Anatomy of a Decentralized Exchange (DEX): A deep dive into the architecture and components of a DEX
 Degen HODLer
Degen HODLer
"Unlocking DeFi: navigating the blockchain", in this series we already learned the basics of blockchain and decentralized finance now we're going to see the different protocols in this revolutionary space and in this blog, we will deep dive into DEXes i.e. Decentralised Exchanges, but wait now you have doubt What is Protocol 🤔 ??? Don't worry in this blog you will get all the basics without any jumpstart, we will gradually pace things and then will look at the technical aspects Enjoy reading !!!
What is Protocol?
Before understanding what is decentralized exchanges? you have to understand what is protocol. We already learned about smart contracts in the previous blog.(Fact:- Bitcoin blockchain network can only store the records of transactions on its Layer 1, for running smart contracts Chain like Ethereum, Solana, etc. used for it.)
Protocols are nothing but applications that use smart contracts that define a set of rules and specifications,how certain financial activities are conducted on a blockchain or a decentralized network like transferring of bitcoins when you meet certain rules.
What is a Decentralised Exchange 📊?
Now you have the basic idea about protocols it's nothing new to you, let's understand what this fascinating word DEX is. In our daily life we do many exchanges by money or by assets and it's just as simple as you do I'm buying chocolate with 5₹ is an example of an exchange. Likewise, we do exchange financial assets like stocks, crypto, bonds, etc. Here we transfer the ownership of the assets from one person to another. In the traditional financial system, we need an intermediatory to do this transfer/exchange so they can transfer assets from one to another and they are called centralized exchanges.
There are many centralised exchanges some of them are Binance, CoinDCX, Robinhood, etc. A decentralized exchange is built upon blockchain technology and smart contracts, enabling users to trade directly with one another without relying on a central authority. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) have revolutionized the way we trade cryptocurrencies and tokens, eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing users with more control over their assets. Some of them are Uniswap, Pancakeswap, DyDx, etc..Each of them has different functionalities.
Why do we need Decentralised Exchanges over centralized ones?
We know how centralization stole our own rights and put its own rules on us indirectly but sometimes it gets too worse, There are plenty of examples of investors losing their money due to a collapse or hack in the exchange we can see it in regulated markets like stocks also but specifically the unregulated market like crypto markets will take all money of the holders if that particular exchange collapse or just they can retrieve penny from it. Examples of such cases are too recent one of the biggest U.S.-based crypto exchange FTX collapsed suddenly due to its unethical handling and use of the money of its users who has their assets in FTX exchange, so for that trading the tokens of decentralized technology we need decentralized exchanges where users can directly trade with each other without relying on a third party, you don't need to put your sensitive data to exchange and cherry on the cake you will get more security than a centralized exchange. I think now you can understand why we need it now let's deep dive into its mechanism.
Introduction to DEX Architecture
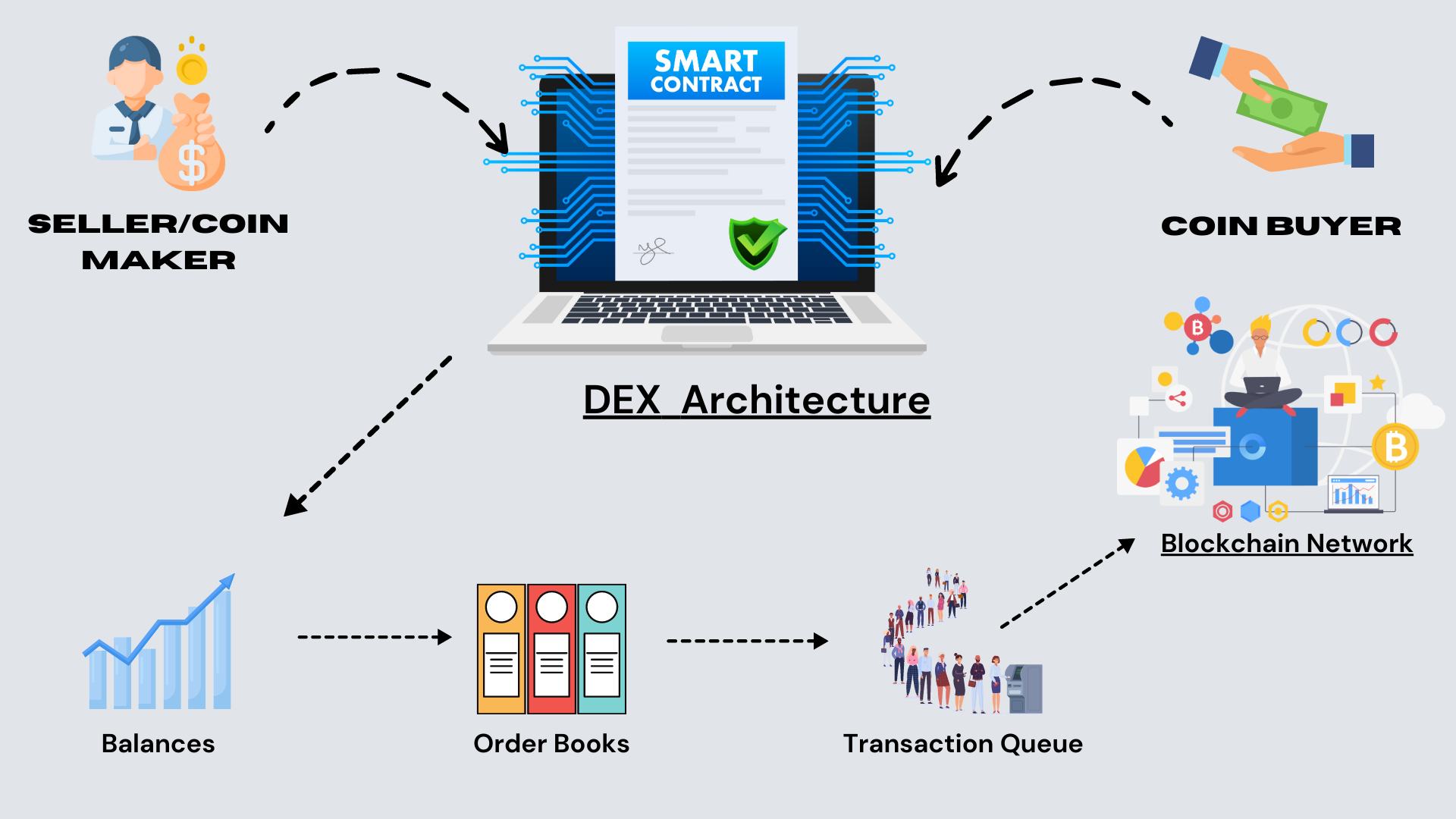
The architecture typically consists of the following components:
