_name" {
type = string
default = "s3_origin"
}
variable "origin_access_control_type" {
type = string
default = "s3"
}
variable "origin_access_control_signing_behavior" {
type = string
default = "always"
}
variable "origin_access_control_signing_protocol" {
type = string
default = "sigv4"
}
variable "cache_behavior" {
type = list(string)
default = ["GET", "HEAD", "OPTIONS"]
}
variable "cache_method" {
type = list(string)
default = ["GET", "HEAD"]
}
variable "geo_restriction_type" {
type = string
default = "whitelist"
}
variable "location" {
type = list(string)
default = ["IN"]
}
output.tf
output "account_id" {
value = data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id
}
output "domain_name"{
value = aws_cloudfront_distribution.s3_distribution.domain_name
}
Step 3: Initialize and Apply Terraform
Open your terminal, navigate to the directory containing your Terraform configuration files, and run the following commands:
#This command initializes Terraform and downloads the necessary providers.
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
Step 4: Set Up Your Code Repository
Set up your code repository in CodeCommit or any other source code management system of your choice. Ensure that your code includes the necessary HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or other assets for your static website.
Step 5: Deploy Your Website
Whenever you push changes to your code repository, CodePipeline will automatically build and deploy your website to the S3 bucket. The changes will be reflected in your CloudFront distribution.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we've learned how to set up a highly available and scalable static website hosting environment on Amazon S3 with Amazon CloudFront and automate the deployment process using AWS CodePipeline, all managed as code with Terraform.
This combination of services allows you to host your static website with ease, automate deployments, and ensure a smooth and reliable web experience for your users. By managing your infrastructure as code, you can easily replicate and scale your static website hosting environment across multiple AWS regions or accounts.
Thank You, Happy Learning
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sharad Tiwari directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