Smart Contracts: These are at the heart of a DEX. Smart contracts handle the settlement of trades, manage user funds, and enforce trading rules.
Order Books: While traditional centralized exchanges use order books to match buy and sell orders, DEXs often employ alternative mechanisms like Automated Market Makers (AMMs). However, some DEXs do offer order book-based trading.
Liquidity Pools: In AMM-based DEXs, liquidity pools are a critical component. These pools are formed by users who provide their tokens as liquidity, enabling others to trade against these pools. Liquidity providers earn a share of the trading fees.
User Wallets: Users connect their wallets (e.g., Metamask) to the DEX interface to execute trades directly from their wallets, maintaining control over their private keys.
Order Book Mechanisms in DEXs
While AMMs are prevalent in the DEX space, some platforms incorporate order books for trading. In these DEXs, the order book is implemented using smart contracts. Key components of order book-based DEXs include:
Limit Orders: Traders can place limit orders specifying the price and quantity they are willing to buy/sell. Smart contracts match compatible orders and execute trades when conditions are met.
Matching Engine: This component matches buy and sell orders by finding pairs with compatible prices. It ensures that trades occur at the most favorable price possible.
Trade Execution: Once orders are matched, the smart contract executes trades by transferring tokens between user wallets. The execution is trustless and automated.
Decentralized Price Discovery Algorithms
Decentralized price discovery in DEXs involves determining the value of assets based on supply and demand within the trading platform. Two primary methods are used:
Automated Market Makers (AMMs): AMMs like Uniswap and PancakeSwap use mathematical formulas to set token prices based on the ratio of tokens in liquidity pools. As the pool's ratio changes due to trades, the price adjusts accordingly.
Order Book Pricing: In DEXs with order books, prices are determined by the buy and sell orders available in the book just like the stock market. The highest bid and lowest ask prices often define the current market price.
Dexes you can check out how they actually work...
Just look at their UI, and how they work ( just for educational purposes no advice or recommendation to use it ), In the future we will deep dive into the mechanisms of each separately.
Some cautions to note while using DEXes...
Everything in the universe comes with both Pros and Cons and we should be aware of both so let's look at some concerns related to DEXes
User Experience Complexity: The user experience on DEXs can be more complex than on centralized exchanges.
Liquidity Issues: DEXs often face challenges in maintaining high levels of liquidity, especially for less popular or newer tokens.
Transaction Fees and Network Congestion: DEX transactions on blockchains like Ethereum often involve gas fees, which might feel more expensive for basic operations.
Security Concerns: While DEXs aim to eliminate counterparty risk associated with centralized exchanges, they can still be vulnerable to hacks and vulnerabilities in smart contracts, leading to loss of funds.
These are some cons associated with DEXes but they can be overcome as blockchain technology evolves at a superfast pace 🚀. Hureyy now you understand the basic mechanism of DEX and actually, you learned your first protocol in DeFi space. Feel free to provide your feedback and subscribe to this series for more knowledgeable content. Thank you.....
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Degen HODLer directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Degen HODLer
Degen HODLer
Passionate web3 enthusiast, dev looking to explore web3.